When we buy pasta sold in plastic bags or boxes, 60% of its packaging space is reserved for air. The packaging used to contain food items like pasta is a major contributor to landfills in the United States. As we slowly make attempts toward a more sustainable future, understanding the waste that food packaging produces provides a viable starting point. Inevitably, the ways we consume food and package food will become more sustainable and a team of researchers in collaboration with Carnegie Mellon University and Syracuse University turned to flat-packing authentic Italian pasta to find out the ways to do it.
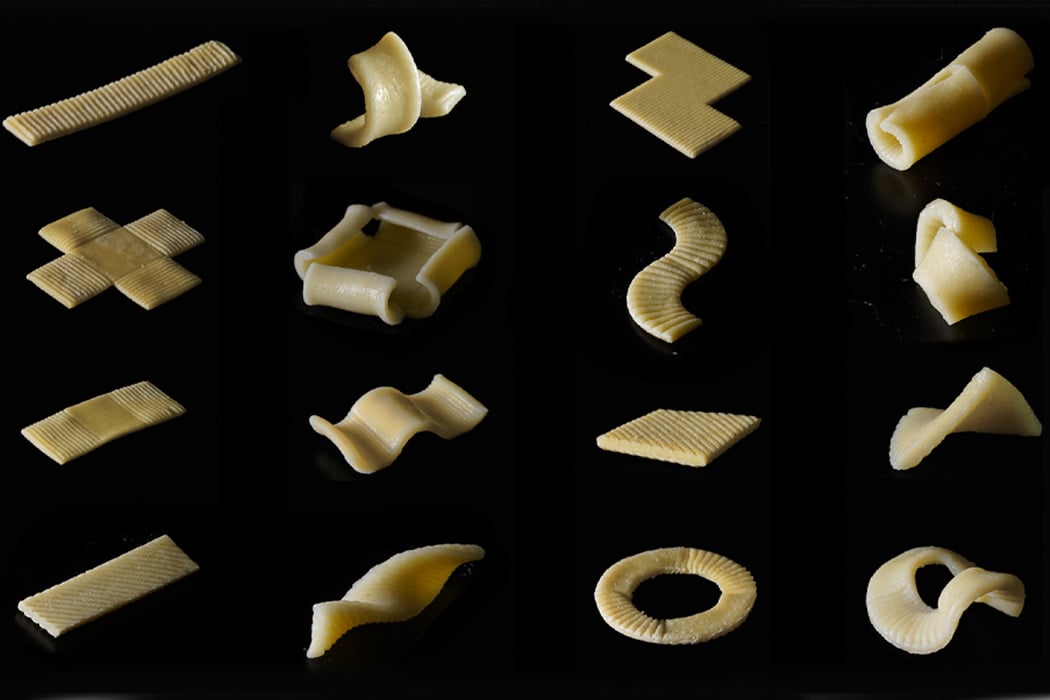
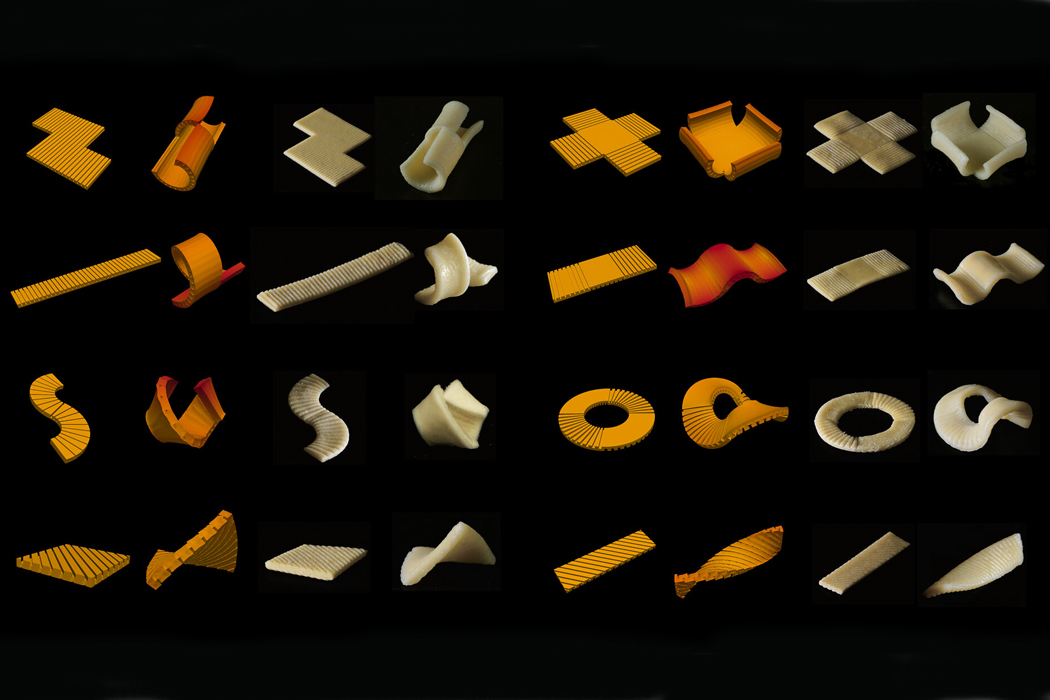
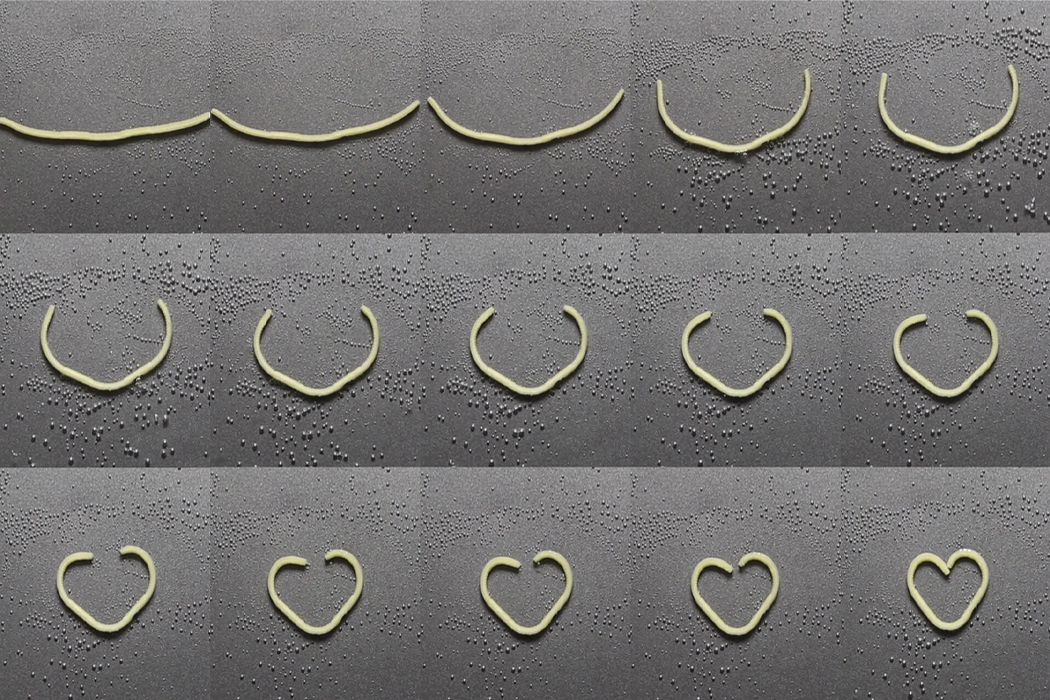
Inspired by the flat-packing of furniture in efforts to save packaging space and reduce the overall carbon footprint produced during the transportation of goods, a team of researchers decided to see if they could do the same for pasta. When we purchase dry pasta, the shape of the pasta we see in the store is typically the same shape we eat at home, only hopefully cooked. The team behind flat-packed pasta has developed a groove-based shape morphing technique using low-cost manufacturing methods to stamp, mold, or cast the pasta which then transforms into the predetermined shape once cooked. Before curling into its predetermined shape, the pasta, made from semolina flour and water, is stamped with grooves that indicate the direction by which the pasta will curl and bend into shape.
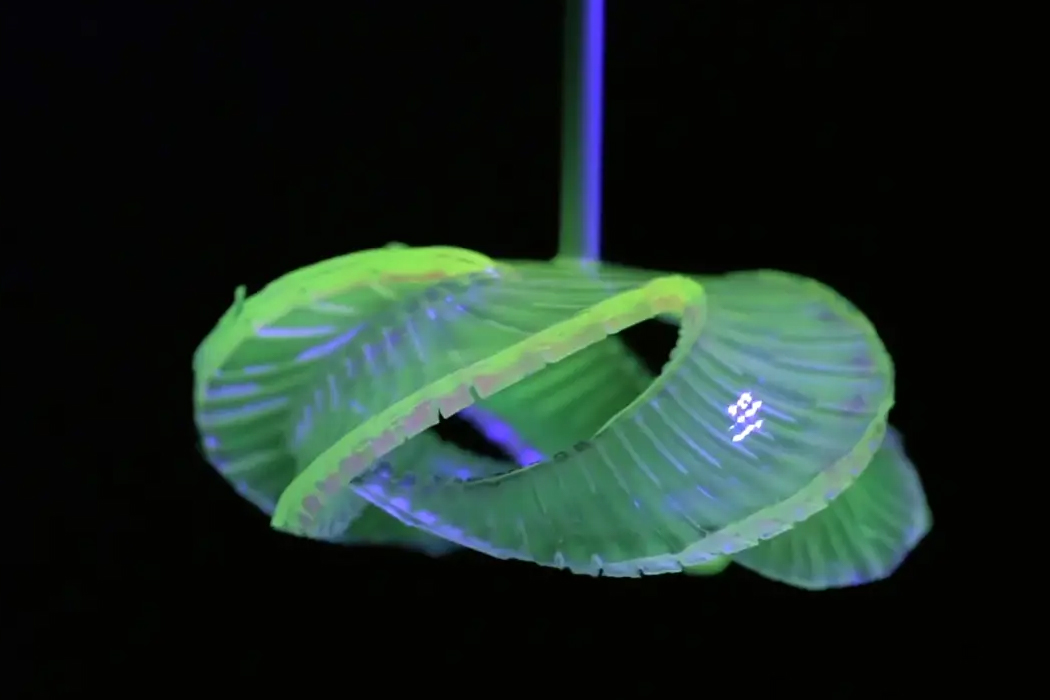
Parametric surface grooving essentially brings on temporary asynchronous swelling or deswelling that transforms flat objects into their preferred three-dimensional shape. The groove-based shape morphing technique allows edible items like pasta to be flat-packed and then change shape when cooked. The process really can be explained when understood through furniture flat-packing. In the same way that flat-packed furniture changes shape after assembly, flat-packed pasta transforms into edible, shapely pasta after cooking.
Designers: Carnegie Mellon University
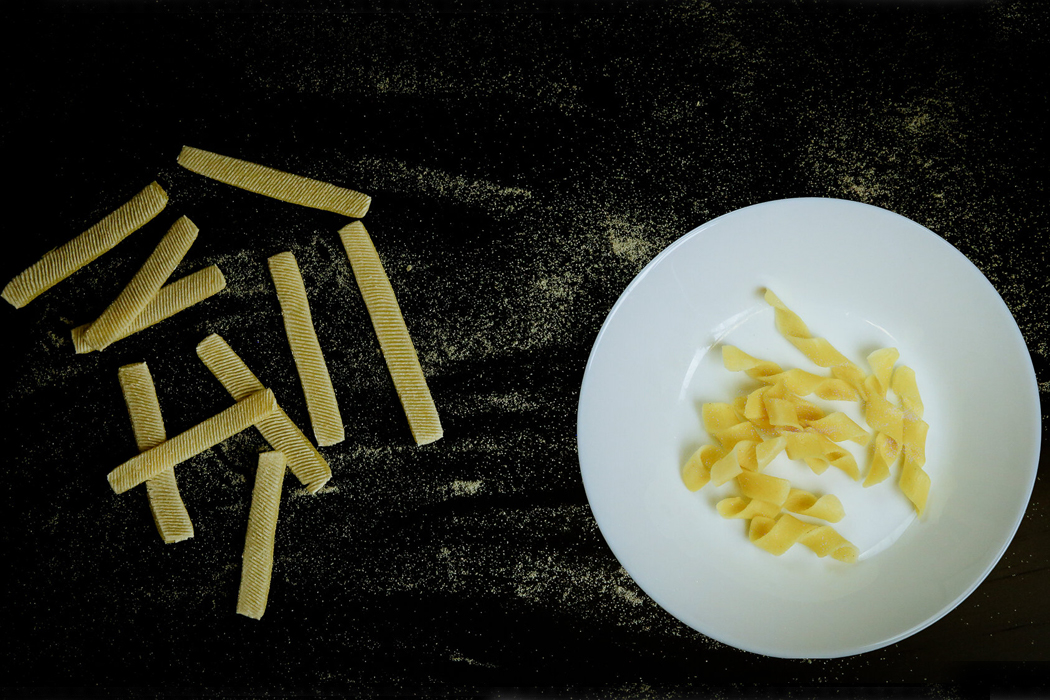
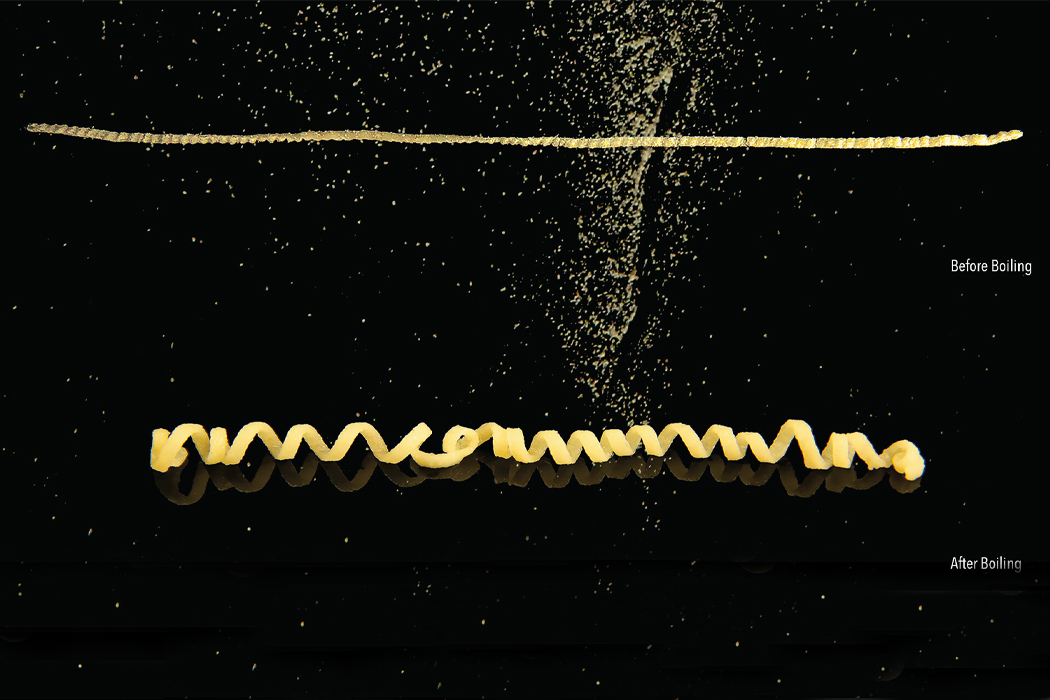



After being stamped with parametric surface grooves, the pasta can be packed tightly into a container and then morph into shape when cooked.
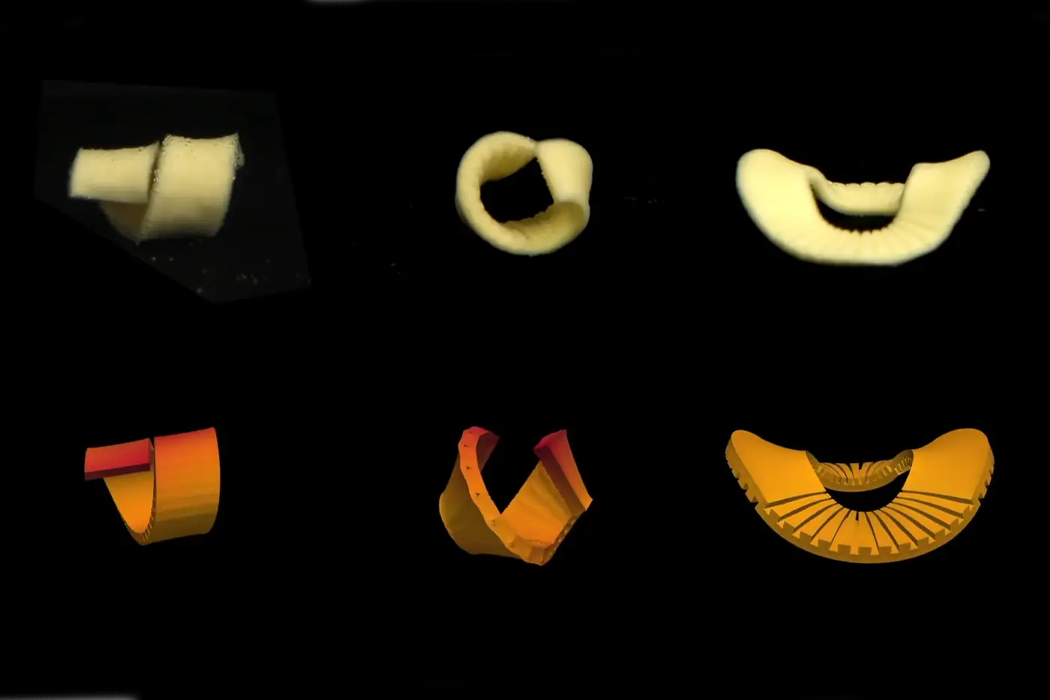
The grooves work as a preset for each piece of pasta to shape into.


The parametric surface grooving works on an array of differently shaped pasta.


Whether it has a radial or more geometric shape, the surface grooving works to create cubic or round pasta.
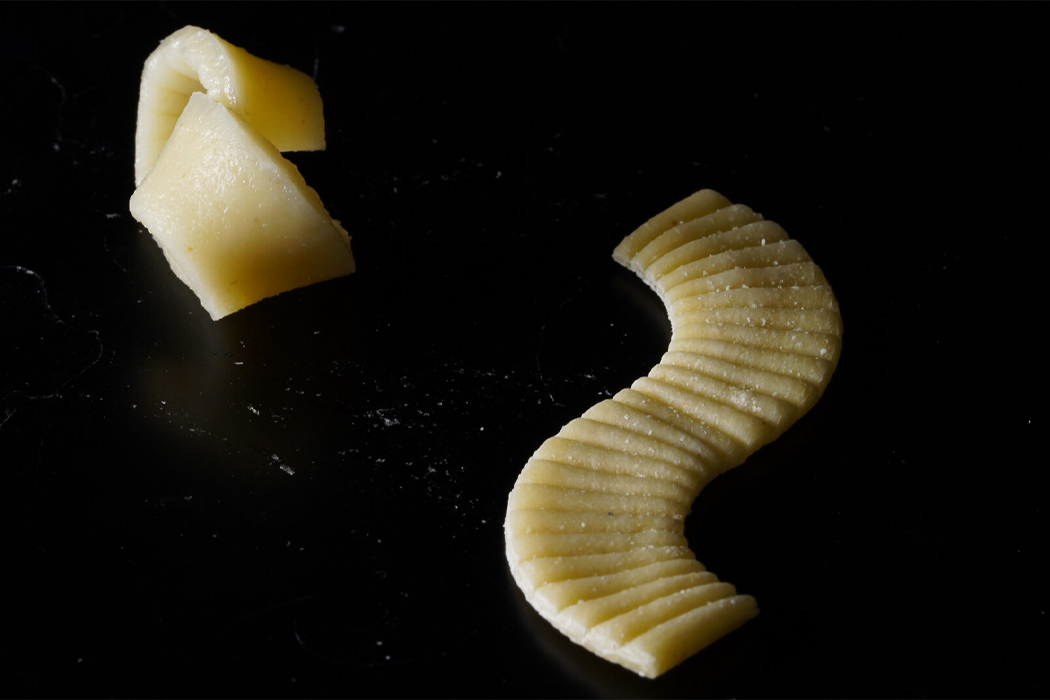
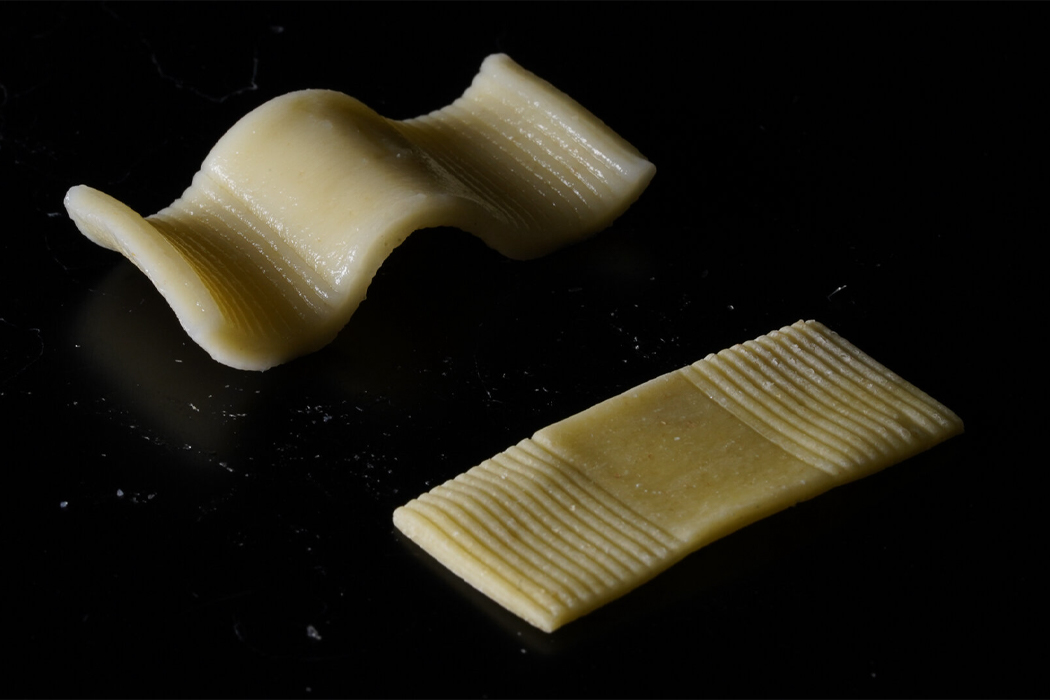
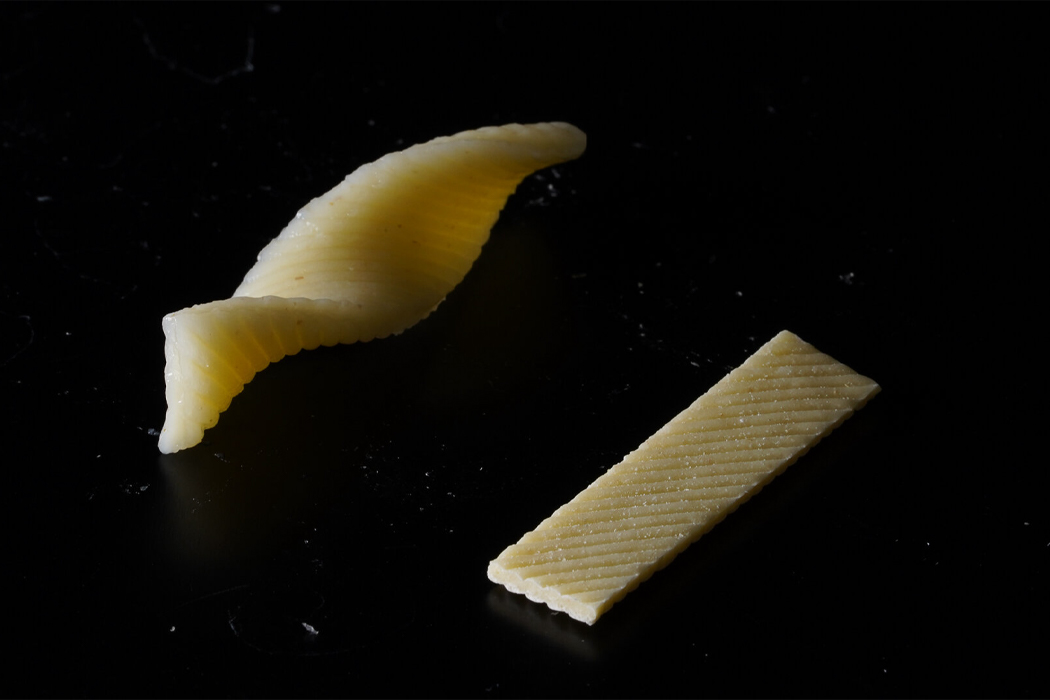



The team of researchers explains the cooking process of pasta, “pasta expands and softens as it is boiled due to water diffusion, the relaxation of the macromolecular matrix, and starch gelatinization.”
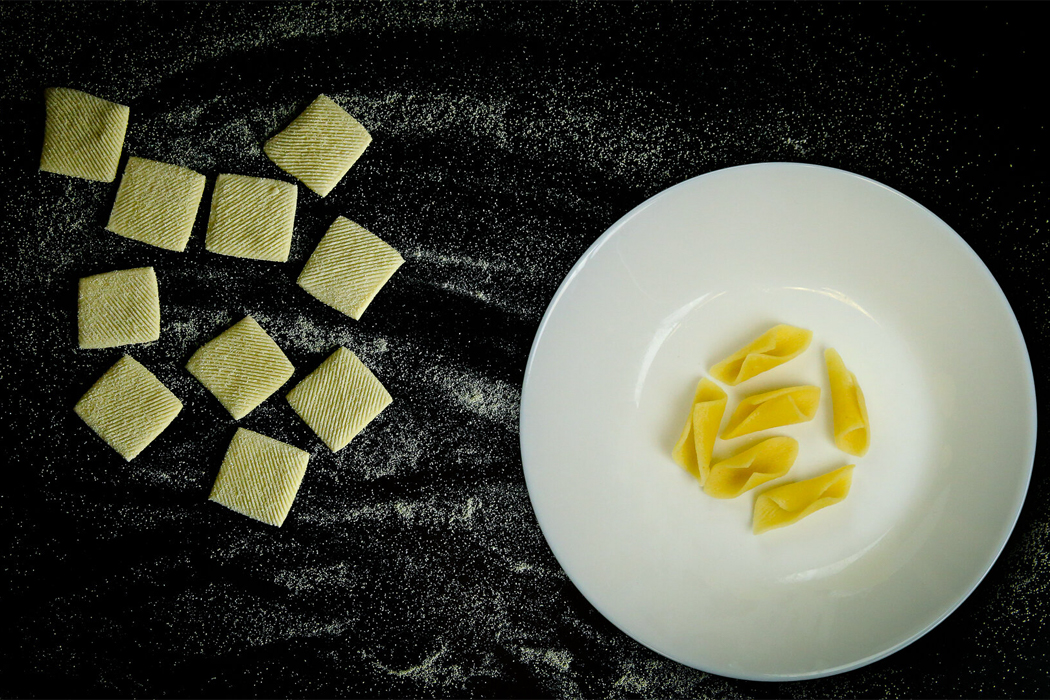
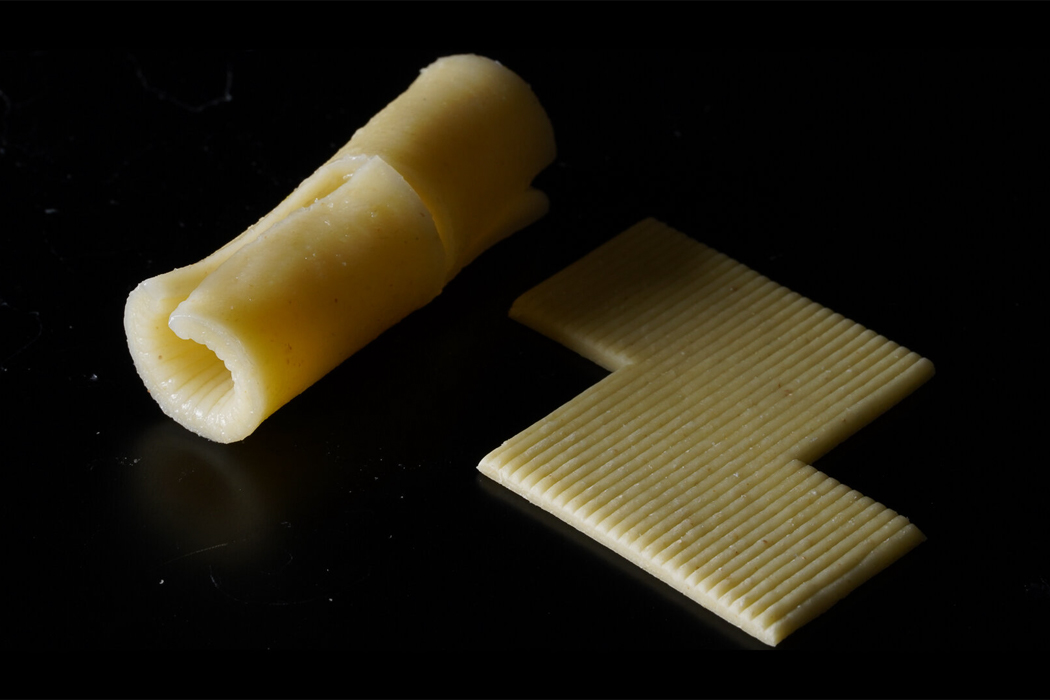

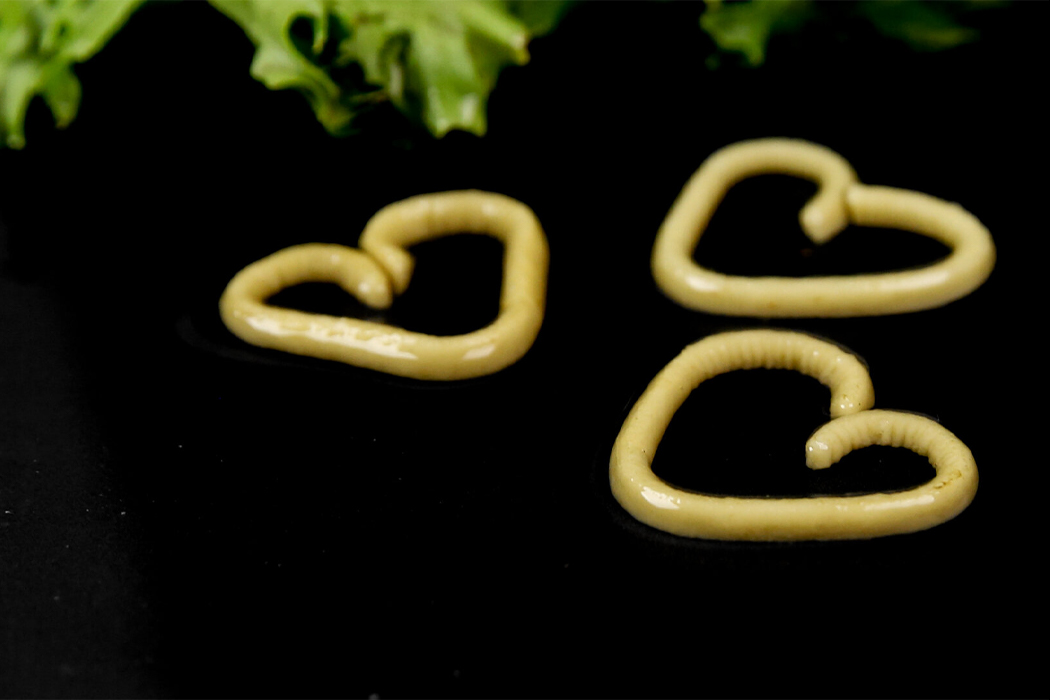
The shape of food doesn’t only directly impact sustainability in regard to packaging, but it impacts the overall food experience, from taste to consistency.
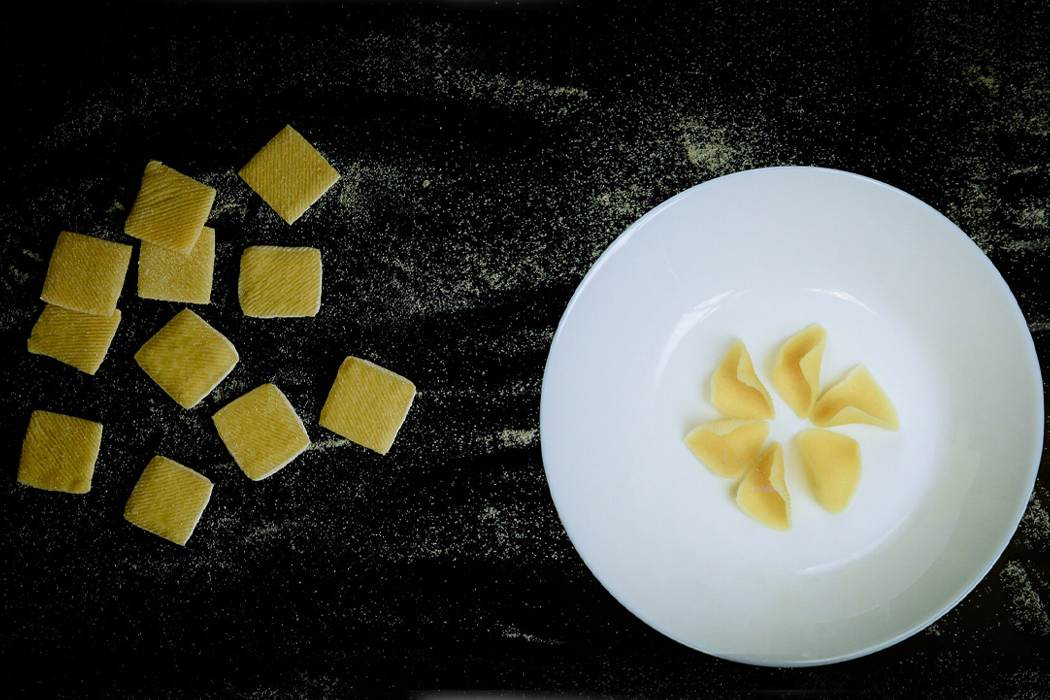


“Further, the shape of food will also impact the carbon footprint during the cooking process. For example, in Italy, 0.7% to 1% of greenhouse gas emissions are due to cooking pasta, and these emissions could be reduced by half if the shape and cooking processes could be optimized.”

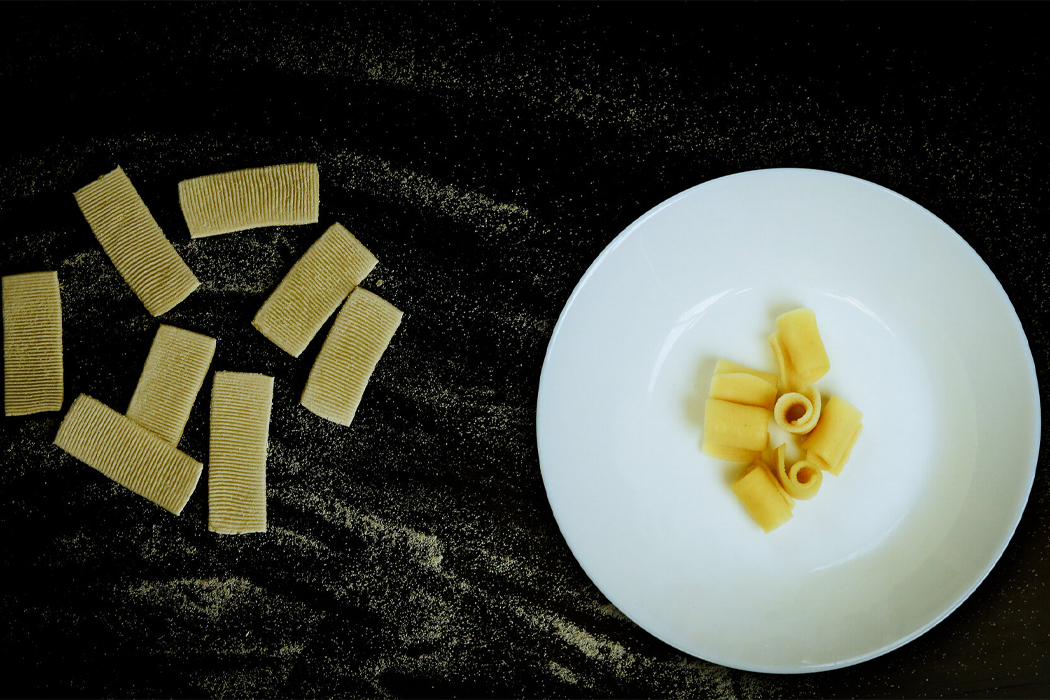
“Flat pasta with surface texture has a larger surface area to volume ratio and can be cooked faster than the ones with an inner cavity (e.g., macaroni).”
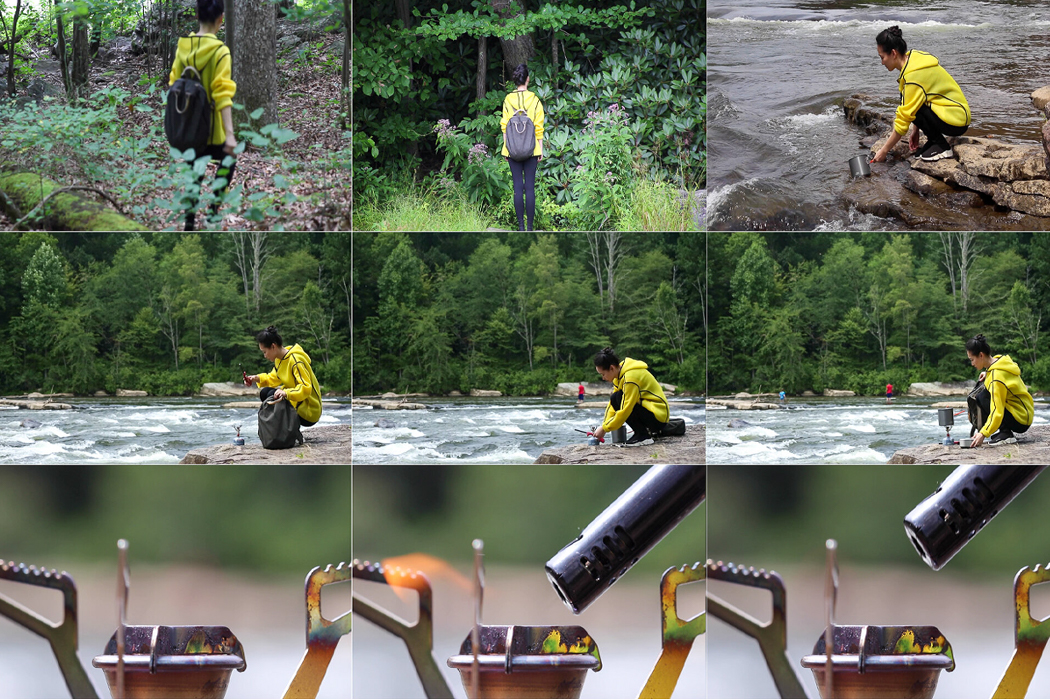


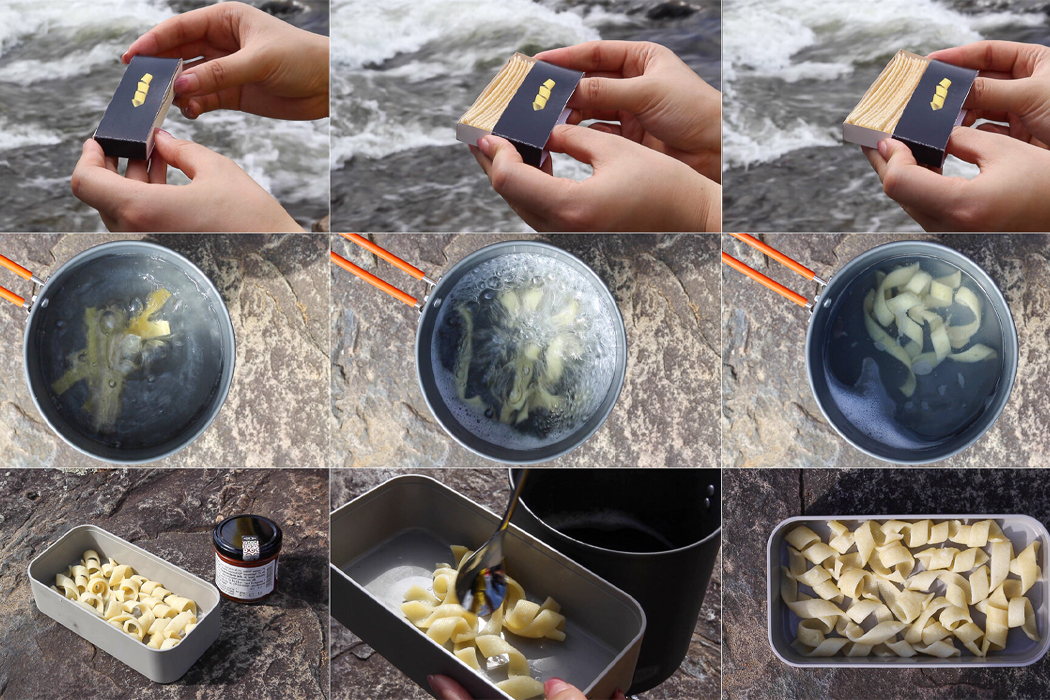
Flat-packed pasta could also come in handy for minimal baggage trips like hiking and camping, where storage availability might be limited.
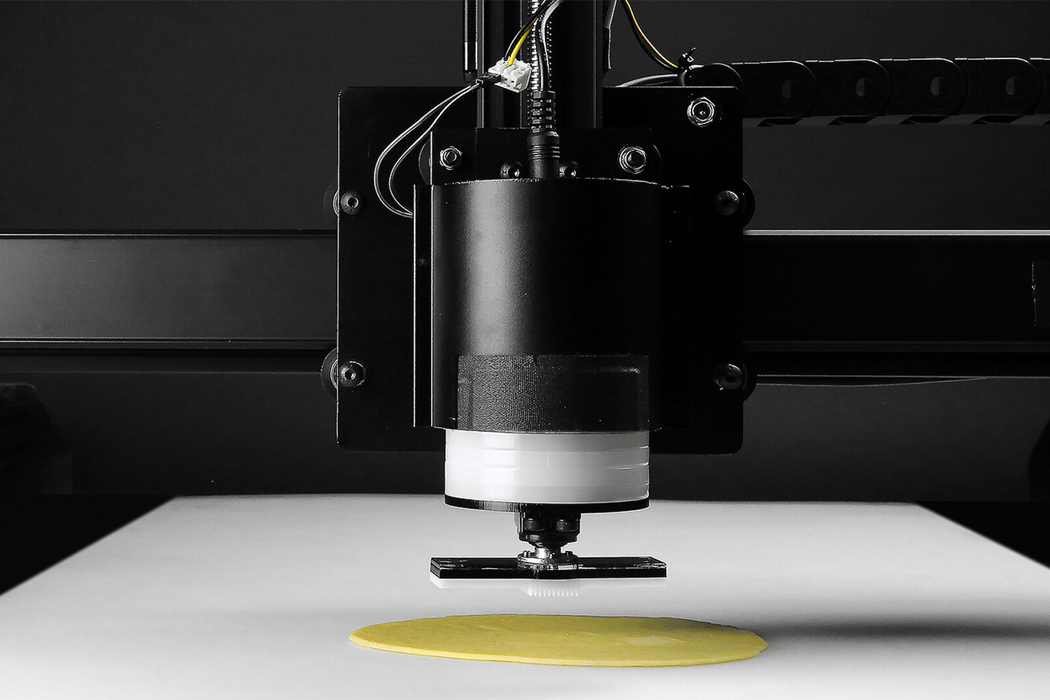

Each piece of pasta is stamped with parametric surface grooving in preparation for packing and cooking.
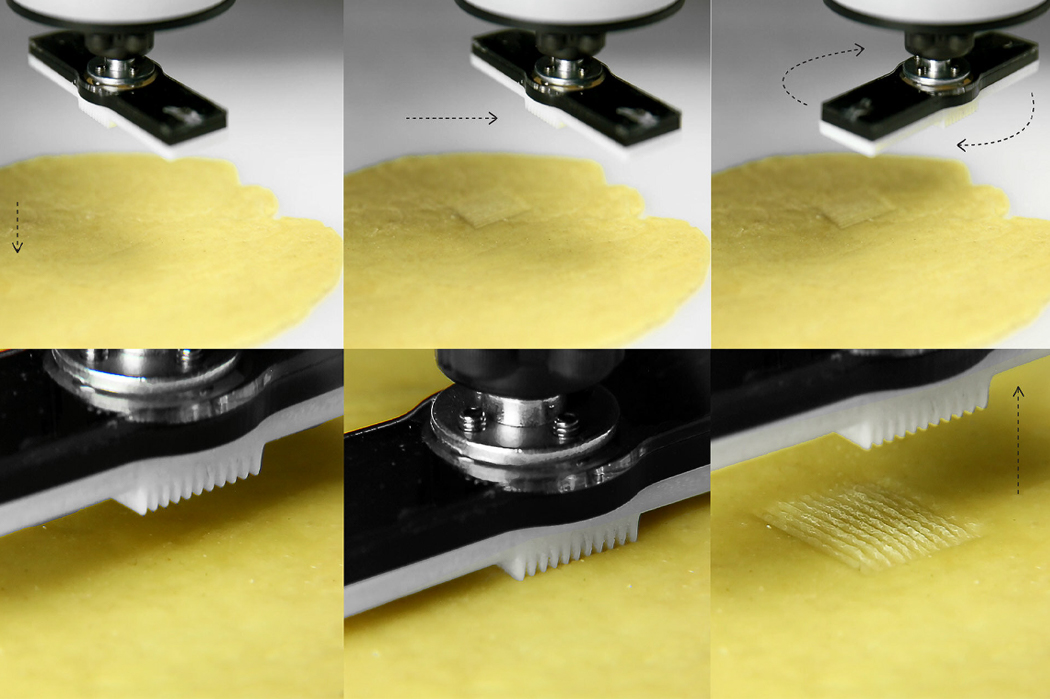
The grooves on each piece of pasta are either manually stamped or made through an automated machine-stamping process.






