Solar power is an amazing source of energy and a sustainable and cleaner alternative to fossil fuels. Today solar energy is being used to power almost everything – from tiny battery packs to whole houses! There are no exceptions. And solar-powered architecture seems to be the new craze and a very green one too! From holiday cabins to tiny homes, solar energy is being used to power and support all kinds of architectural structures. And we’ve curated a collection of well-designed, functional, and solar-powered architectural designs that are comfortable to live or work in, aesthetic to look at, and also a boon to the planet. These structures coexist in harmony with their surroundings and do not drain but in fact, respect the natural environment around them!
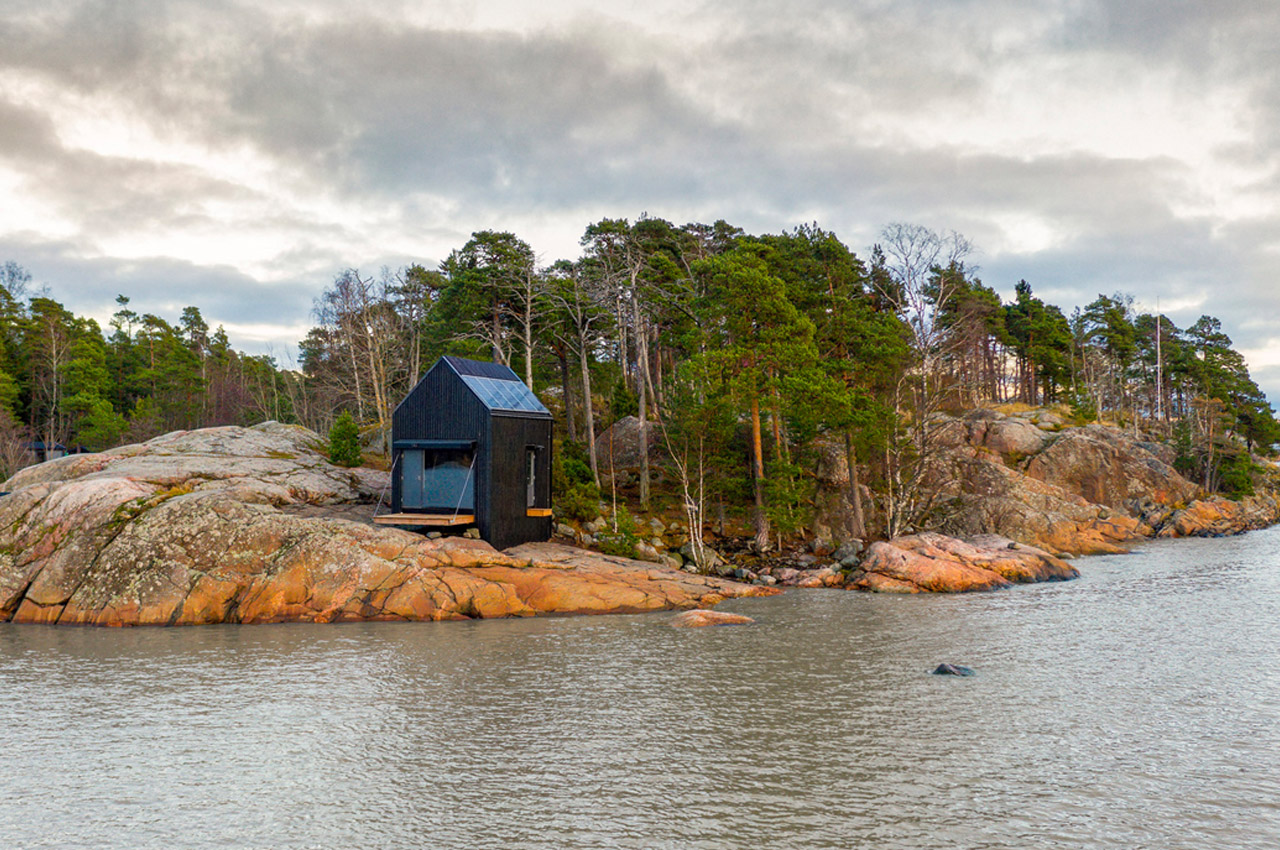


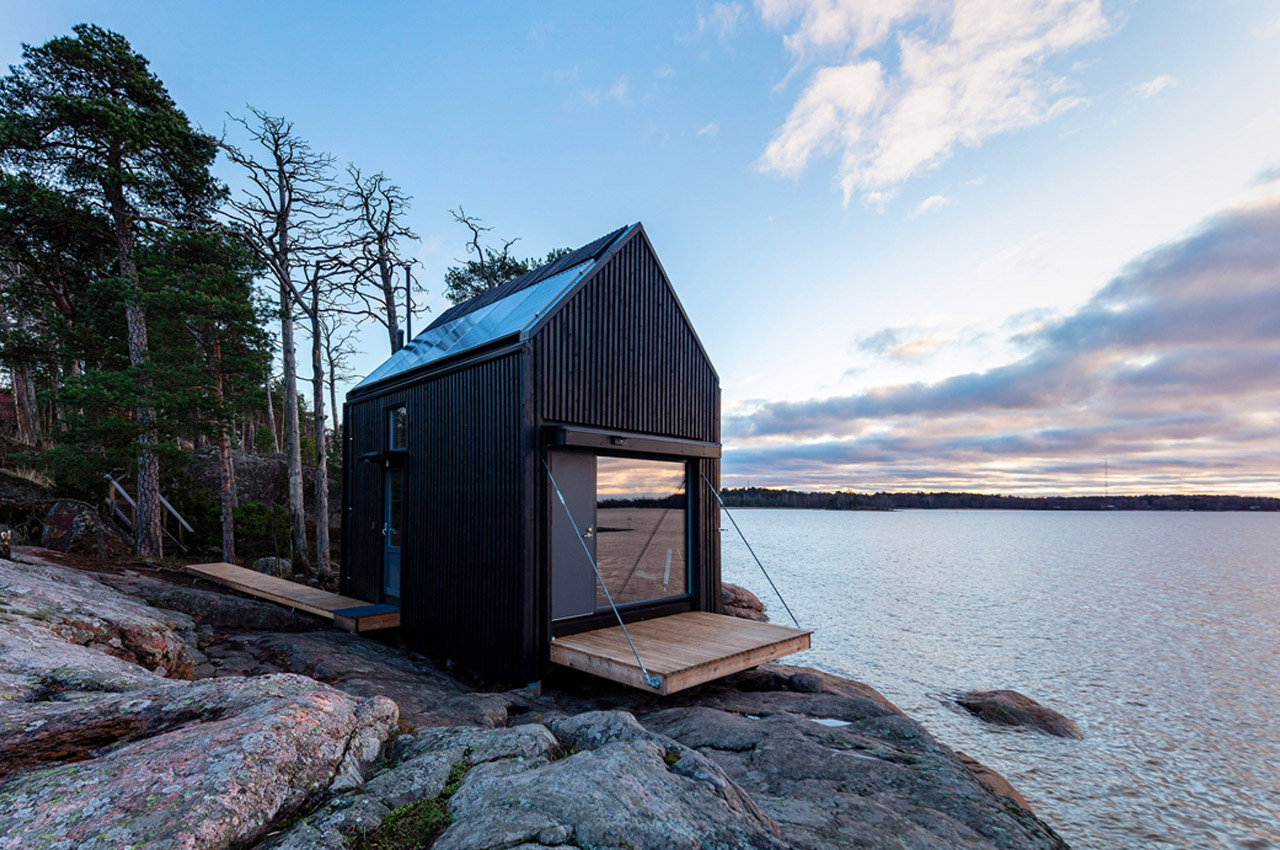
Pekka Littow’s Majamaja concept was born from life on Finland’s archipelago and essentially speaks to a building tradition that prioritizes harmony between humans and nature. Majamaja Wuorio units are prefabricated, transportable, and by making use of off-grid technologies such as solar panels and a recirculating water treatment system, the units can be situated anywhere. The tiny cabin’s closed-loop water treatment system collects both rainwater and air humidity in order to store it, then sends it to the integrated water purification system for residents to use in the shower, kitchen, or bathroom. Waste from dry toilets is also composted and reused as fertilizer. The water purification system is powered by solar panels and a fuel cell, which also provides green energy storage for additional household appliances such as stovetops, air conditioners, and light fixtures.
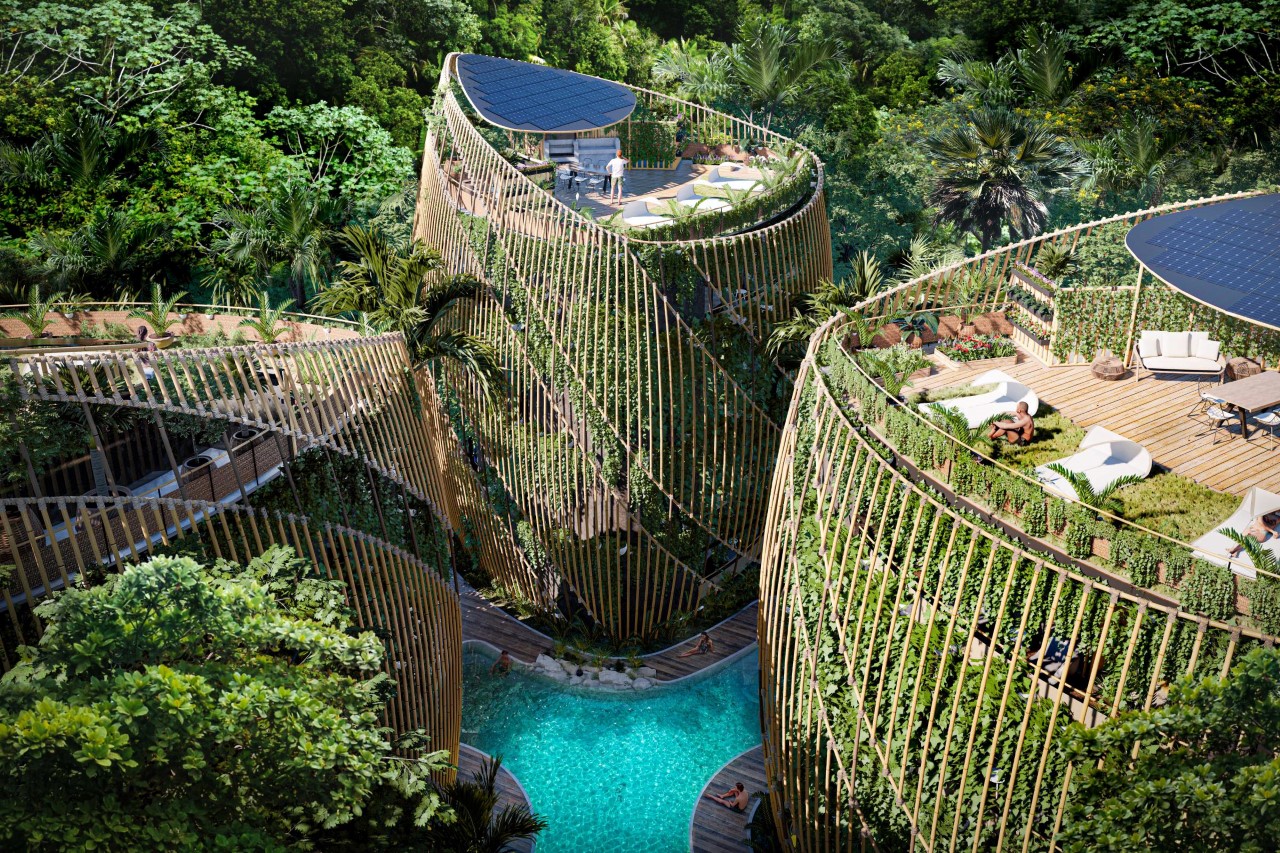
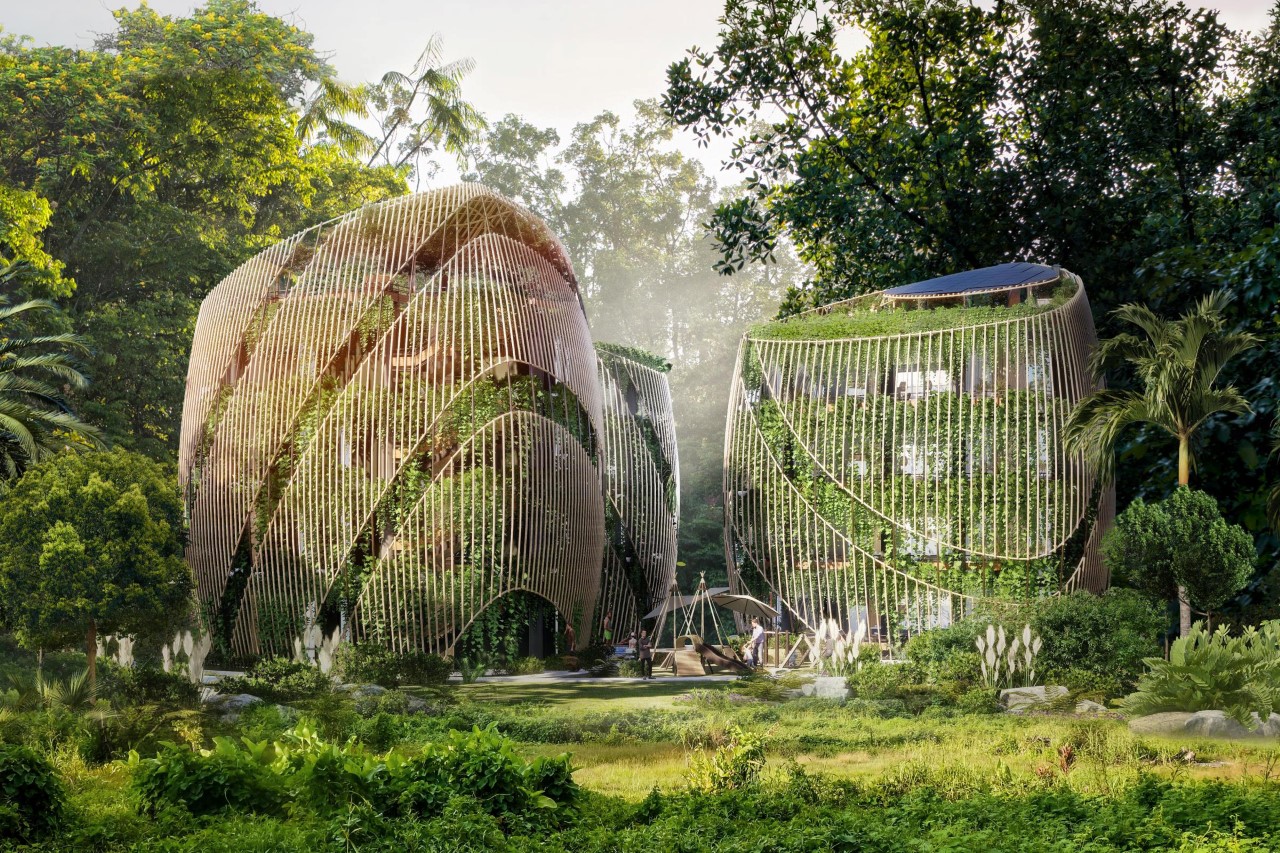


Designed by Mexico-based Sanzpont Arquitectura, ‘Living In The Noom’ puts you in the lap of nature and luxury. Its sanctuary-esque design focuses on three broad pillars – Wellness, Sustainability, and Flexibility. The community features multiple 4-storeyed houses with a uniquely alluring triangular shape, characterized by vertical bamboo channels and a vertical forest growing on the outer facade of the building. Finally, the structure culminates in a terrace on the fifth floor that has solar panels for harvesting energy, and an urban garden where the residents can grow their own food.
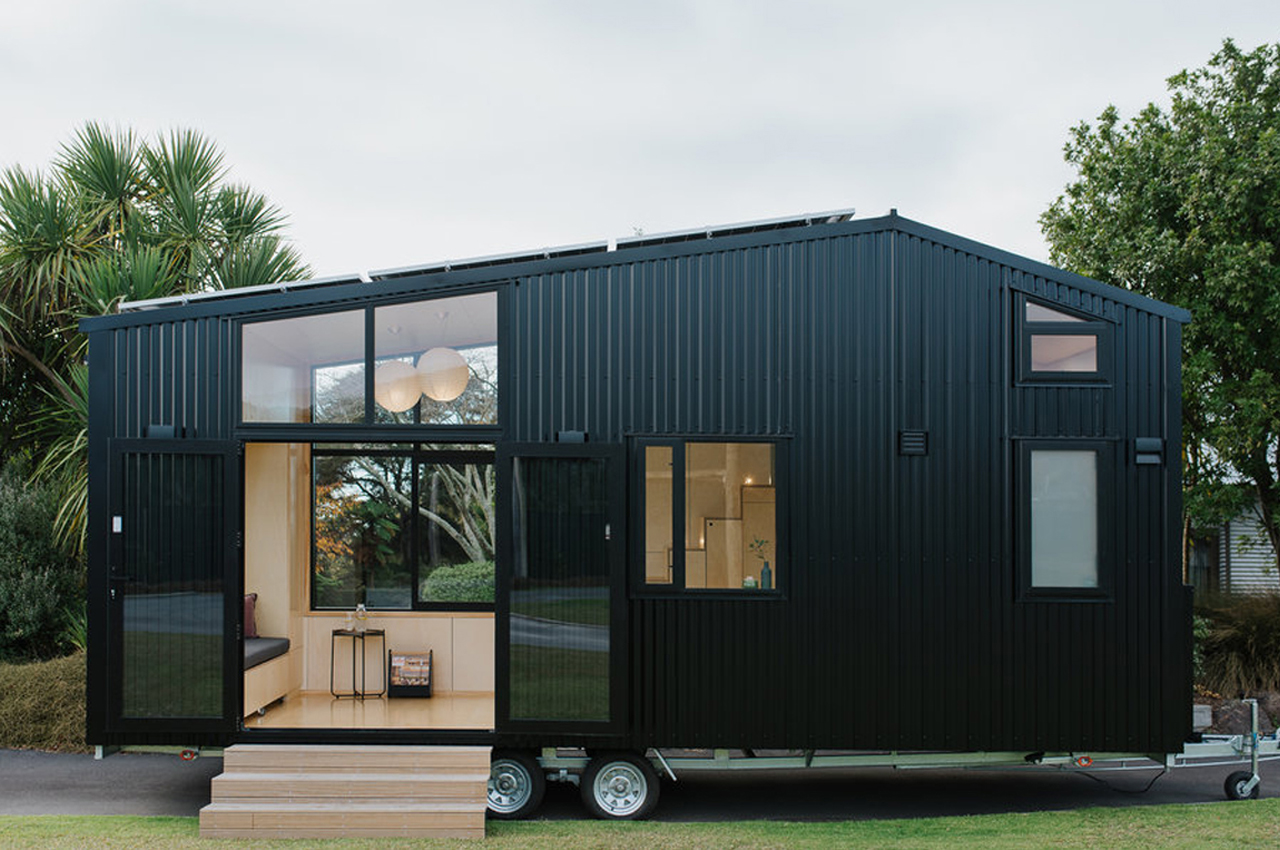
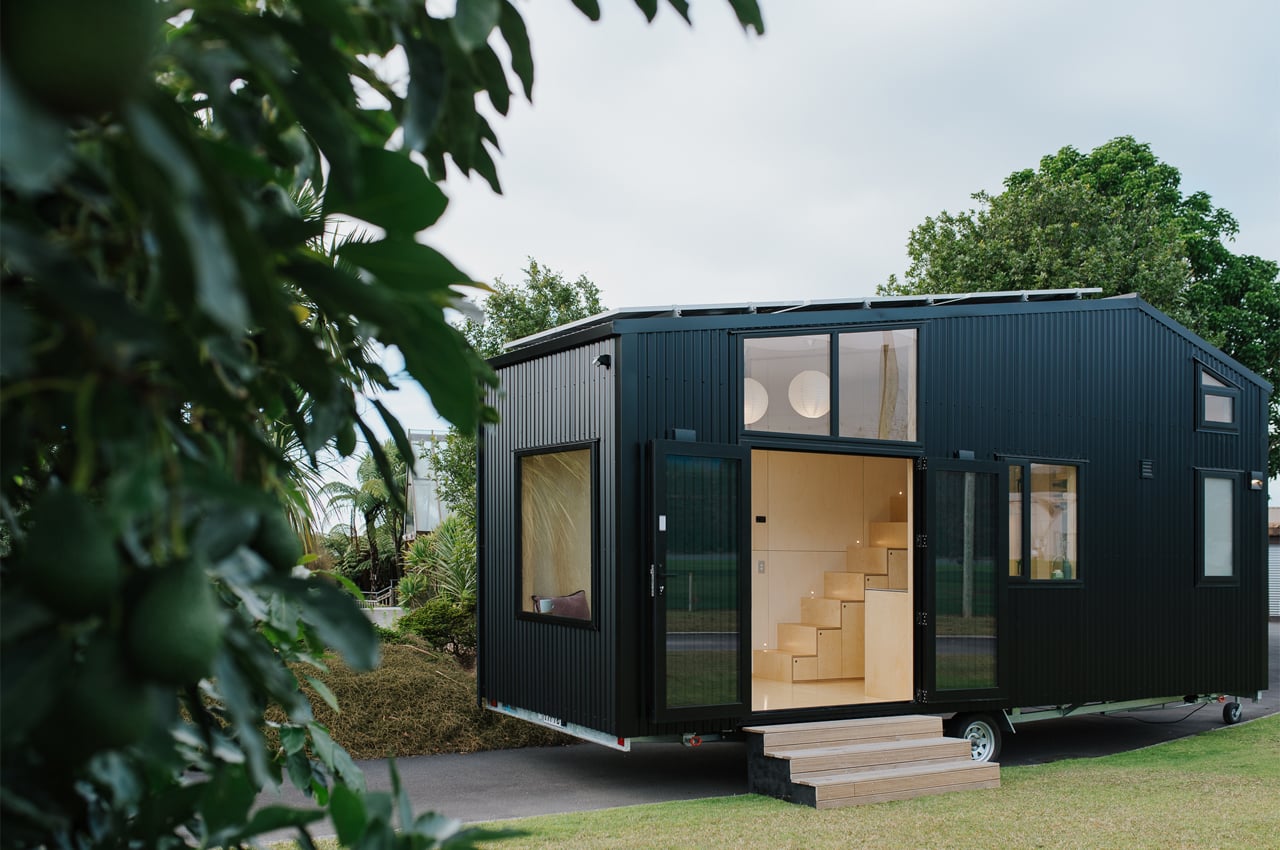


Catering to the necessities and casual family pastimes, the tiny home is doused in modular and multifunctional design that’s surrounded by creamy poplar plywood walls and silvery fittings that add a touch of refinement to an otherwise bare interior. Ohariu’s roof is asymmetrical with six solar panels lined up on its longer side and a mezzanine bedroom cozying up beneath its sloped short side. Entirely powered by the solar panels that make a grid on the roof, Ohariu is net-zero, featuring amenities like an LPG gas cylinder, LED lighting, low-water usage fittings, as well as a composting toilet. Enhancing the tiny home’s sustainable build, the materials used to construct Ohariu are recyclable for the most part and low-maintenance, durable, and locally sourced.
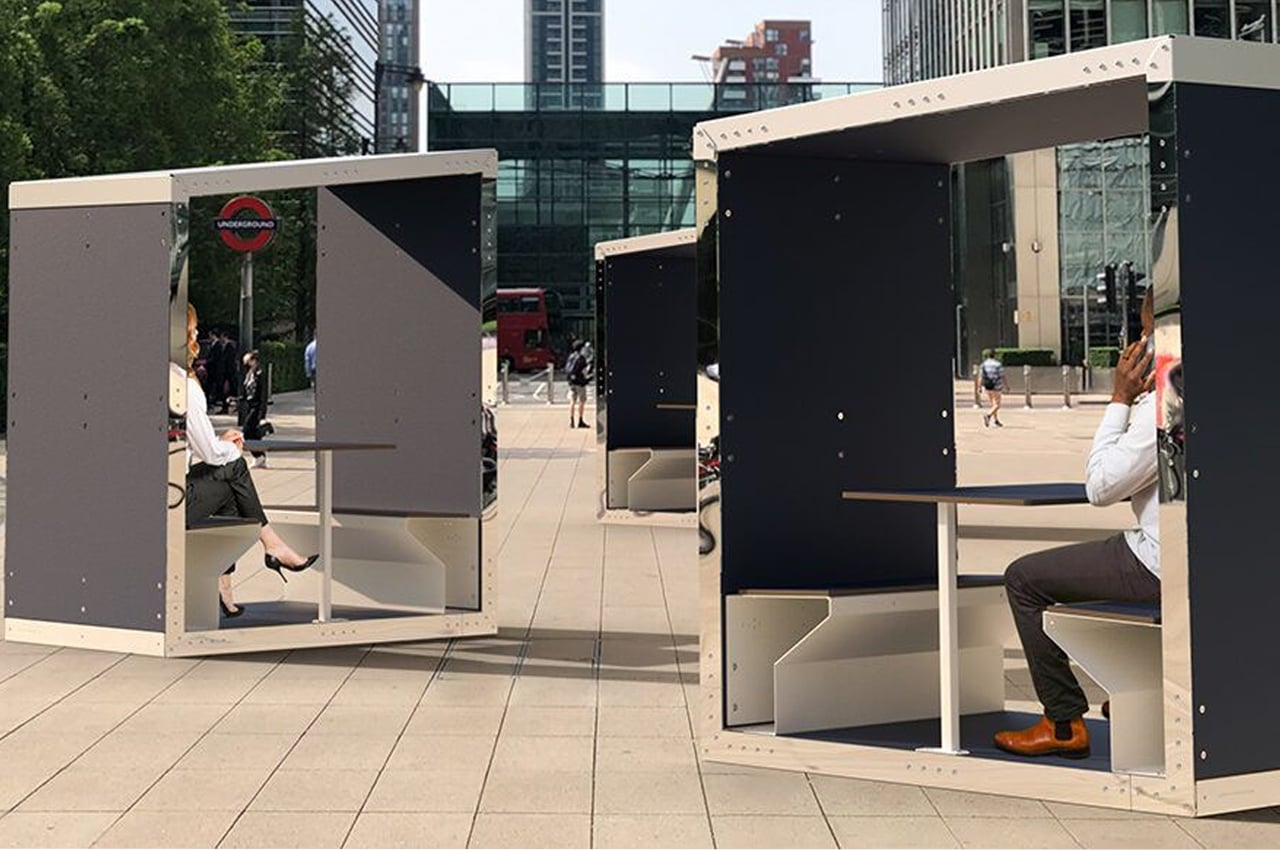
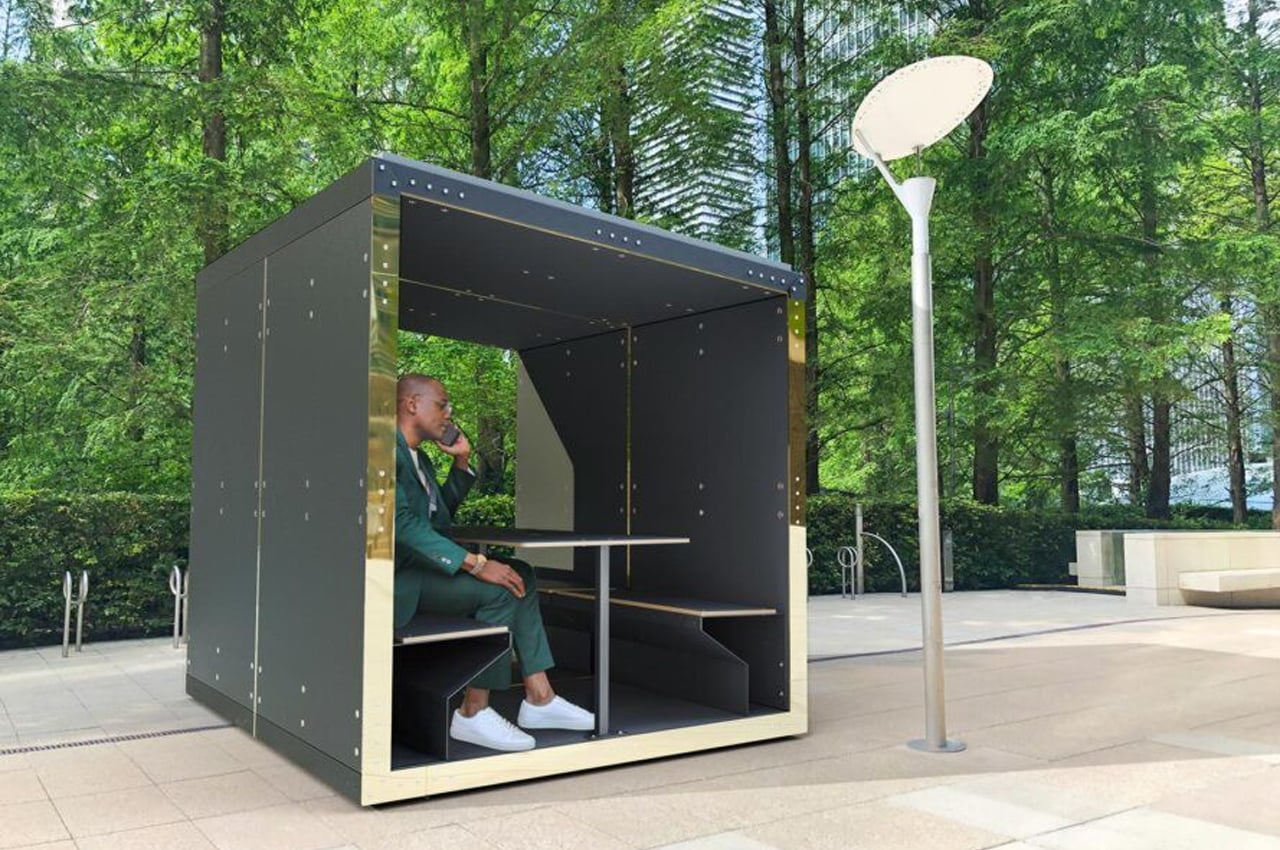


Offering their own solution to the unpredictable circumstances of today’s world, furniture studio Duffy London debuted the Minka Solar Pod, an outdoor companion to their indoor office pod. The Minka Solar Pod operates primarily as an alternative to meeting places and WFH spots like WeWork and cafes with WiFi. Unlike their indoor counterpart, the Minka Solar Pod and its amenities are entirely powered by photovoltaic panels and lithium-ion batteries. Using solar energy for power allows Minka Solar Pods to be placed anywhere, from busy city plazas like Union Square or public grounds like Hyde Park. Designed to be an outdoor working space, Minka Solar Pods come complete with four USB ports for charging and acoustic panels to quiet outdoor noise while amplifying the conversations taking place inside the pod.
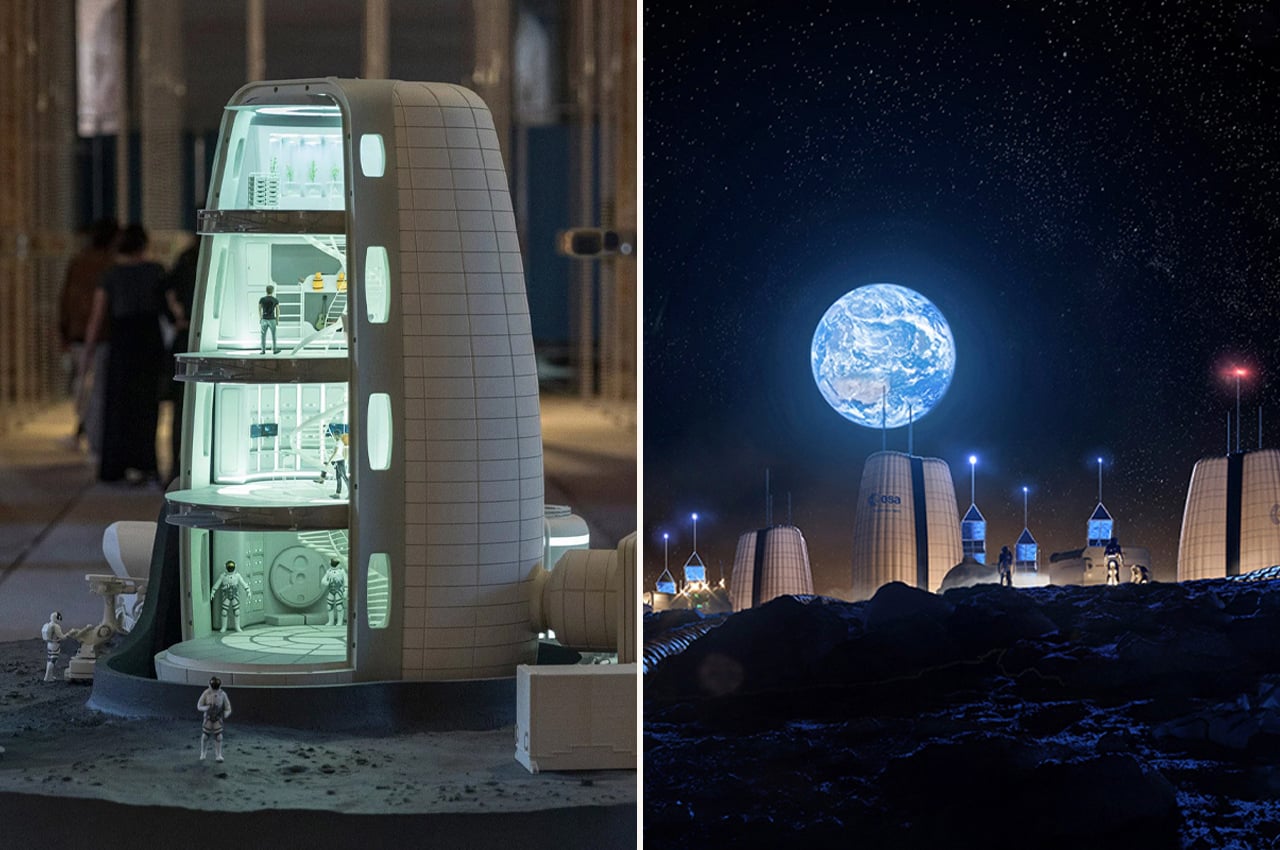
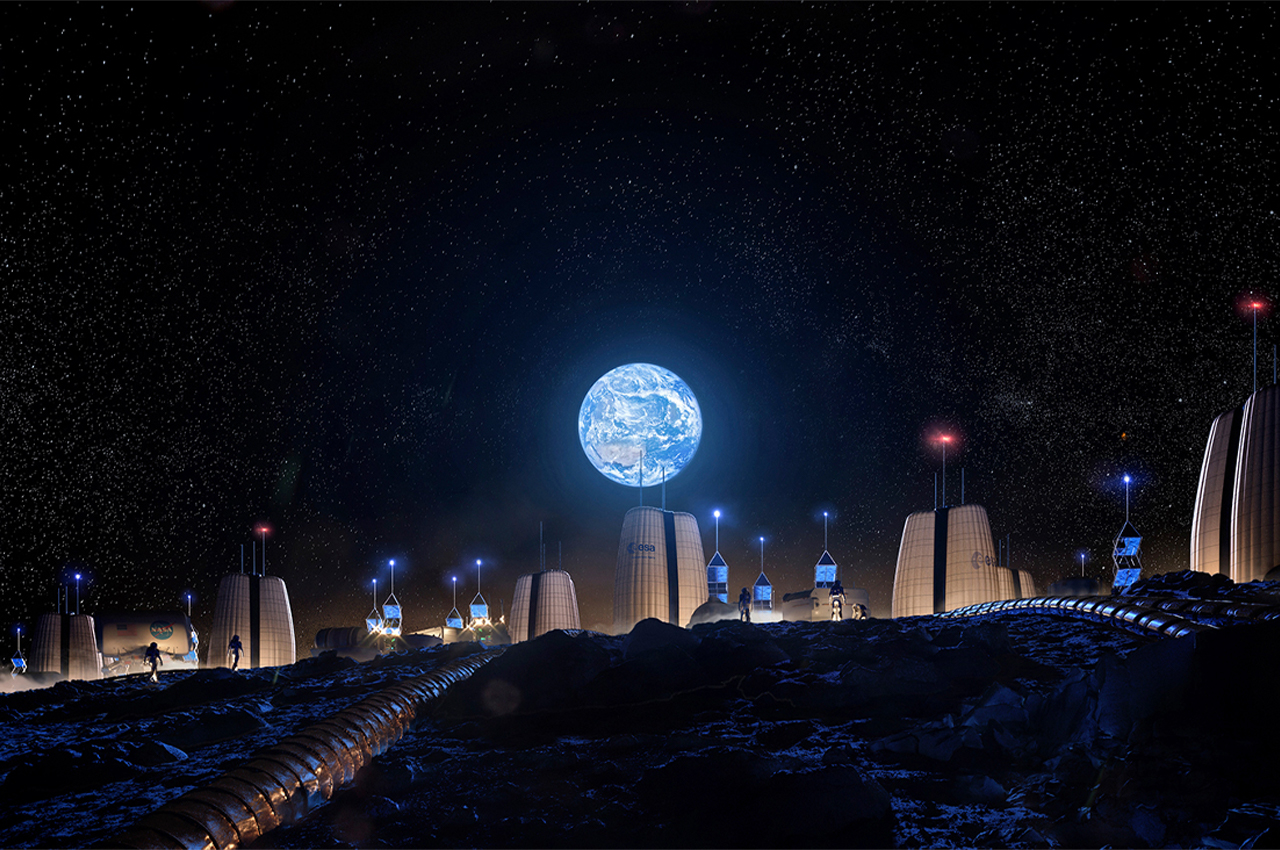


Primarily conceived of as a cluster of research stations, Moon Village would host an array of functions spanning from sustainability research opportunities to the future prospect of Moon tourism. The south polar region of the Moon supports the possibility of a self-sufficient settlement, receiving near eternal sunlight that could be harnessed and stored for energy. This part of the Moon also hosts a variety of untouched matter that could offer insight into the Solar System’s early history as well as the general emergence of our larger universe. Above all else, the structure of each individual hub comprises a modular frame and protective exterior to cater to the varied projects taking place inside.
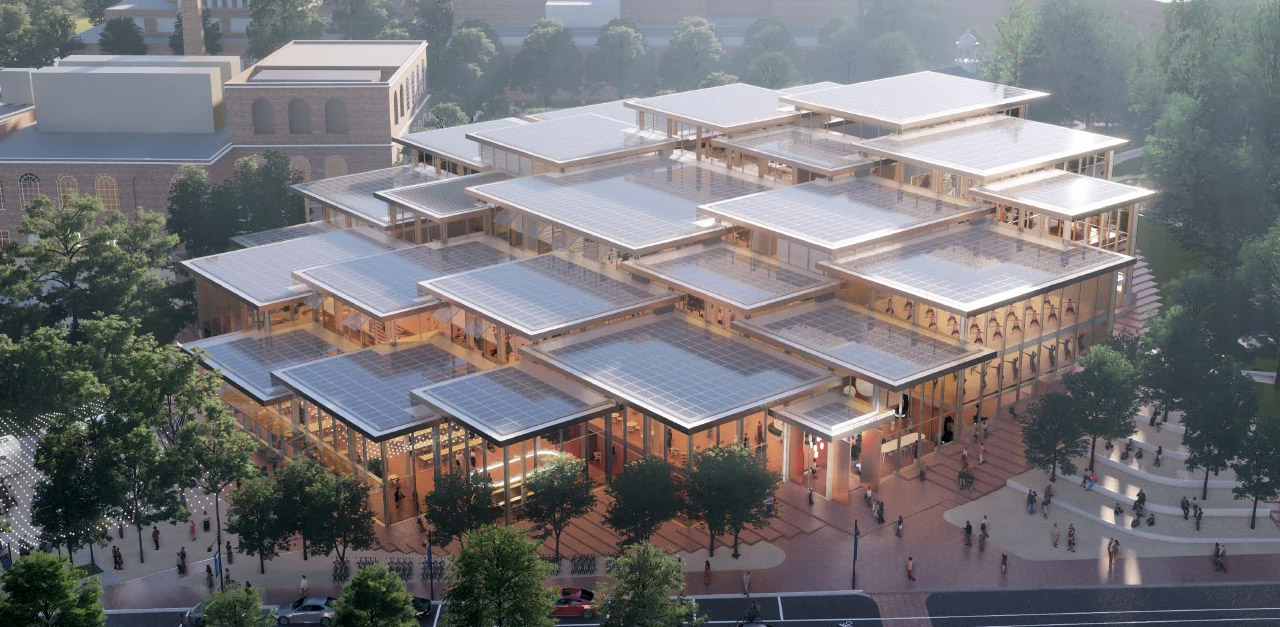
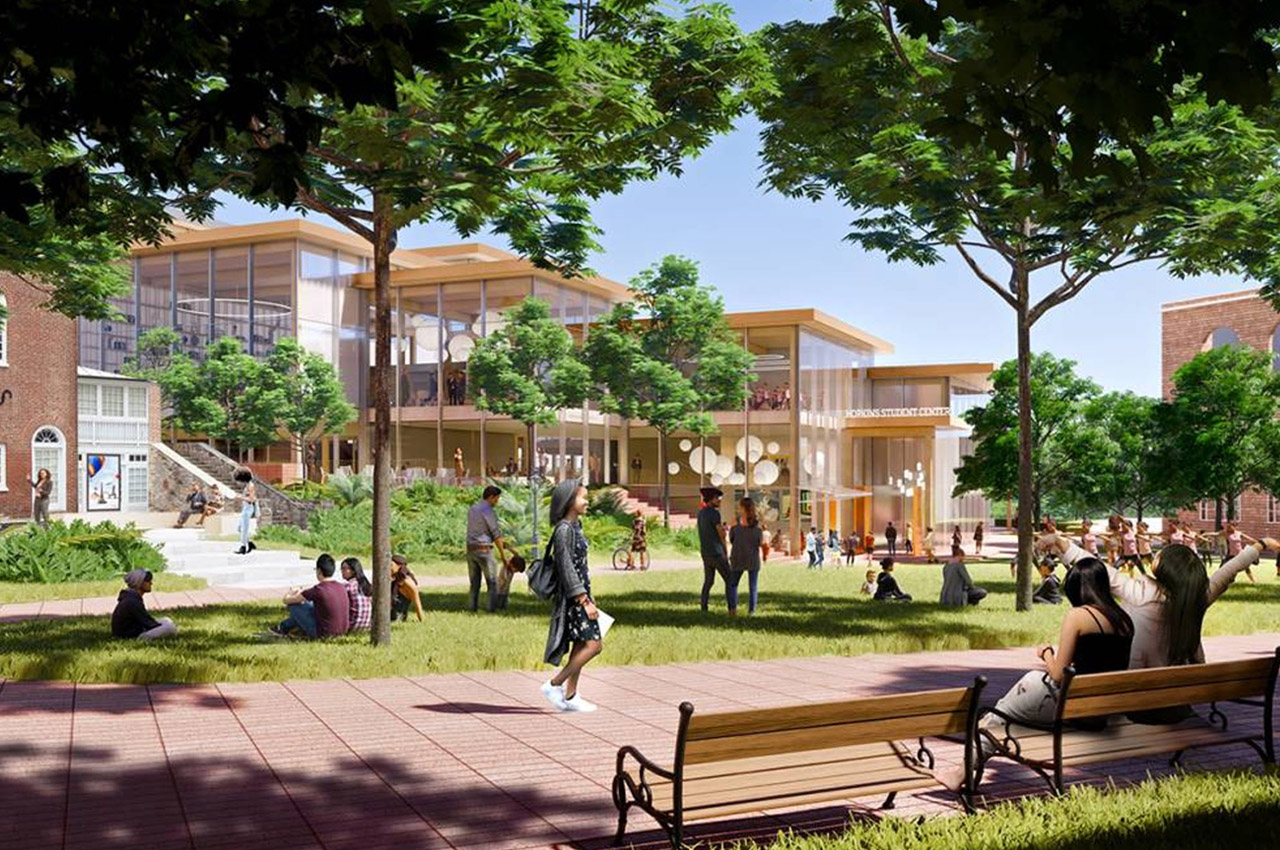


Bjarke Ingels designed a student center for John Hopkins University’s Homewood Campus in Baltimore, Maryland. The 150,000 square foot building will function as a social engagement hub for all the students, with spaces for relaxation, performing arts, support services, lounges, and more. It will be a mass timber structure with photovoltaic roof panels, creating a warm, comfortable and sustainable space!
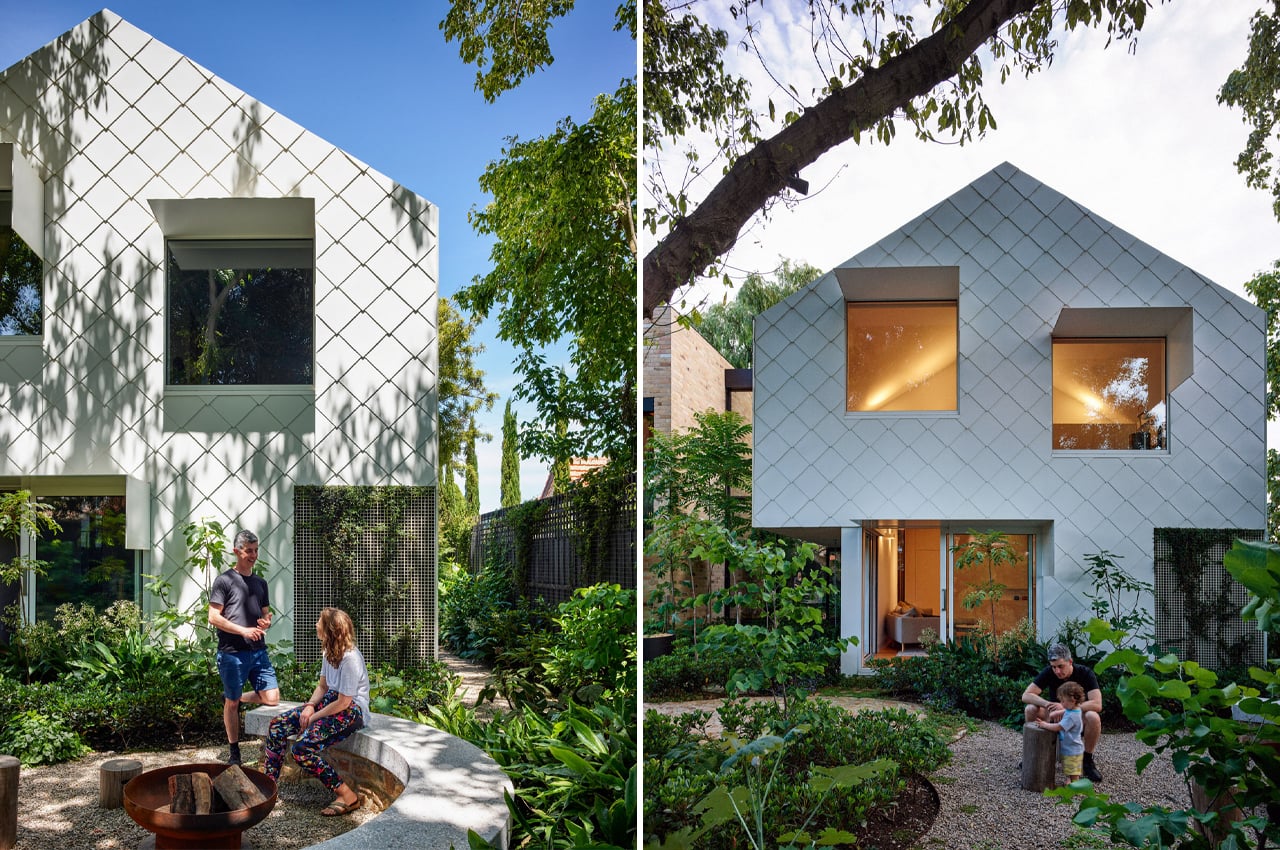


On average, the Australian home uses 19 kWh of energy on any given day. Turning that statistic on its head, Garden House produces 100kwh of energy with help from a 26 kWh Tesla battery. Finding the future of home sustainability through this sharing of energy, Garden House is powered by solar energy and powers the block’s shared energy grid. Since many Australians utilize solar panels to power up their homes, Garden House is in good company on a narrow street filled with garden oases and blooming greenery. Careful not to disrupt the natural terrain in and around the house’s lot, AMA developed Garden House’s layout and connected pavilions based around the network of pre-existing garden spaces and trees. This set the stage and literally the foundation for the home’s commitment to producing more sustainable energy than it requires to run.
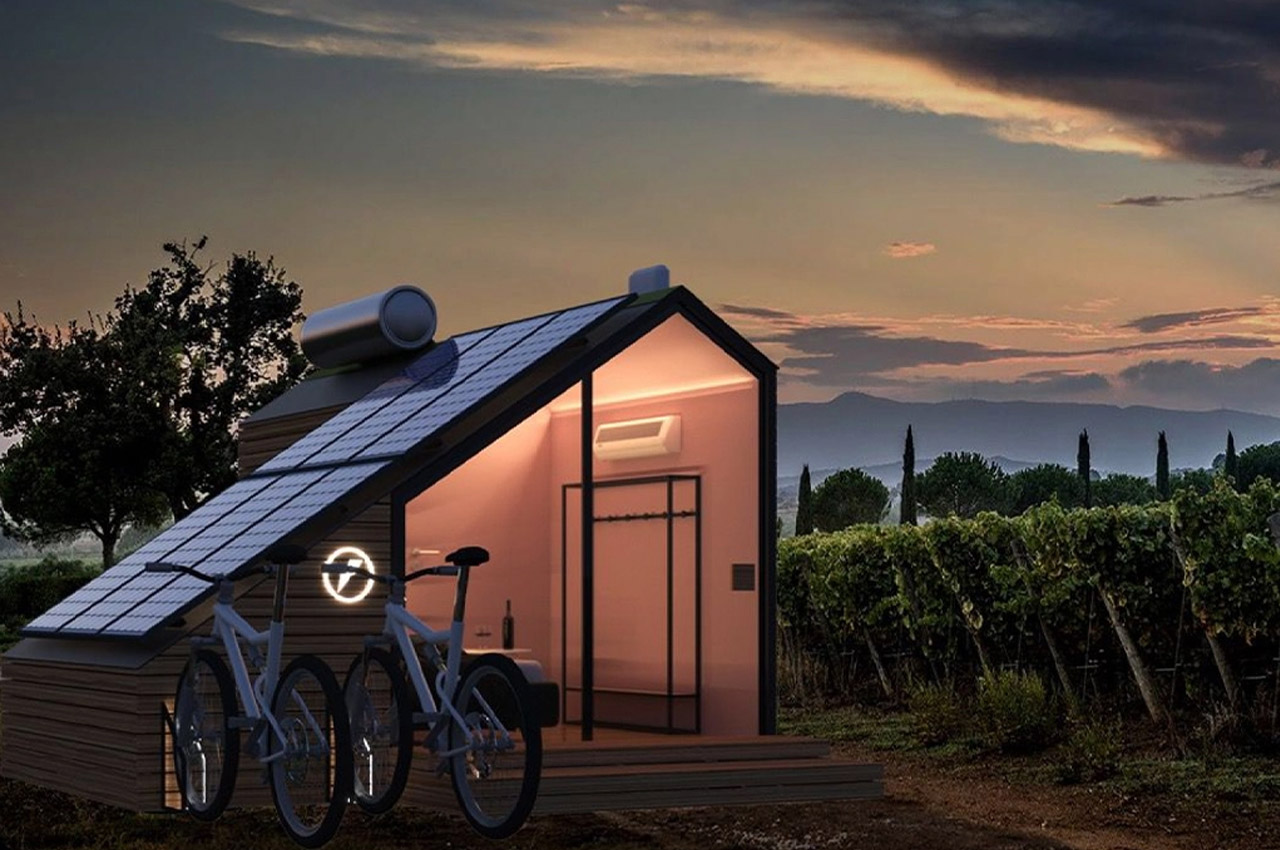
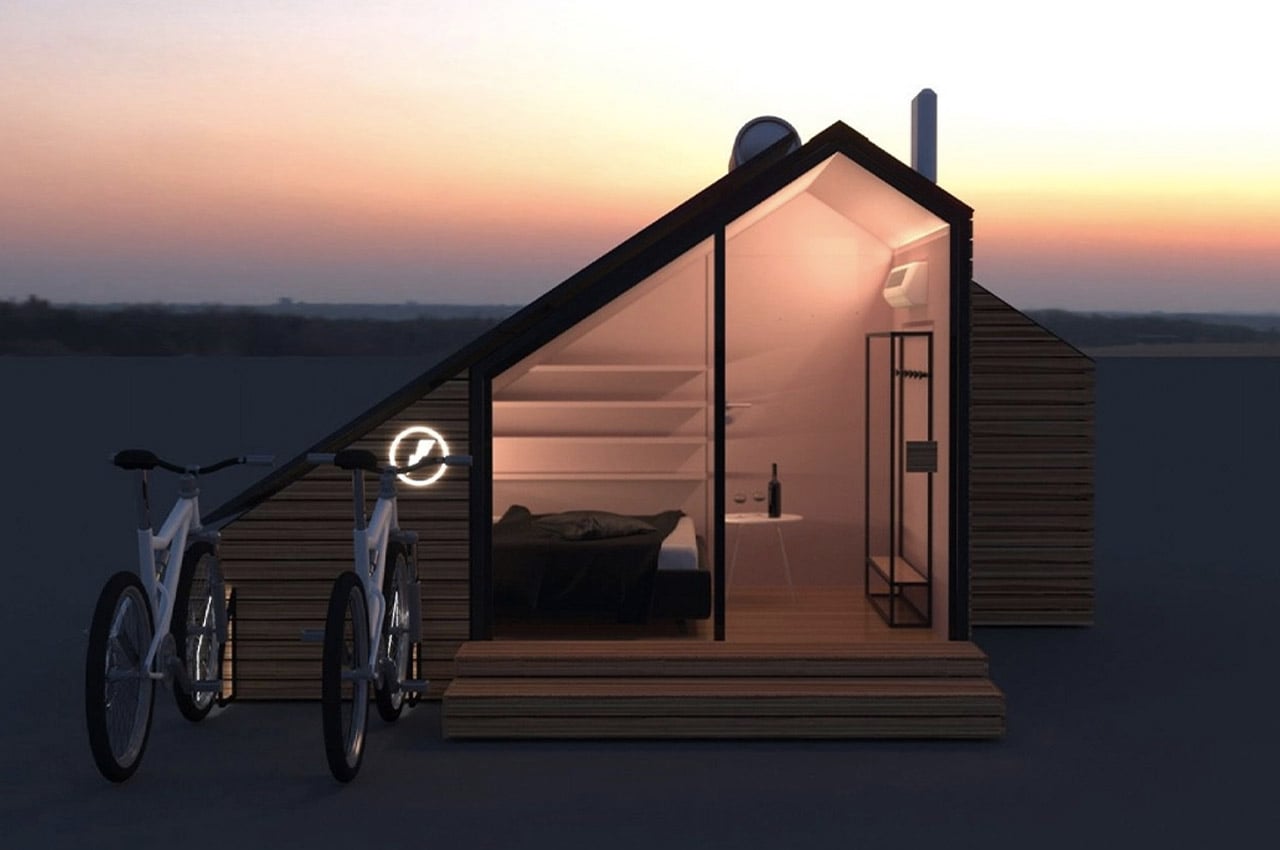


E-glamp is a product/service that has been designed to boost economic and tourist development in rural areas. Think of it as an Airbnb-style tiny house merged with a biking network like Bird or Lime. It is an integrated system of modern cabins that are all independently powered by solar panels. These tiny homes are also fitted with smart tech and are connected to the e-bike system which encourages carbon-neutral exploration of the landscape. Biking not only helps to maintain the pristine air quality of the rural area but also helps in getting an enjoyable workout in. All the E-glamp houses are modular, movable, and constructed with sustainable materials like timber. Along with solar panels, it will be interesting to see how the design is able to also repurpose and reuse rainwater for the guest’s needs.
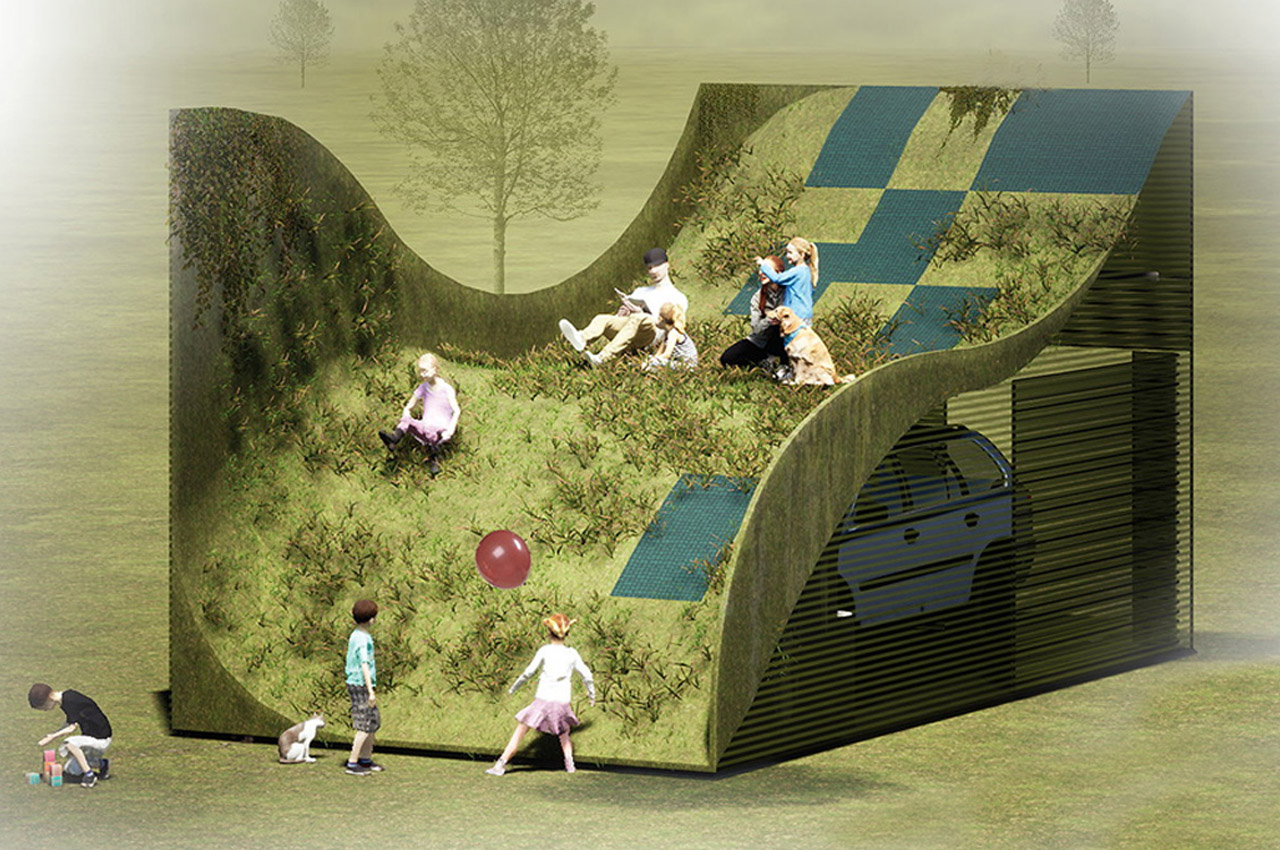
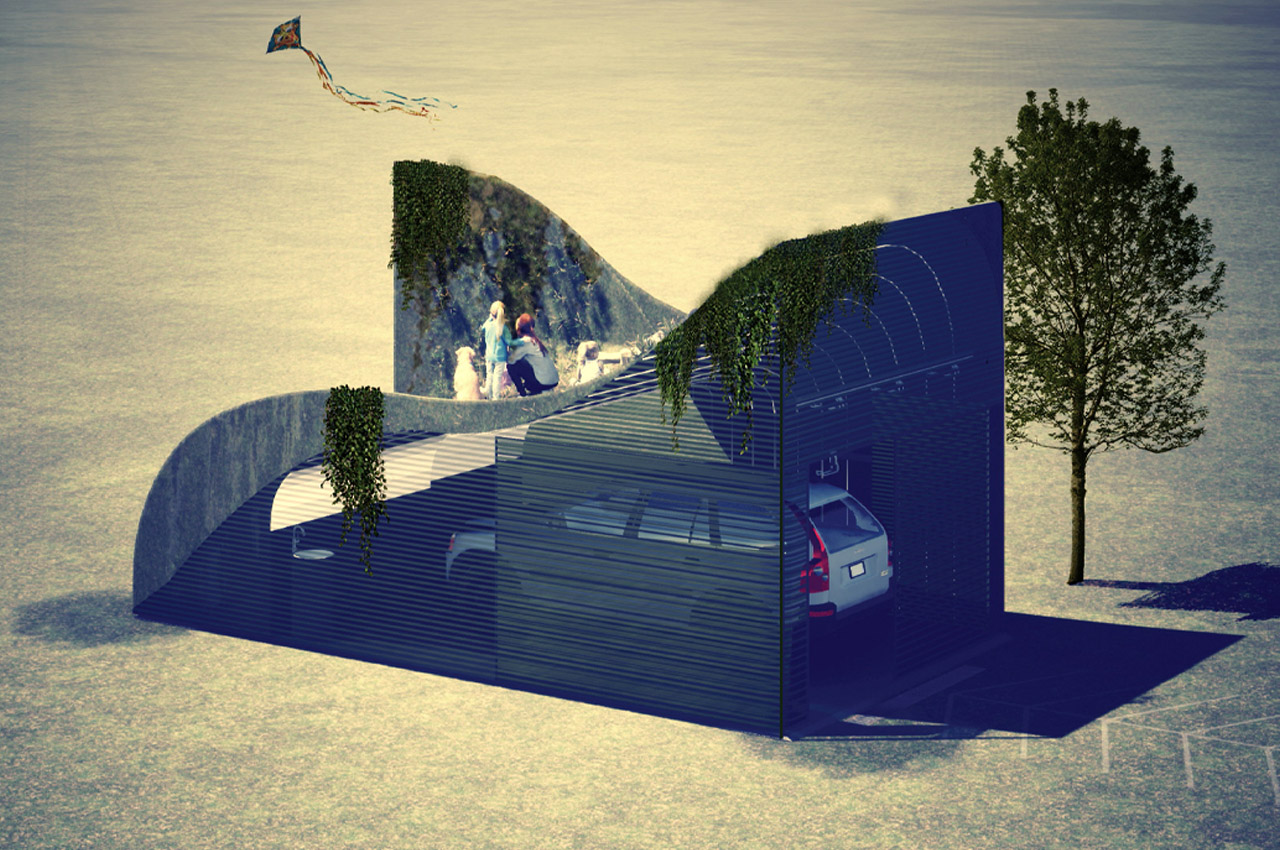


Reimagining the garage space as an interactive family space and biophilic greenway, Montreal designer Tiam Maeiyat’s Parking Parc was chosen as the winning concept for merging clean design with sustainability. Parking Parc was inspired by the pun in its own name– Maeiyat reinterpreted the garage as both a space for parking the vehicle and as an actual greenway that resembles a children’s park. Shaped like a rolling hillside, Parking Parc provides a storage area for parked vehicles that rests beneath the garage’s grassy, recreational exterior. As currently conceptualized, photovoltaic panels punctuate the taller regions of the garage’s exterior, providing clean energy for Volvo’s XC40 Recharge to well, recharge, and enough energy to sustain the rest of the garage’s inside operations.
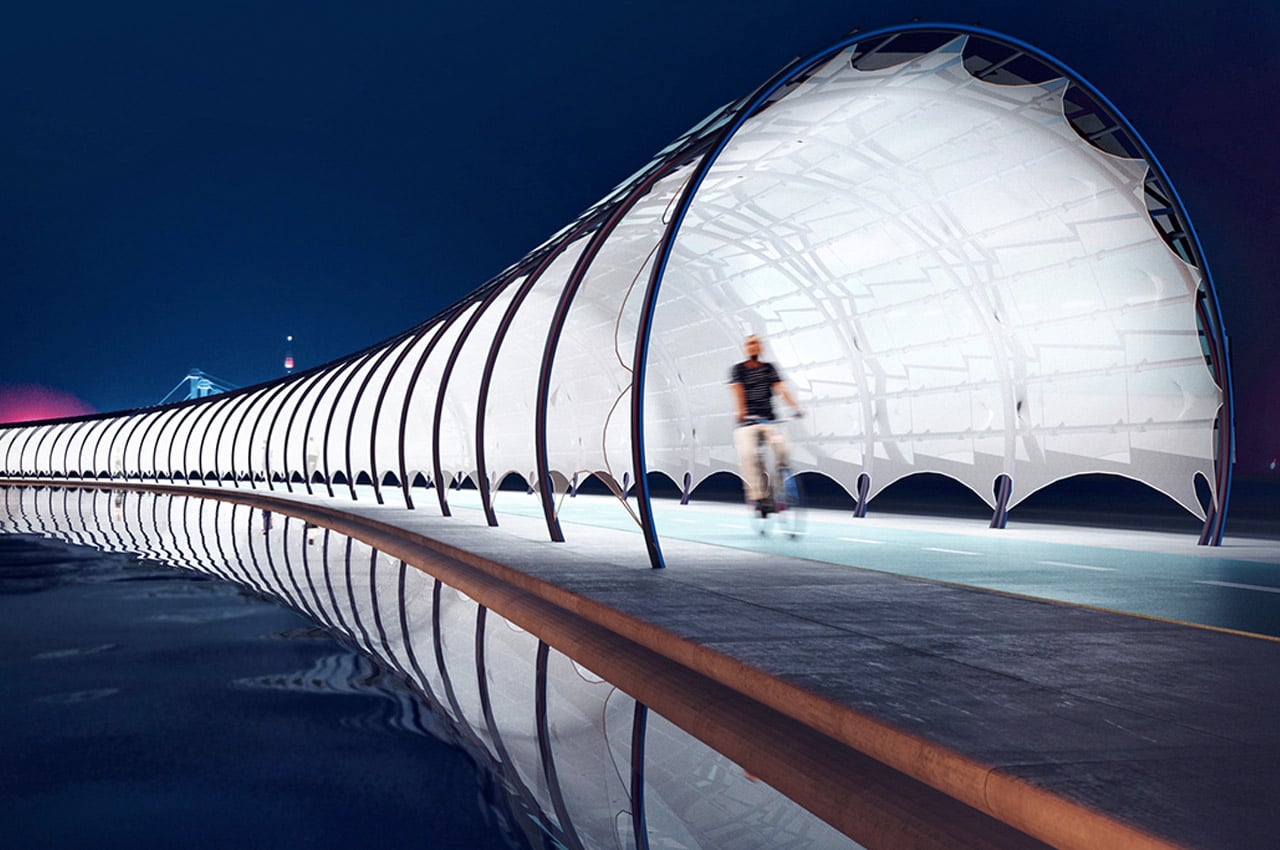

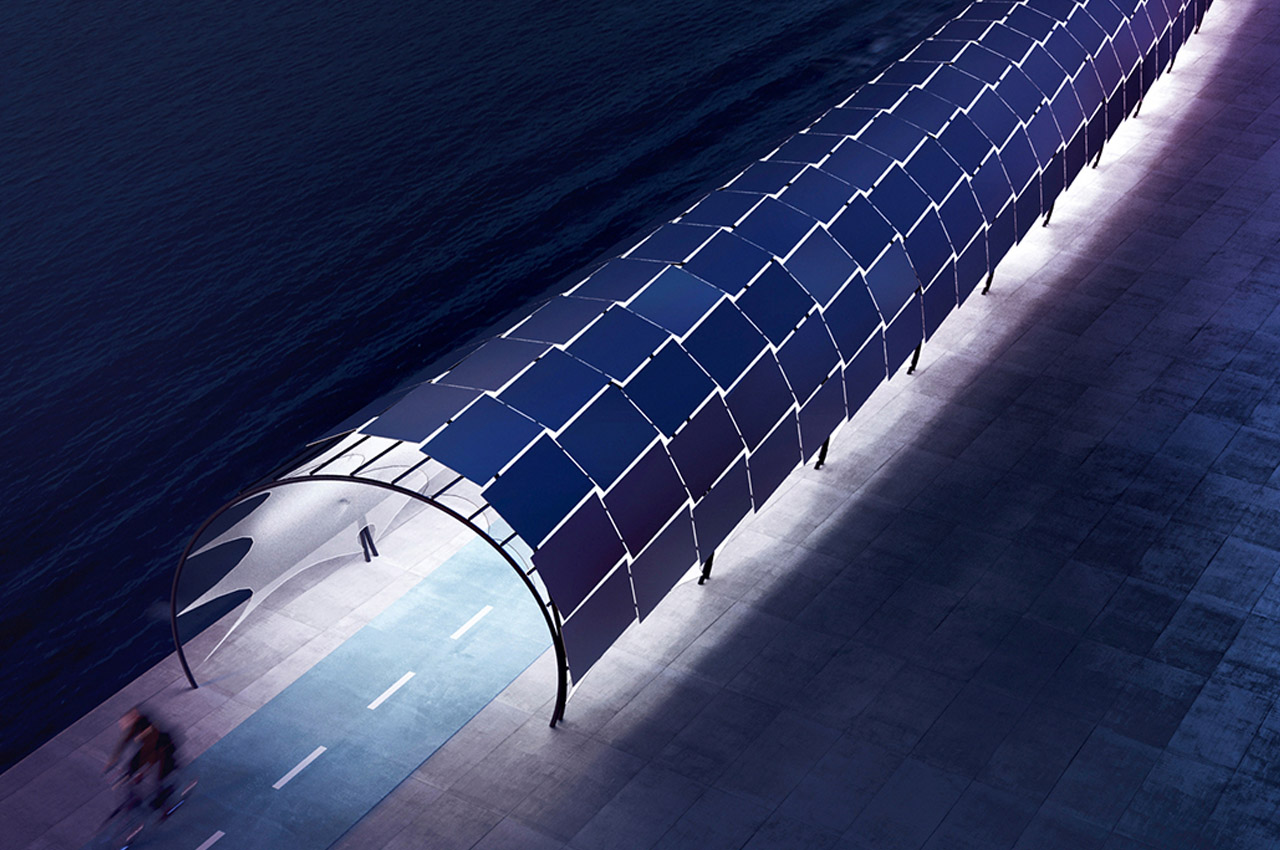
Many people who live in cities are taking to biking for their preferred mode of transportation, prompting designers and city officials to reimagine bike paths and public transport. Bike roads, also known as Veloroutes are steadily becoming city staples, even mainstays for commuters on foot or bike. With the demand for Veloroutes increasing, Kuczia created a Solar Veloroute that comprises a photovoltaic tunnel structure that serves as a solar canopy for cyclists and pedestrians as well as a public facility where commuters can enjoy lit pathways at night and charging stations for bicycles or smartphones. Solar Veloroute presents as a partly-enclosed, rounded archway constructed from overlaid non-reflective glass-glass solar panels, which are attached to round tube steel purlins.






