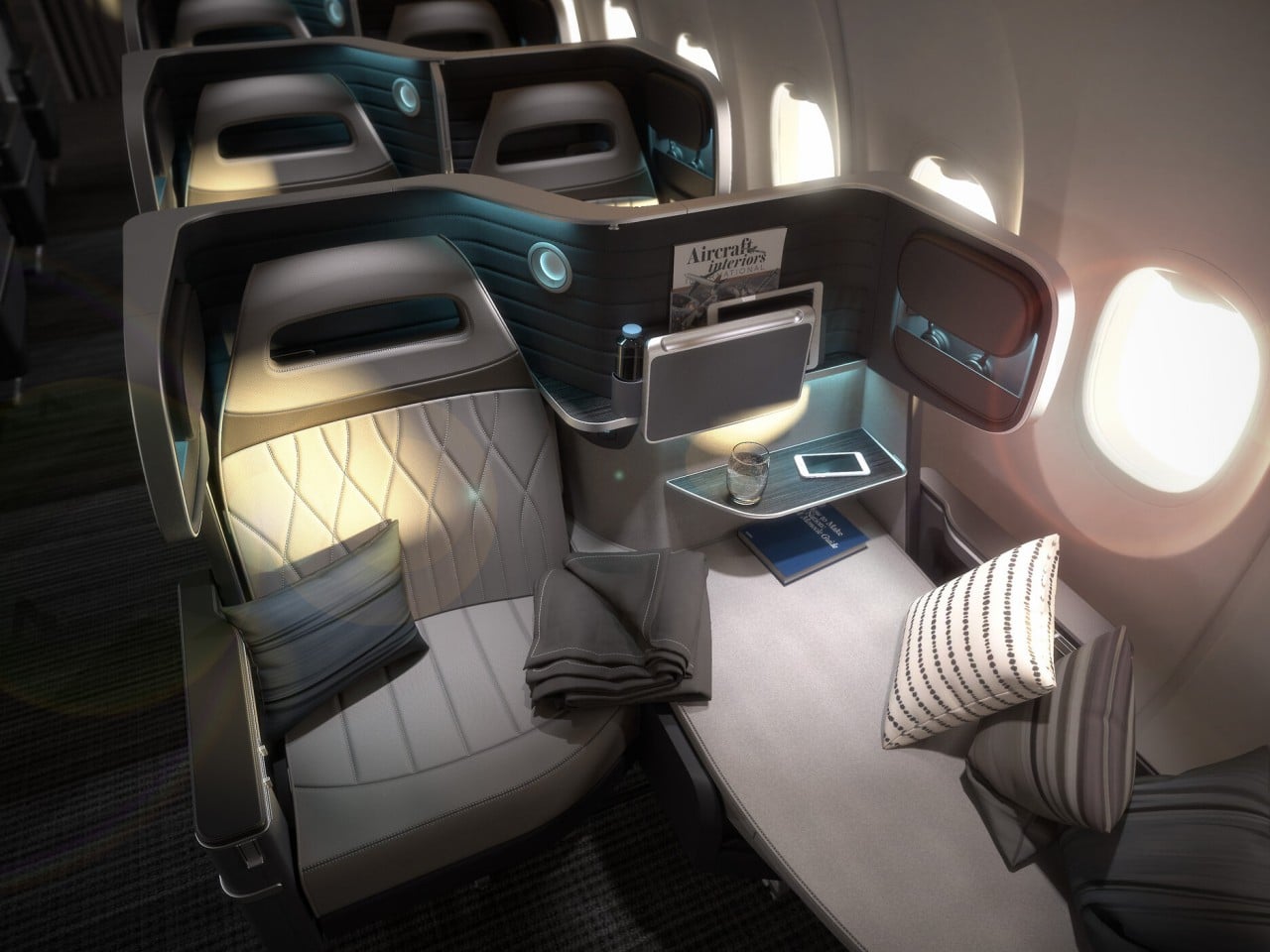
Air travel has always been one of the crowning glories of human innovation, proving that mankind can conquer almost anything if they put their minds to it. Over the decades, the aviation industry has been pushing the envelope of speed, efficiency, and safety, but much of the evolution doesn’t happen only on the outside of airplanes. Interior design has also been changing at an even more rapid pace, and a more visible struggle can be seen beyond seat class boundaries. Comfort, luxury, cost-efficiency, and profitability have always been the goals of all airlines, but these sometimes conflict with each other, creating an almost never-ending tug-of-war between maximizing airline profits and ensuring passenger comfort. We take a deeper close into the design philosophies and elements that define airline seating and the effects they have on the economy, the planet, and of course, human comfort.
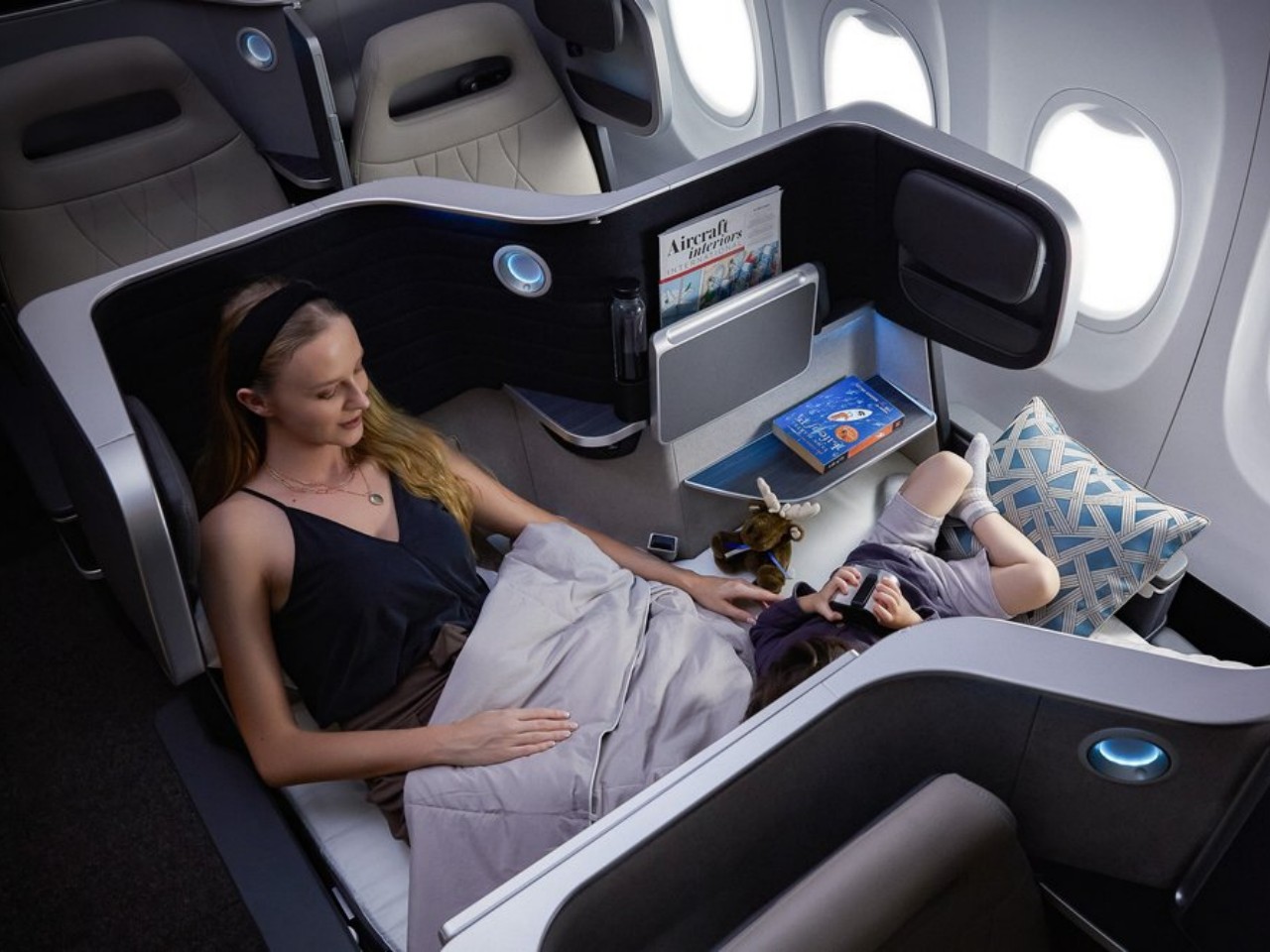
Designer: James Lee (Butterfly Seating)
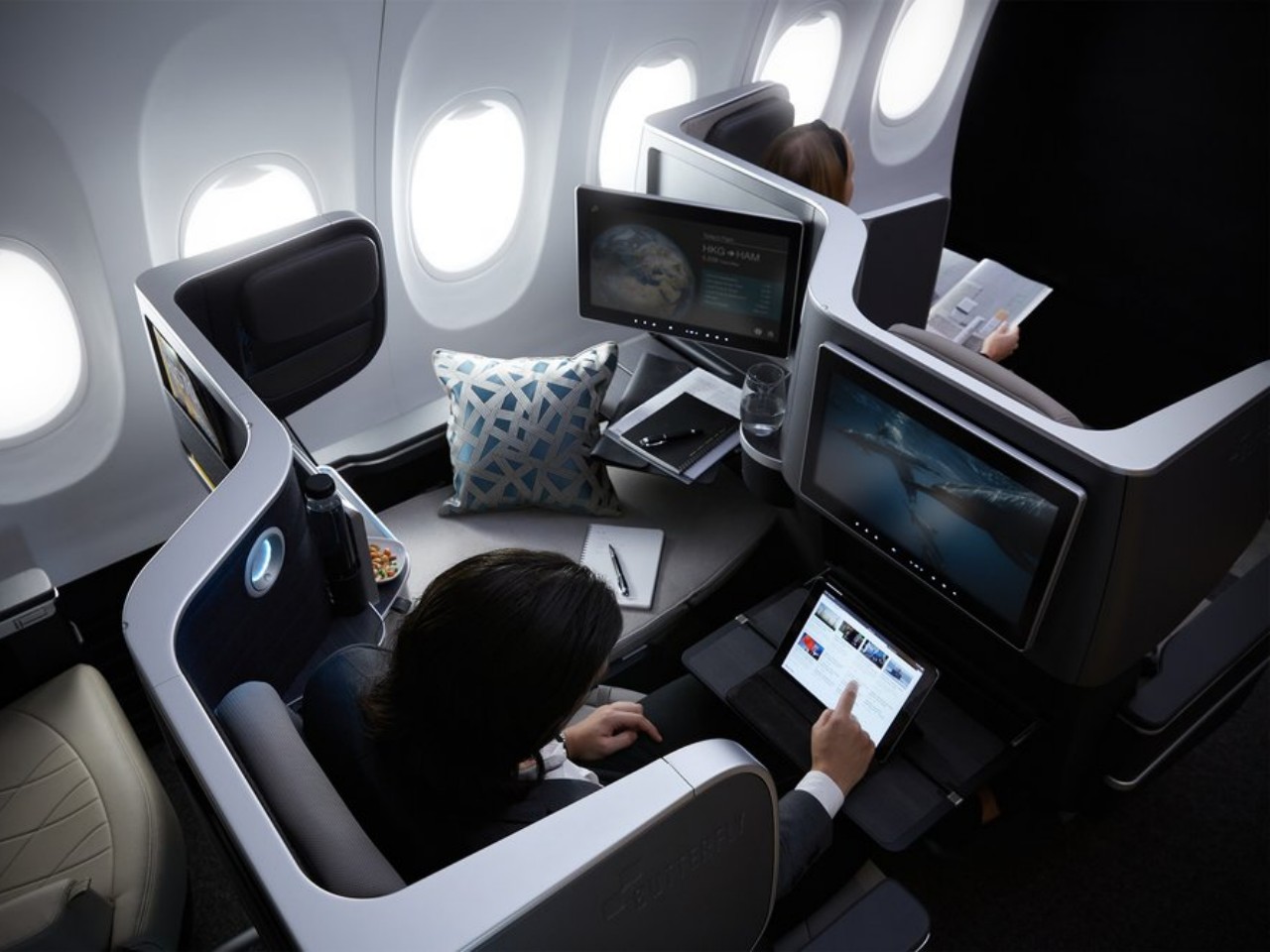
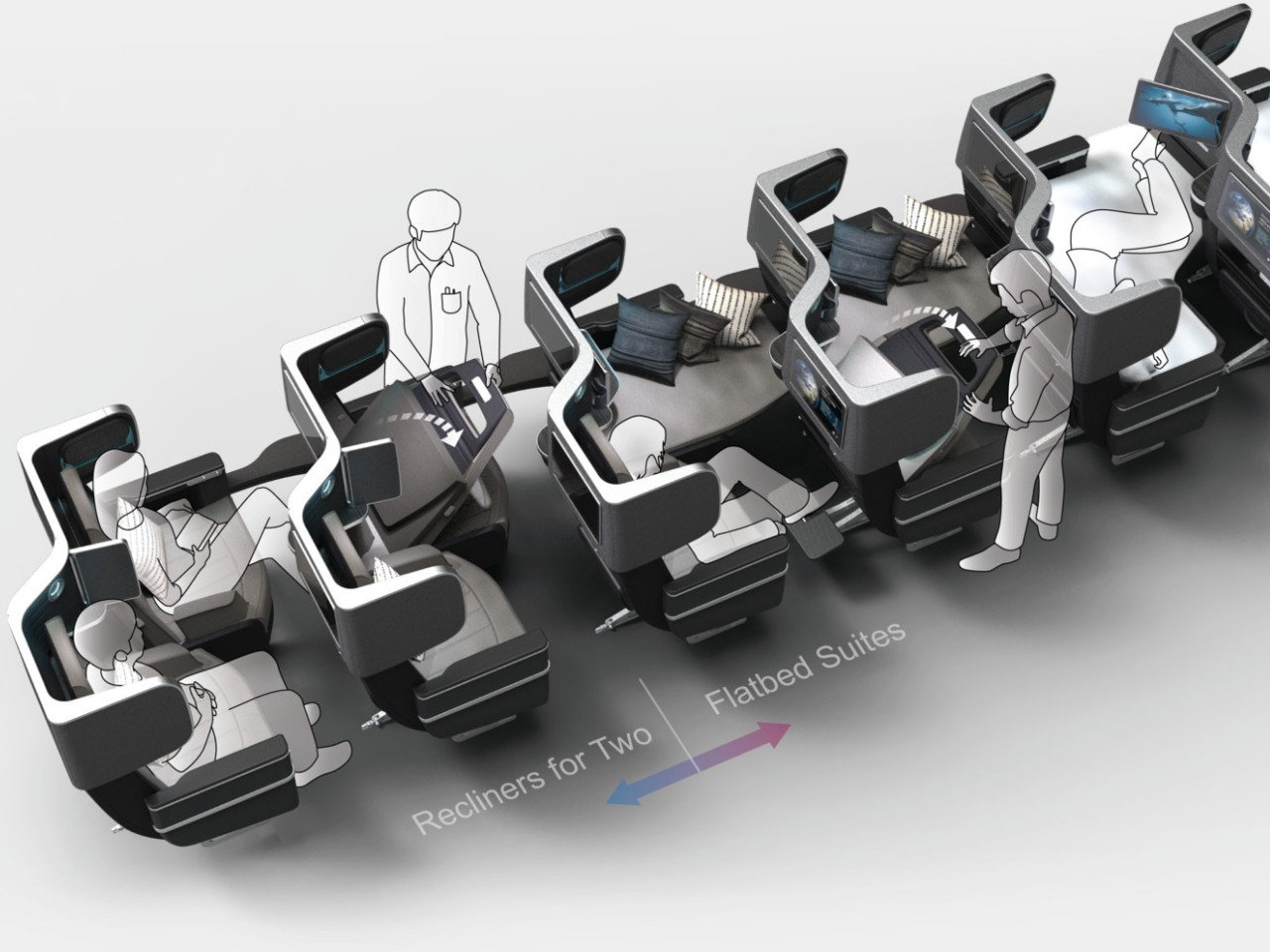



Minimalism vs. Luxury: A Deep Dive into Design Philosophies
Airline seat design has always fluctuated between two extremes, often exemplified by the division between economy and first-class sections. You have minimalism that focuses on efficiency and functionality on one end, and you have luxury that emphasizes premium experiences almost to the point of exclusivity on the other end. Of course, both philosophies are ideal to have in both seating classes to different degrees, but they also have different priorities that define the final seat design.
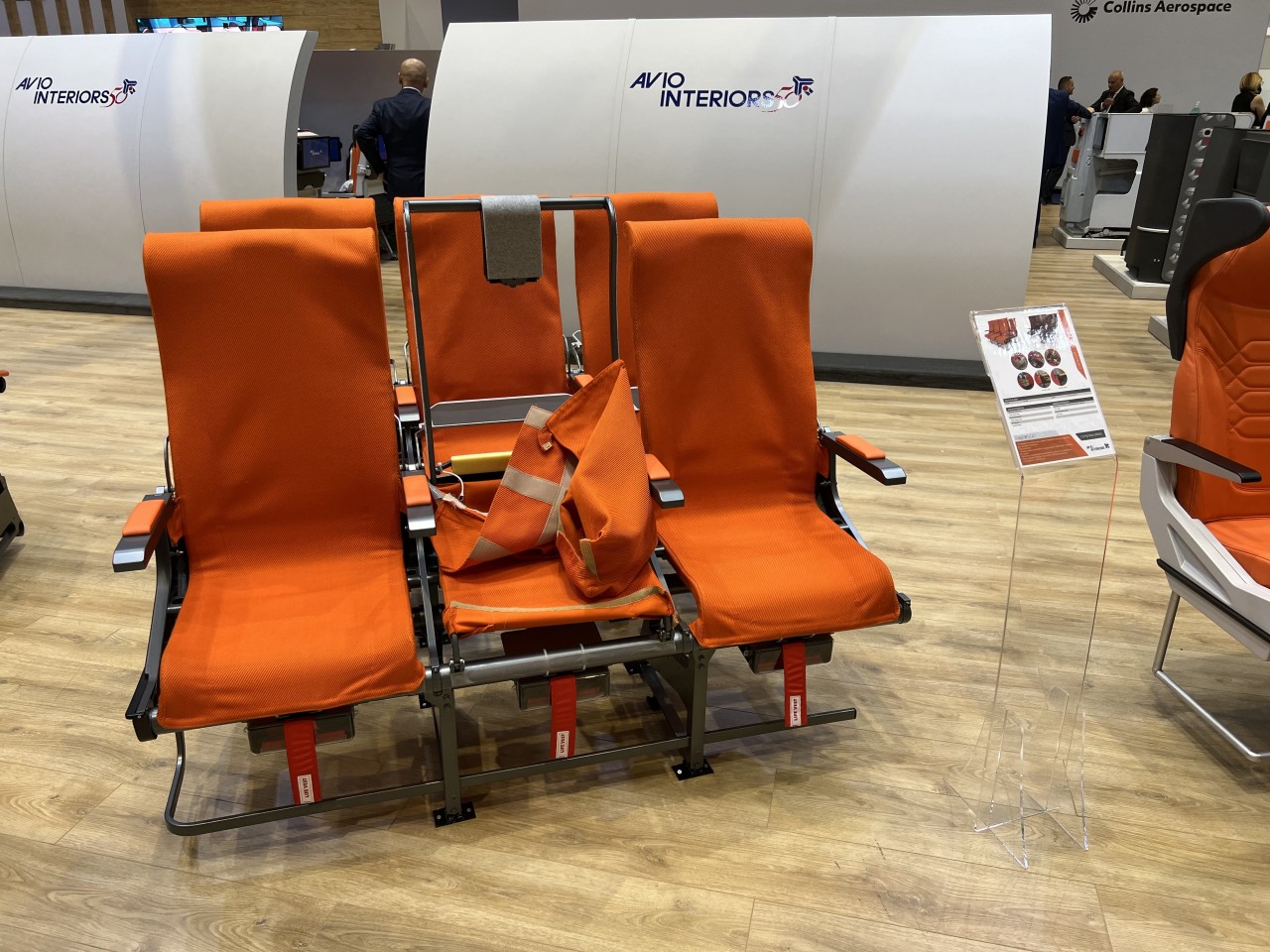
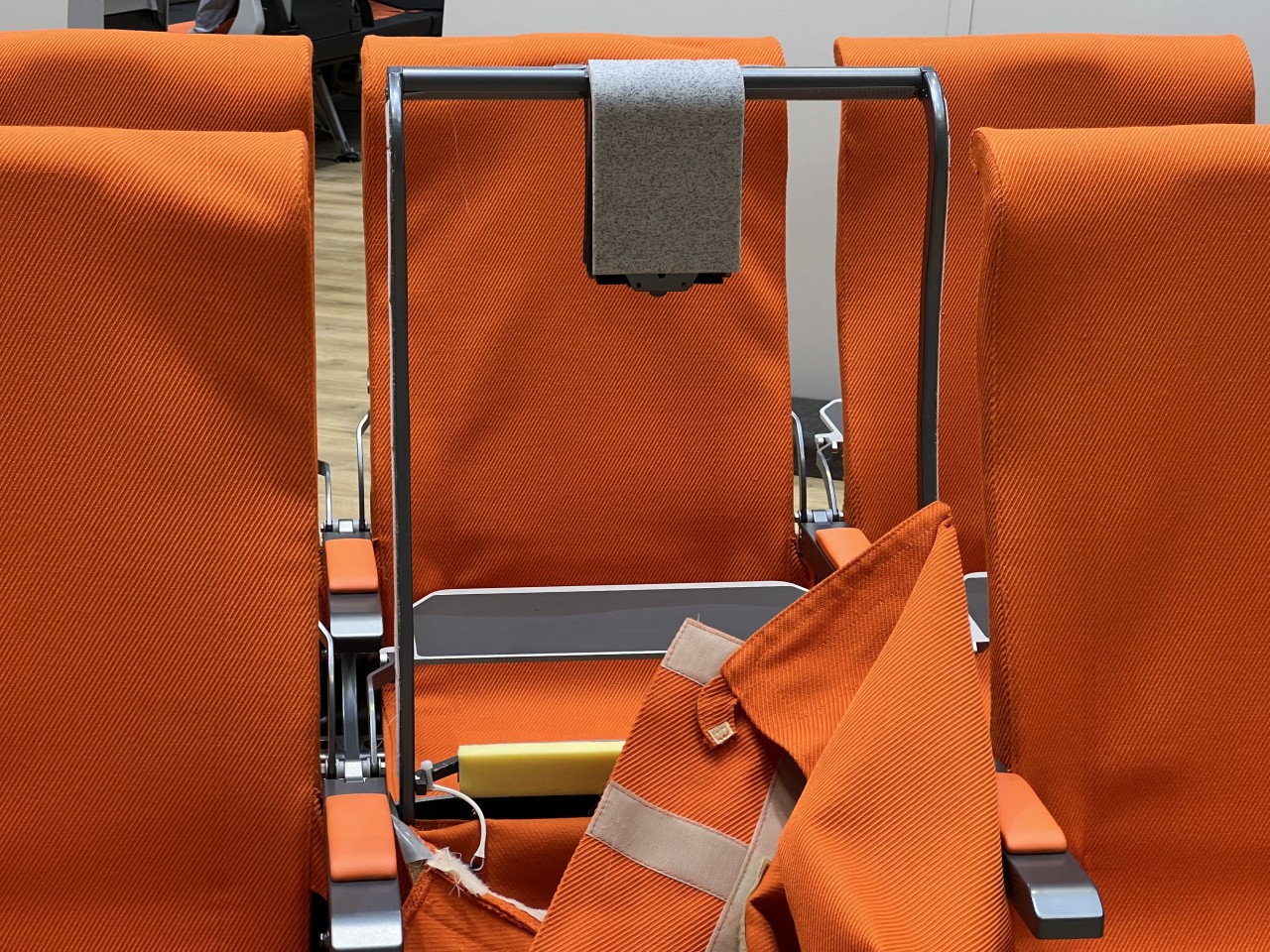
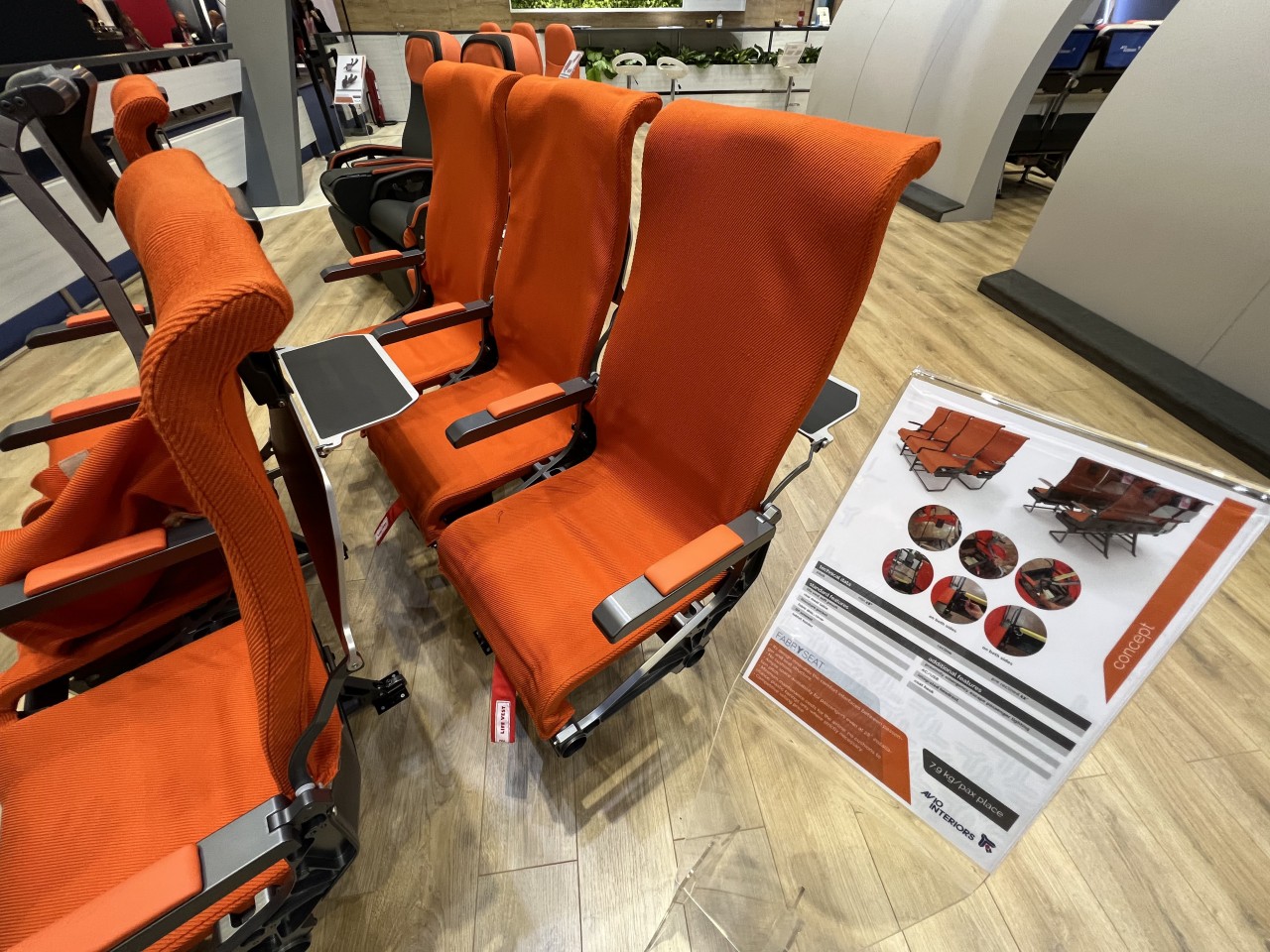
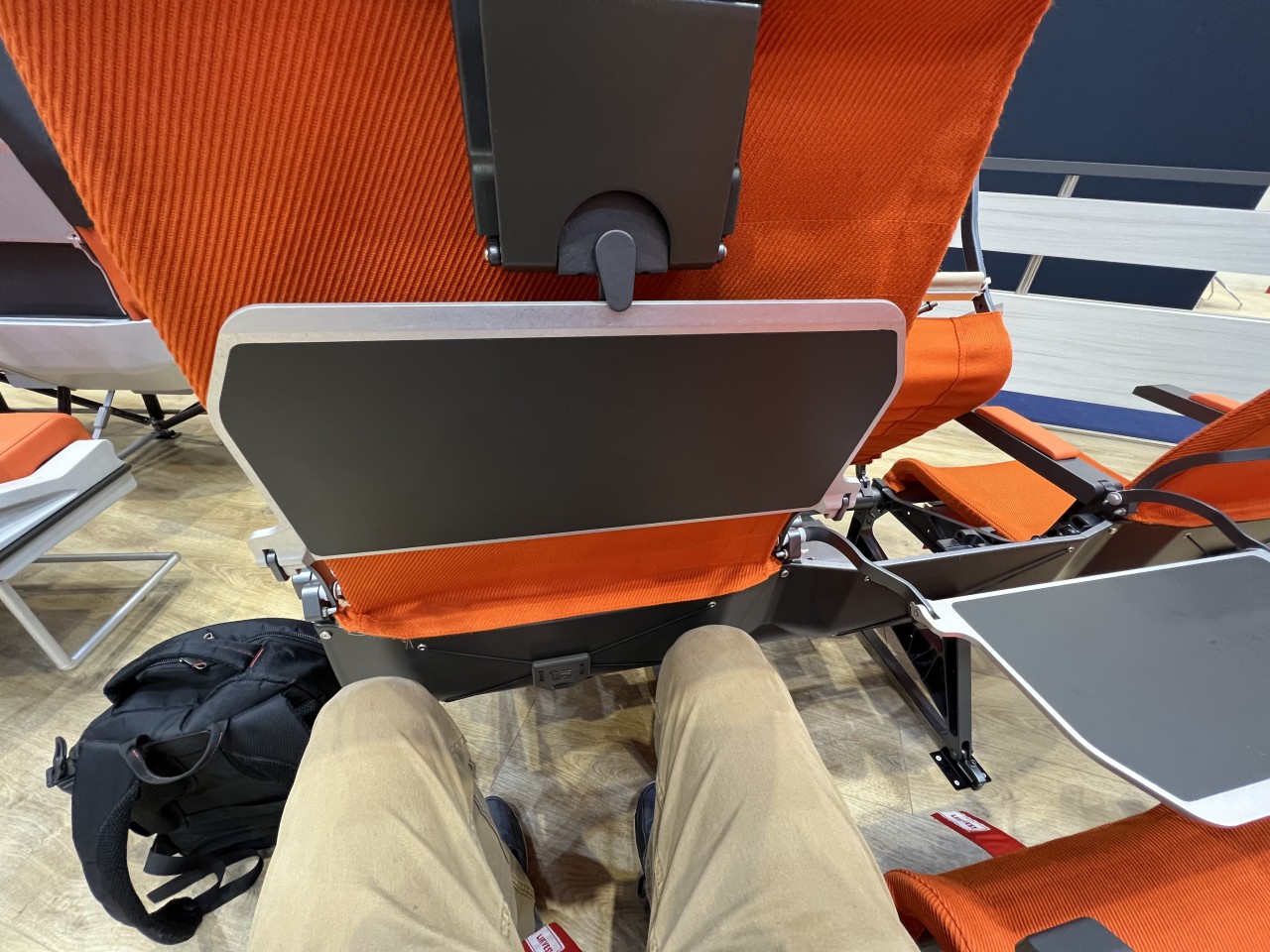




Designer: Aviointeriors (via Jason Rabinowitz)
Minimalist seats, for example, prioritize space efficiency and cost-effectiveness in order to both lower ticket prices as well as increase profits. By minimizing the space occupied by seats, using more lightweight materials, and adopting streamlined designs that are easier to clean, airlines can minimize operation costs while also increasing ticket sales and, therefore, increasing Revenue per Available Seat Mile or RASM figures. This is mostly seen in economy class seats and budget airlines, of which the likes of Ryanair and Spirit Airlines are best known. Aviointeriors’ 7.5kg “FABRYSEAT” concept is an example of extreme minimalism, pretty much just a metal frame with a fabric covering and a small headrest.
On the opposite end of the spectrum, luxury designs put comfort and convenience above all, even if it means increasing costs for both the company and the passenger. There is enough space to completely recline the seat into a bed and airlines offer extra amenities not available to other passengers. Given the price involved, these luxuries are only offered to business and first-class passengers, and Singapore Airlines and Etihad Airways are perhaps the most popular examples of such premium experiences.



Designer: Etihad Airways
Economic Impact of Different Seat Designs
Just like how airplanes themselves require a delicate balancing act to stay airborne, every aspect of seat design has an overall effect not just on passenger comfort but also on the airline economy in general. Two of the most important elements to be considered for seat configurations are the seat pitch and the seat width. Seat pitch, which refers to the space between one seat and the one in front of it, and the width of the seat not only affects passenger comfort but also how many passengers you can fit in the cabin.
You might think that having more seats and more passengers will always be beneficial for the airline, but that isn’t always the case. Cramped spaces are likely to also decrease customer satisfaction, leading to lower customer loyalty, and more seats and passengers will also weigh the plane down as well, requiring more fuel, interior modification, and, in the long run, higher operating costs. The duality between these two elements isn’t always clear-cut as well. For example, United Airlines has an Economy Plus that offers more legroom but at a higher price. This conundrum is at the heart of that tug-of-war that both airlines and even regulators face, balancing profit maximization and passenger satisfaction.
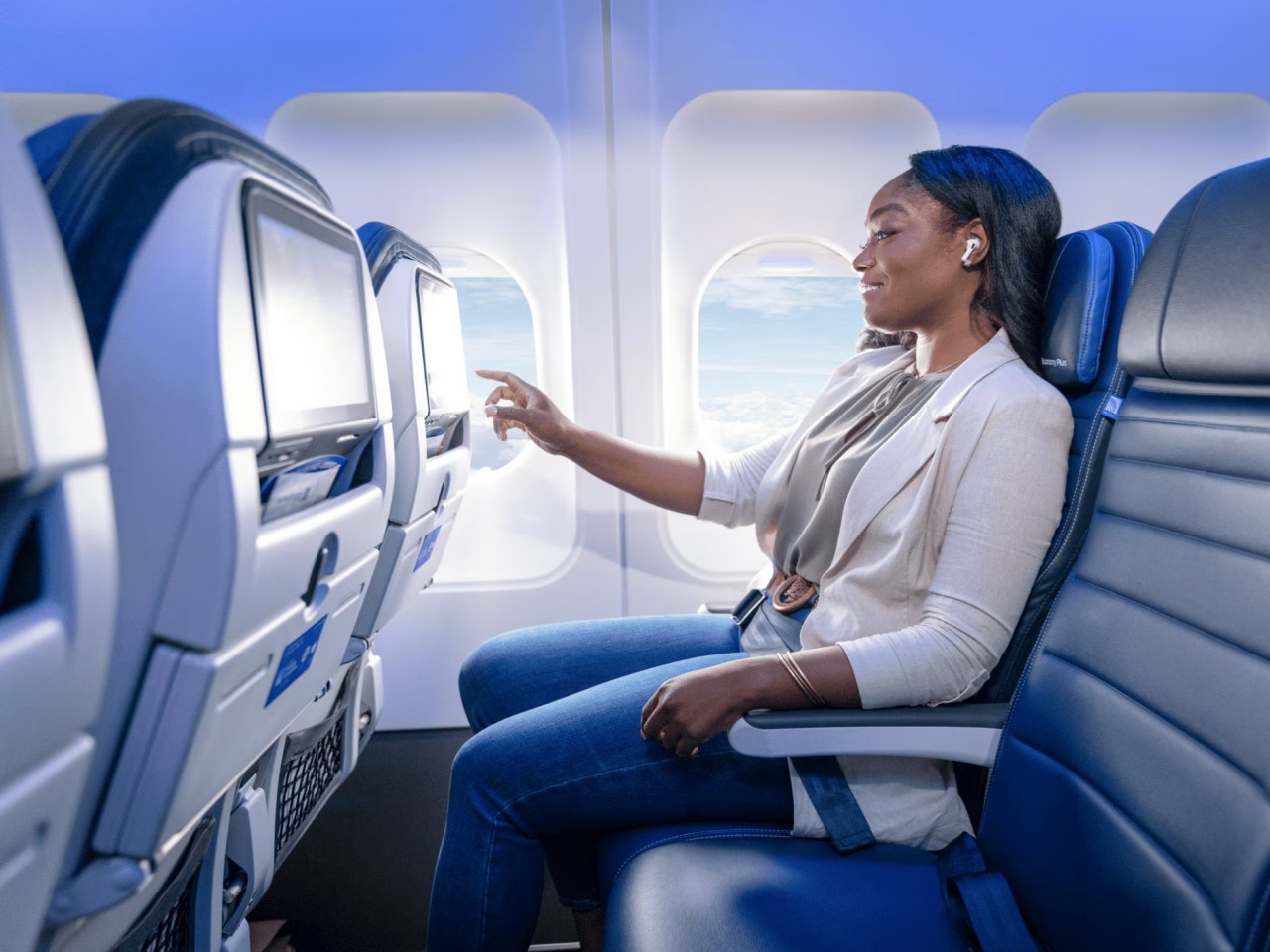


Designer: United Airlines
Ultra-Luxirious First-Class Seats vs. High-Density Economy Seats: A Few Case Studies
With dozens if not hundreds of airlines in operation around the world, there are just as many seat designs available that cover the spectrum between extreme minimalism and posh luxury. There are, however, a few that have stood out over the years, almost becoming representatives of these two design philosophies. Of course, business is more complicated than that, and most airlines have different sections or even aircraft that cater to different audiences and budgets.
On the luxurious side of flights, Etihad Airways is quite famous for its “The Residence,” offering a three-bedroom suite, a shower, and even a personal butler. Singapore Airlines’ Suite isn’t far behind with its full-length bed, 32-inch TV, and privacy sliding doors. Both airlines offer hotel-like amenities and luxuries available to those who can afford the rather steep price tag.
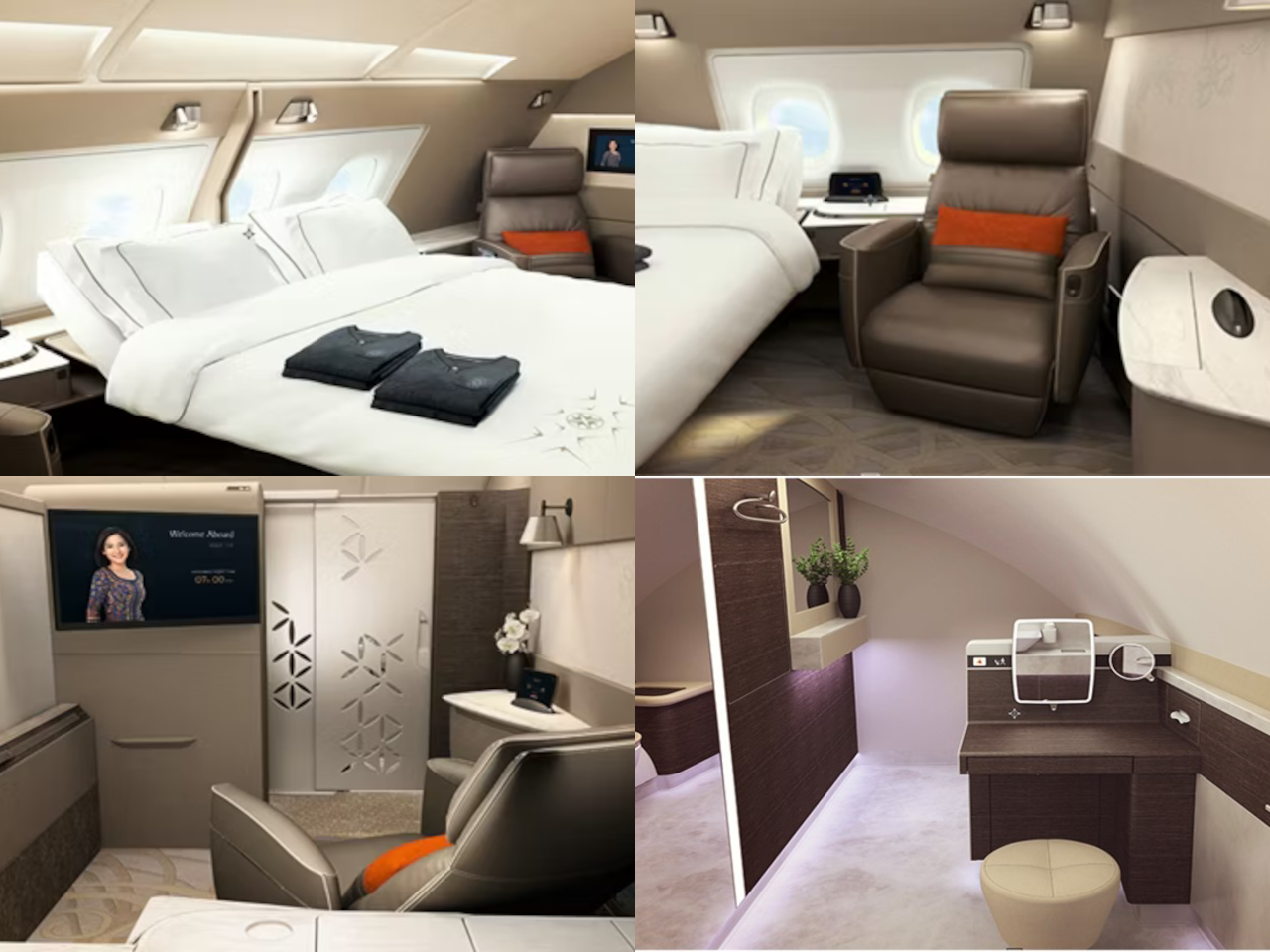

Designer: Singapore Airlines
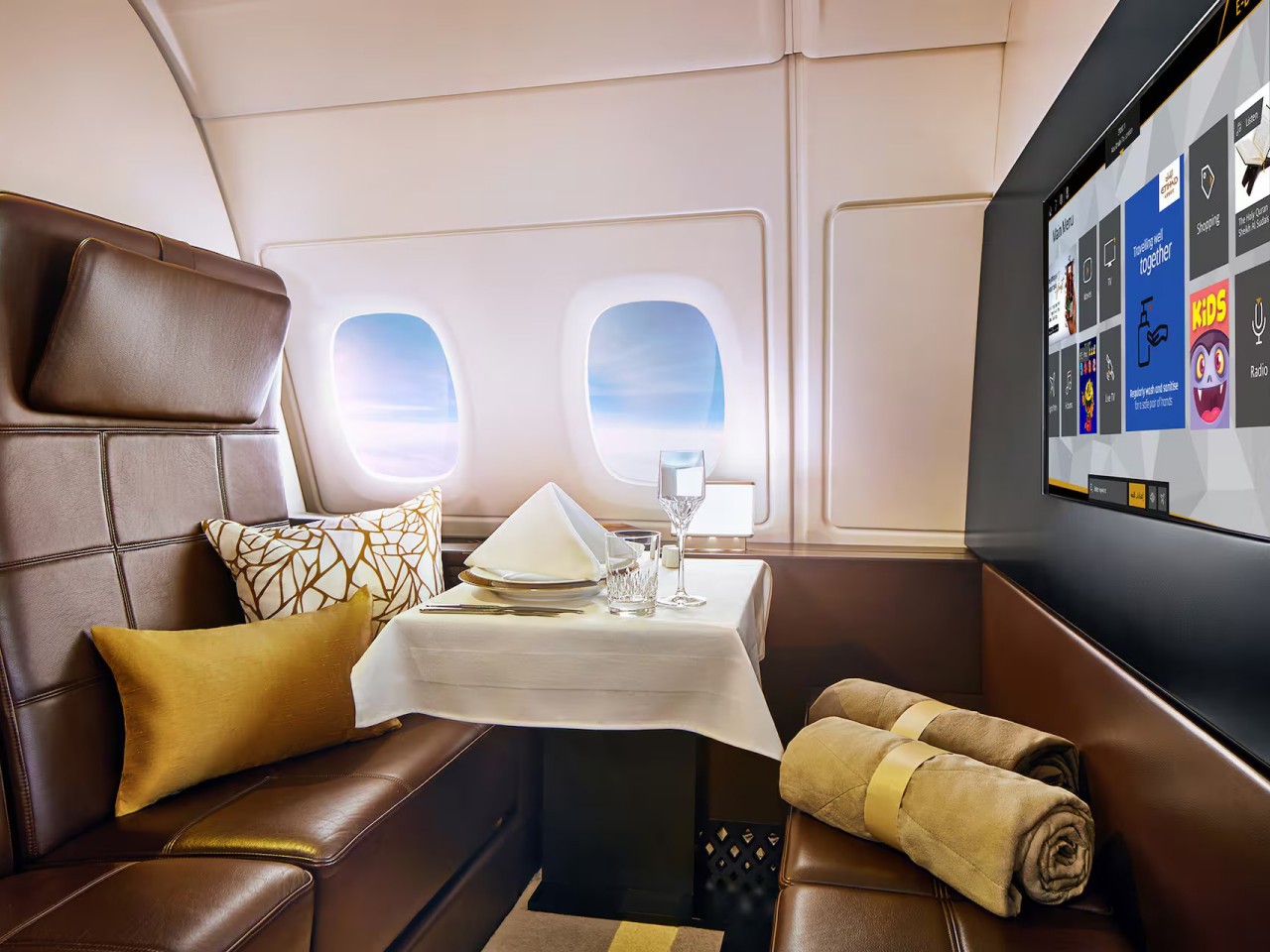
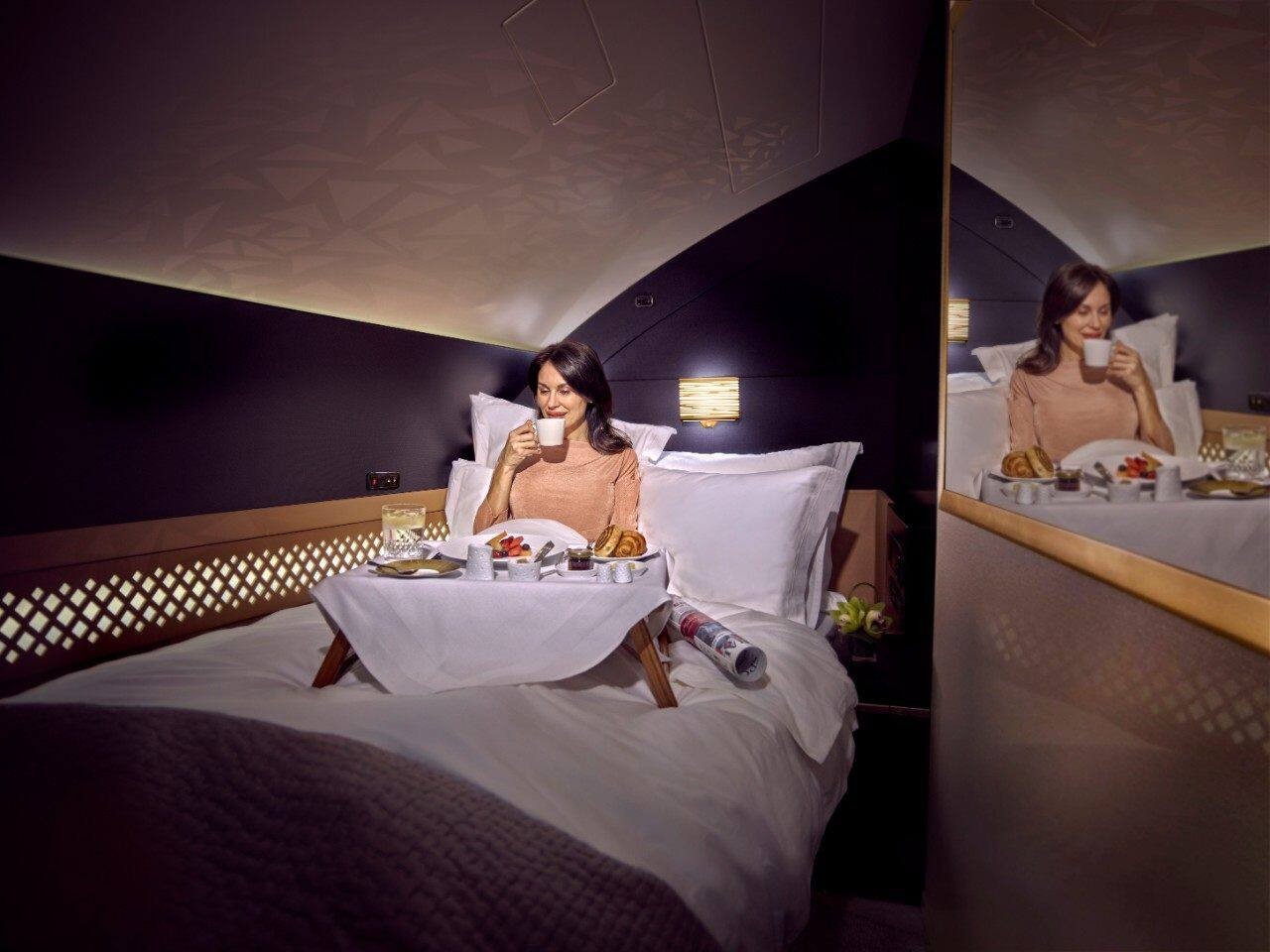



Designer: Etihad Airways
Conversely, Ryanair and Spirit are poster children for high-volume, low-cost economy seats, with seat pitches averaging 30 inches or lower. Most of the designs are minimalist and utilitarian, employing mass-produced materials to keep costs low and tickets affordable. It might sound uncomfortable, but these configurations are quite popular with budget travelers, especially frequent flyers who simply need to get from A to B without much fuss.
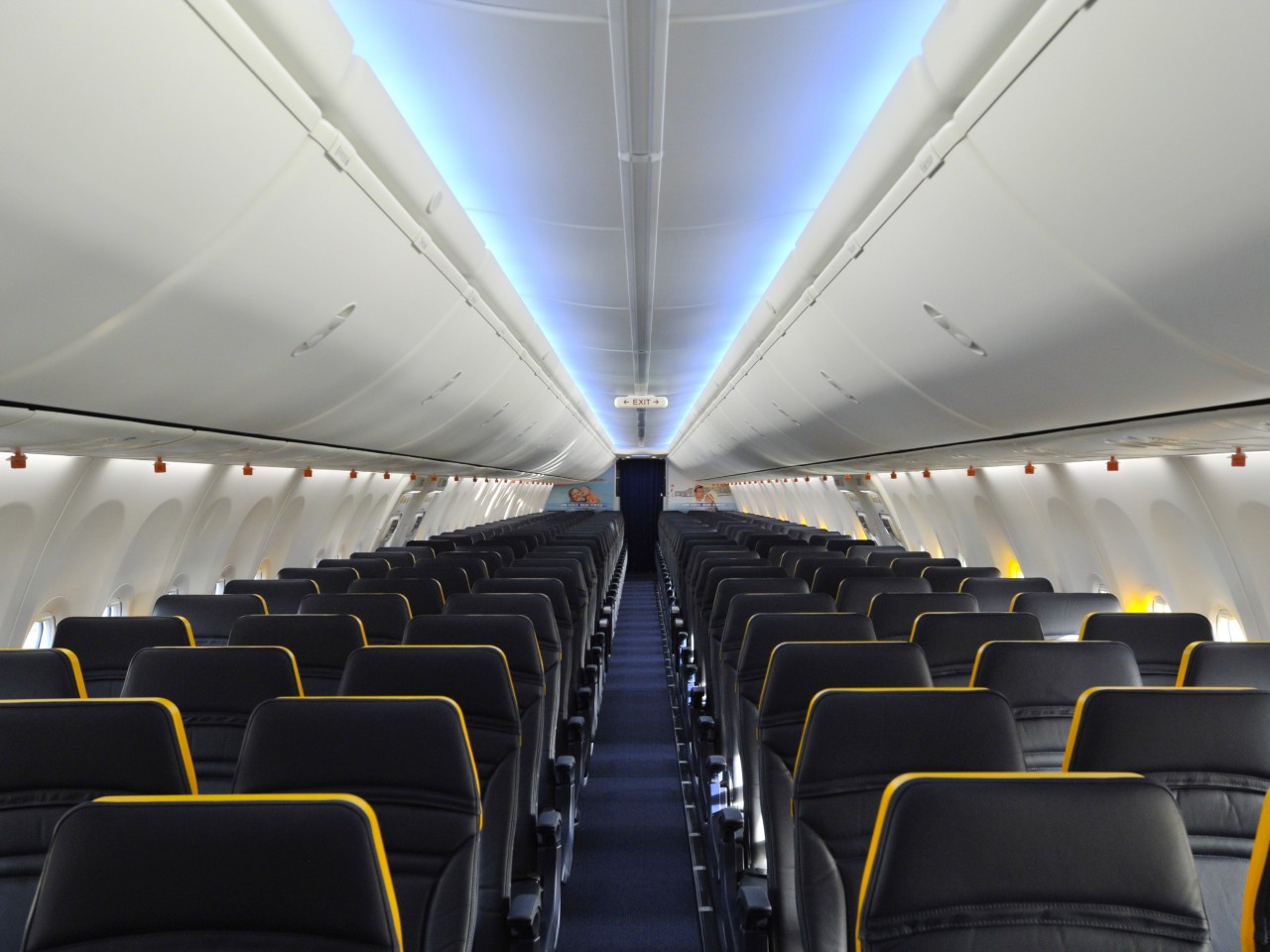



Designer: Ryanair
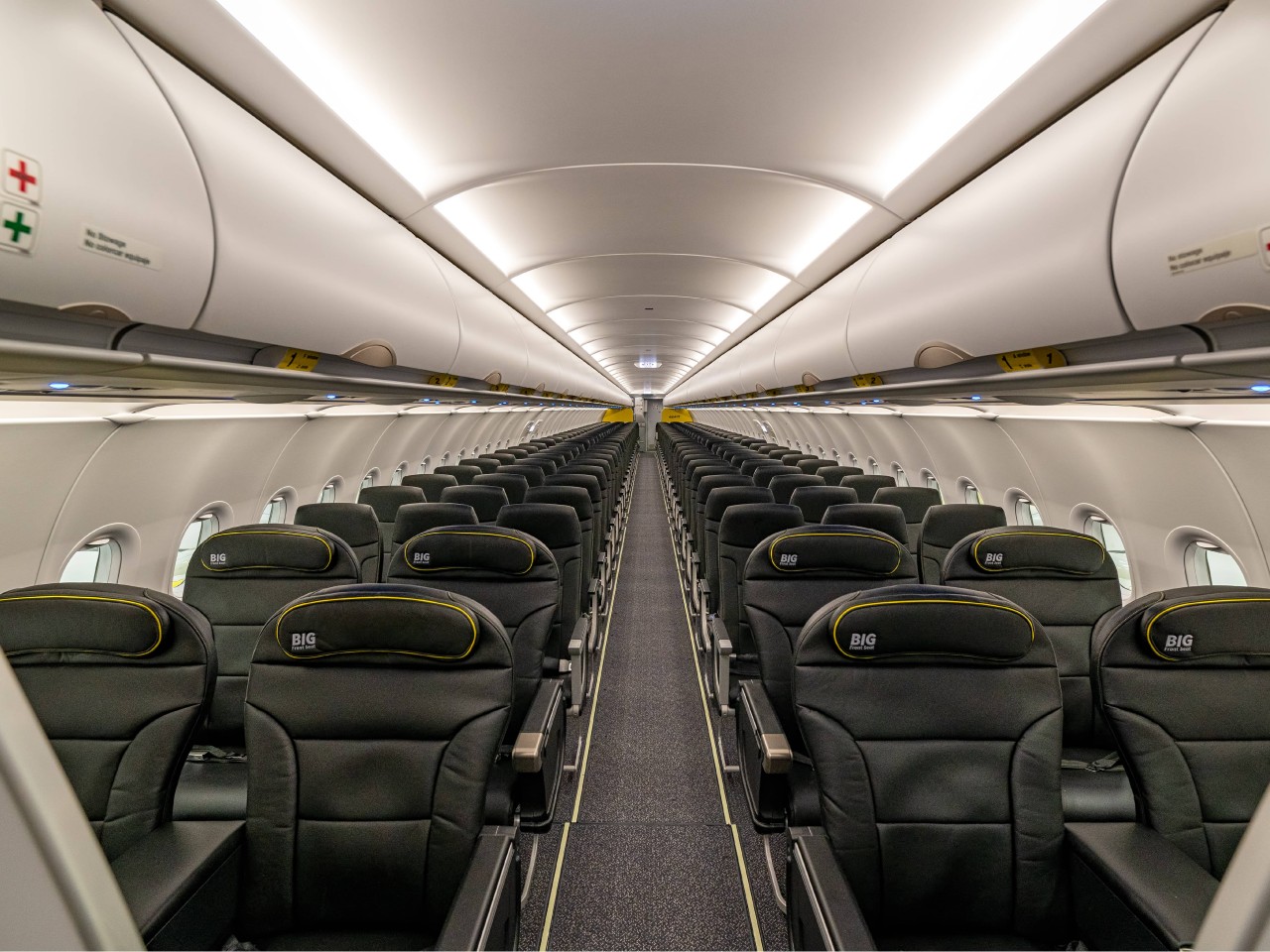
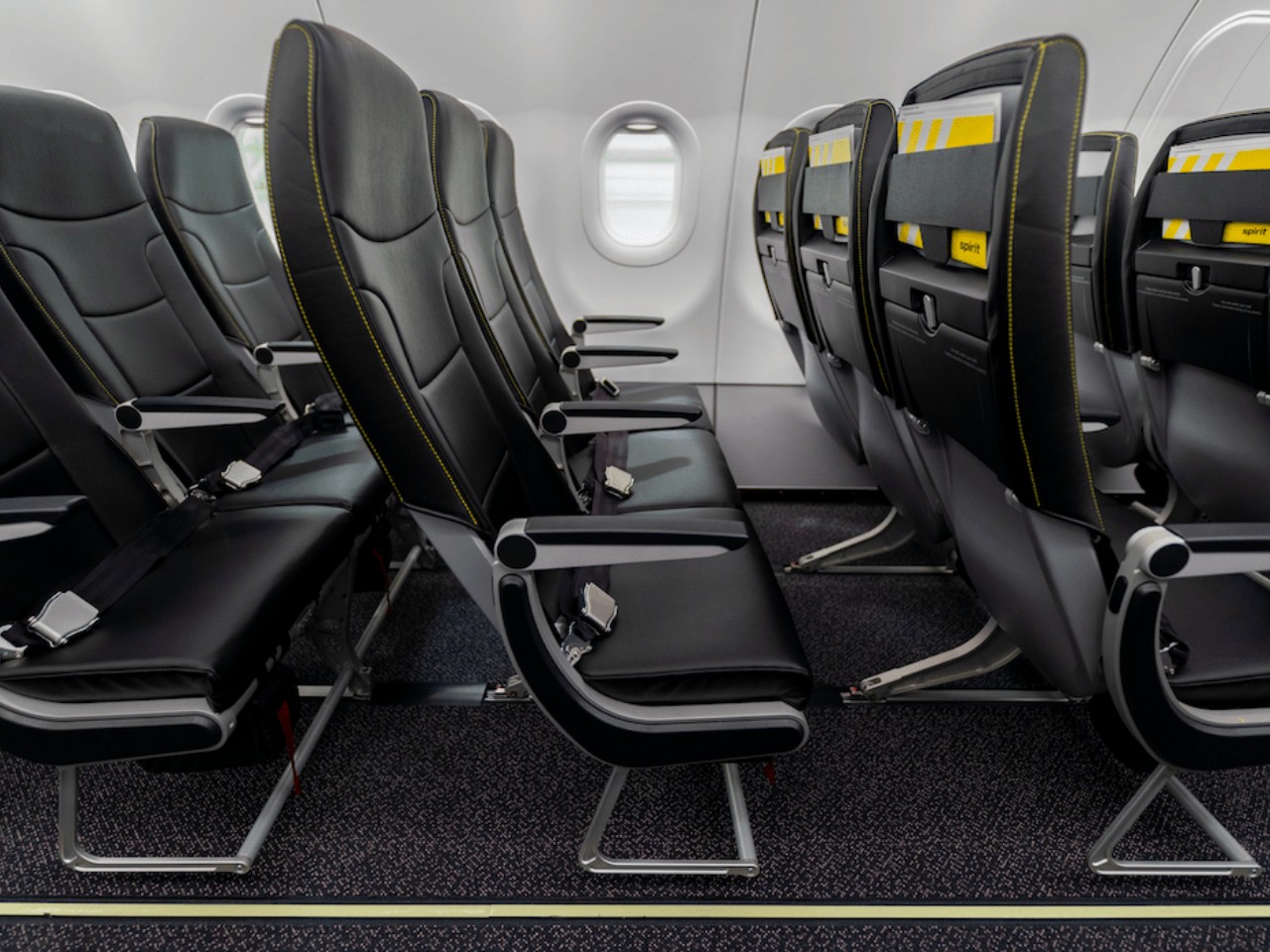
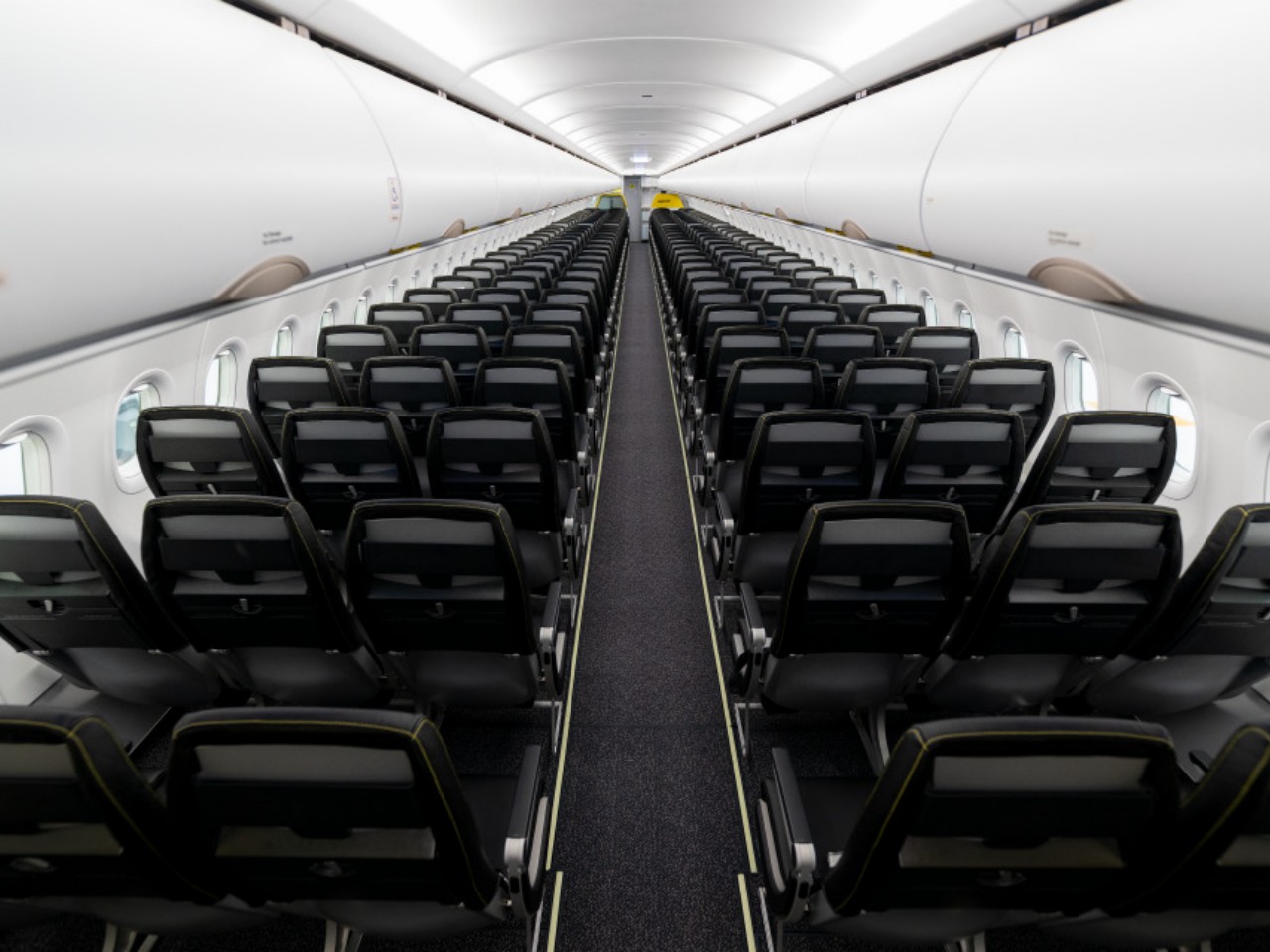



Designer: Spirit Airlines
Sustainability in the Air: Balancing Eco-Friendly Designs with Cost and Comfort
These days, it’s no longer enough to be cost-effective or luxurious. Sustainability has become a major consideration in airline seat design, and to some extent an added complication. Companies and designers now also have to consider using eco-friendly materials that won’t compromise comfort and cost, and that’s not always an easy feat even for normal product designs.
There are a few airlines that have started that arduous journey, like Air New Zealand’s use of plant-based leather alternatives, or Recaro’s SL3510 carbon fiber-reinforced plastic to make seats lighter. There are also other concepts that not only utilize lightweight materials but also apply simpler structures and mechanisms to reduce the number of parts needed. Lighter and recycled materials can help lower a plane’s overall carbon footprint, but these materials can sometimes also cost more, so airlines have to balance the pros and cons of these as well.
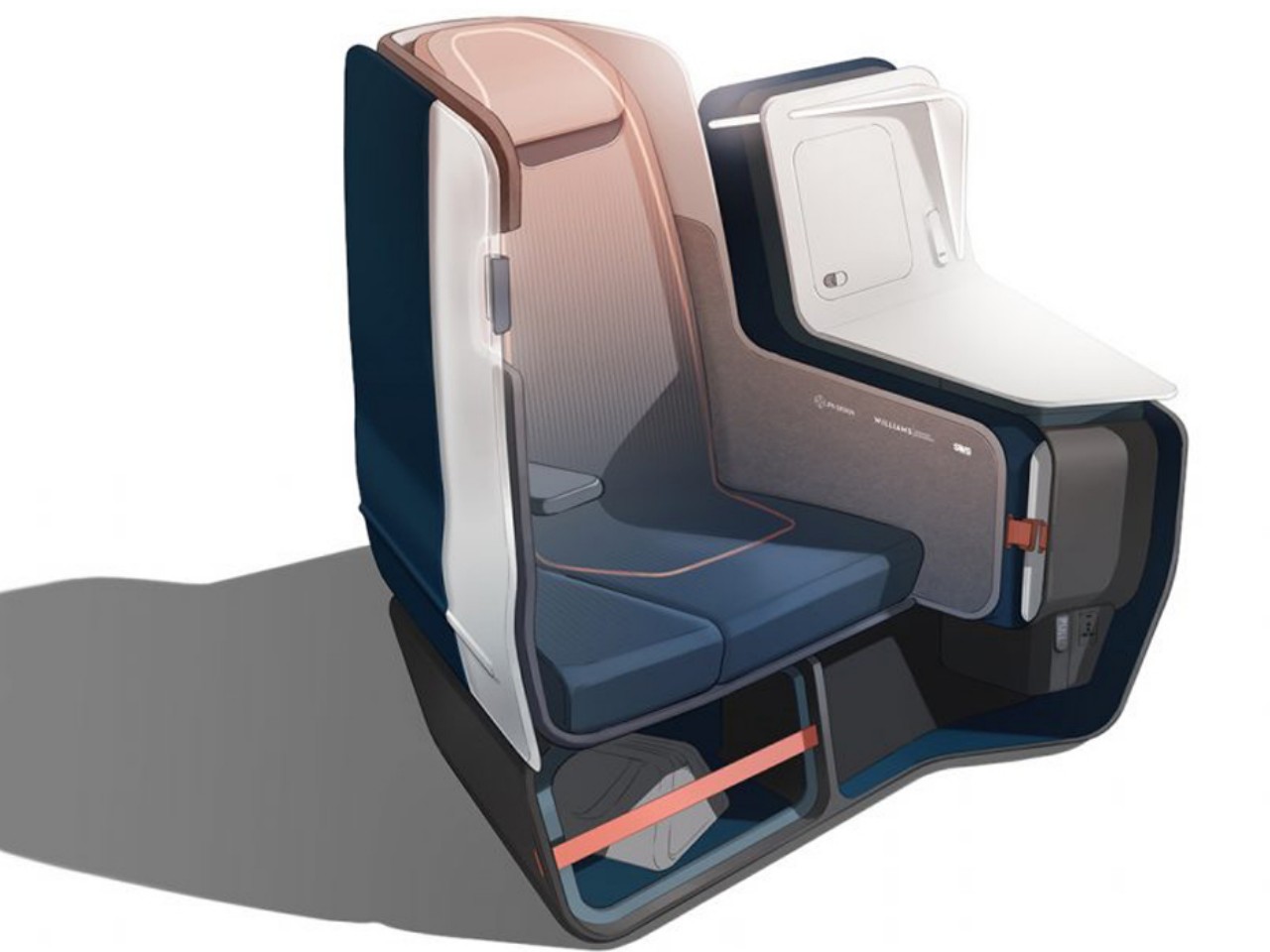
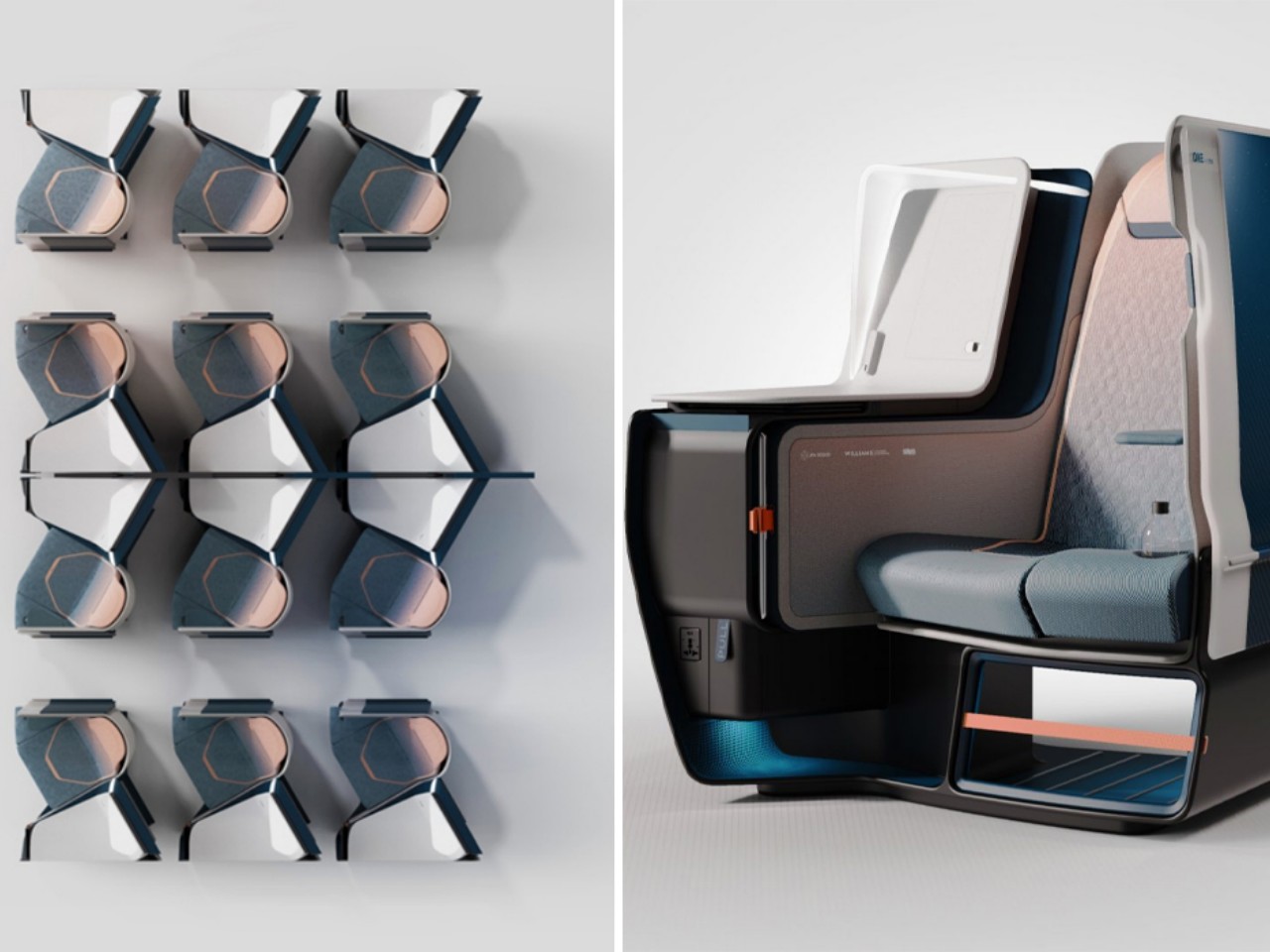


Designers: JPA Design x Williams Advanced Engineering x SWS Aircraft Certification
Successes and Failures: Lessons From Both Past and Future
Aviation history is filled with stories of winners and losers, not just in flyer programs but also in seat designs. Some have become more notorious than others, while the rest served as lessons to be learned. JetBlue, for example, coined its own “Mint” business class, offering lie-flat seats and artisan dining to its transcontinental flights, a move that proved to be quite successful and popular with business travelers. In stark contrast, American Airlines’ decision in 2017 to reduce its seat pitch to below 30 inches was faced with much backlash that the company eventually backtracked.
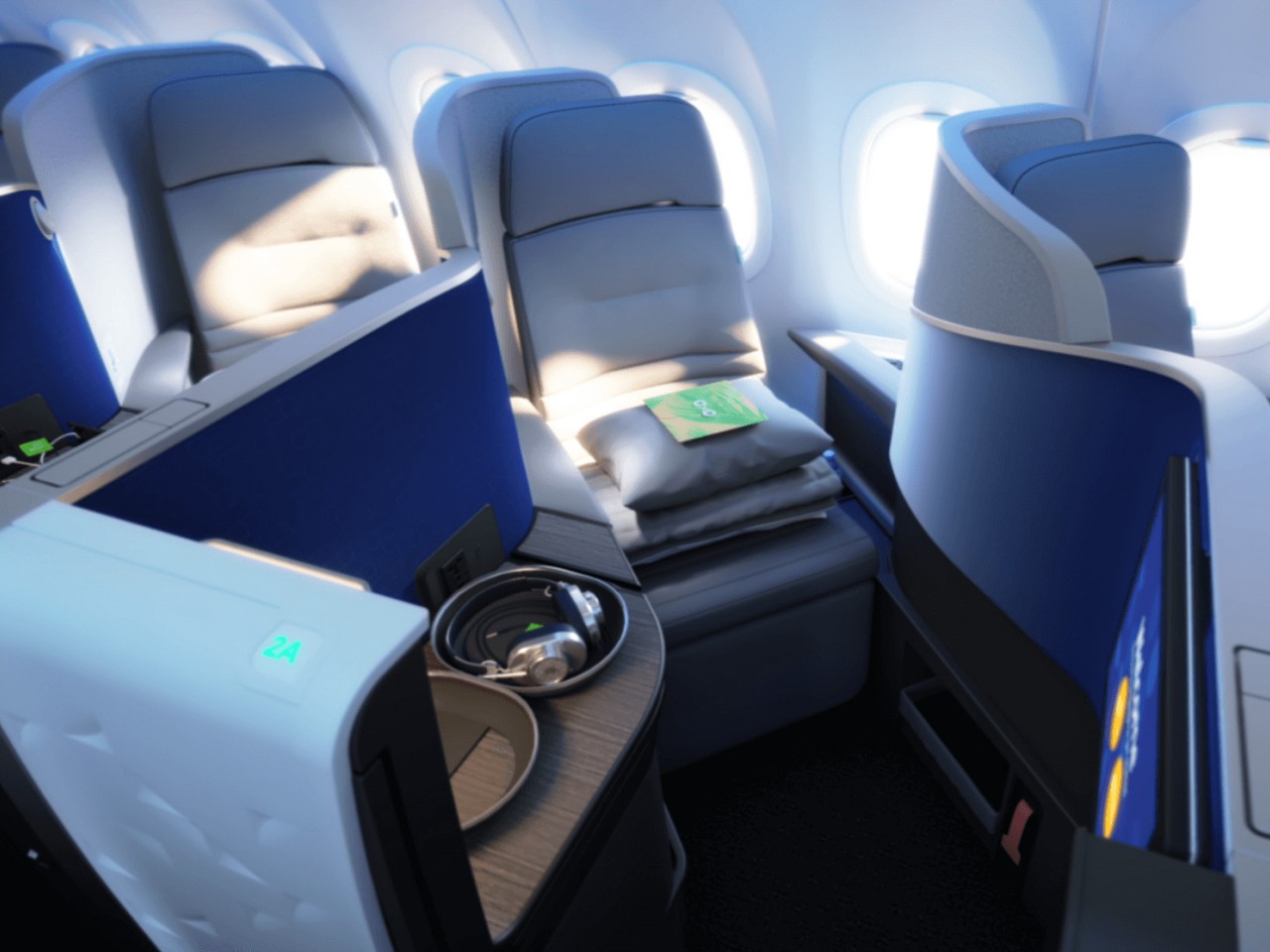
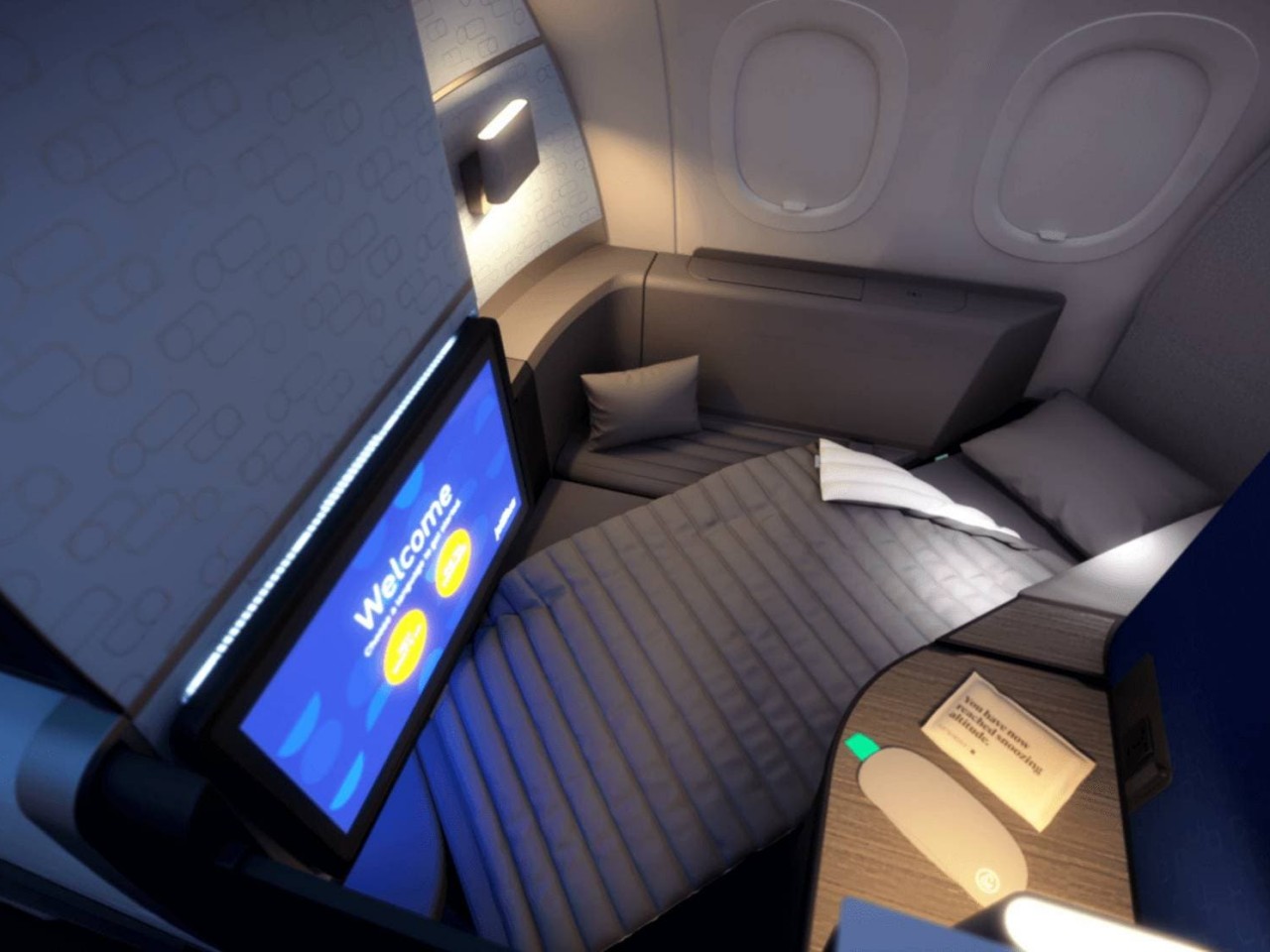



Designer: JetBlue
Even in the realm of concept designs, there are a few that seemed to be too far-fetched and uncomfortable that they were immediately met with ridicule and even contempt. While not everyone will oppose having more seats on a plane to accommodate more passengers, a few designs seemed to prioritize that over passenger comfort, feeling like they were more interested in helping airlines game more profit instead.
The Economy Class Cabin Hexagon concept, for example, made use of a zig-zagging layout that would make some passengers, some of whom might be complete strangers, awkwardly facing each other. The Chaise Longue design, on the other hand, implemented the “double-decker” idea that would theoretically give more legroom for people on the “lower” decks but also make them feel more cramped and almost claustrophobic. Neither concept has so far been implemented, but there are also plenty of examples out there that miss the mark, one way or another.
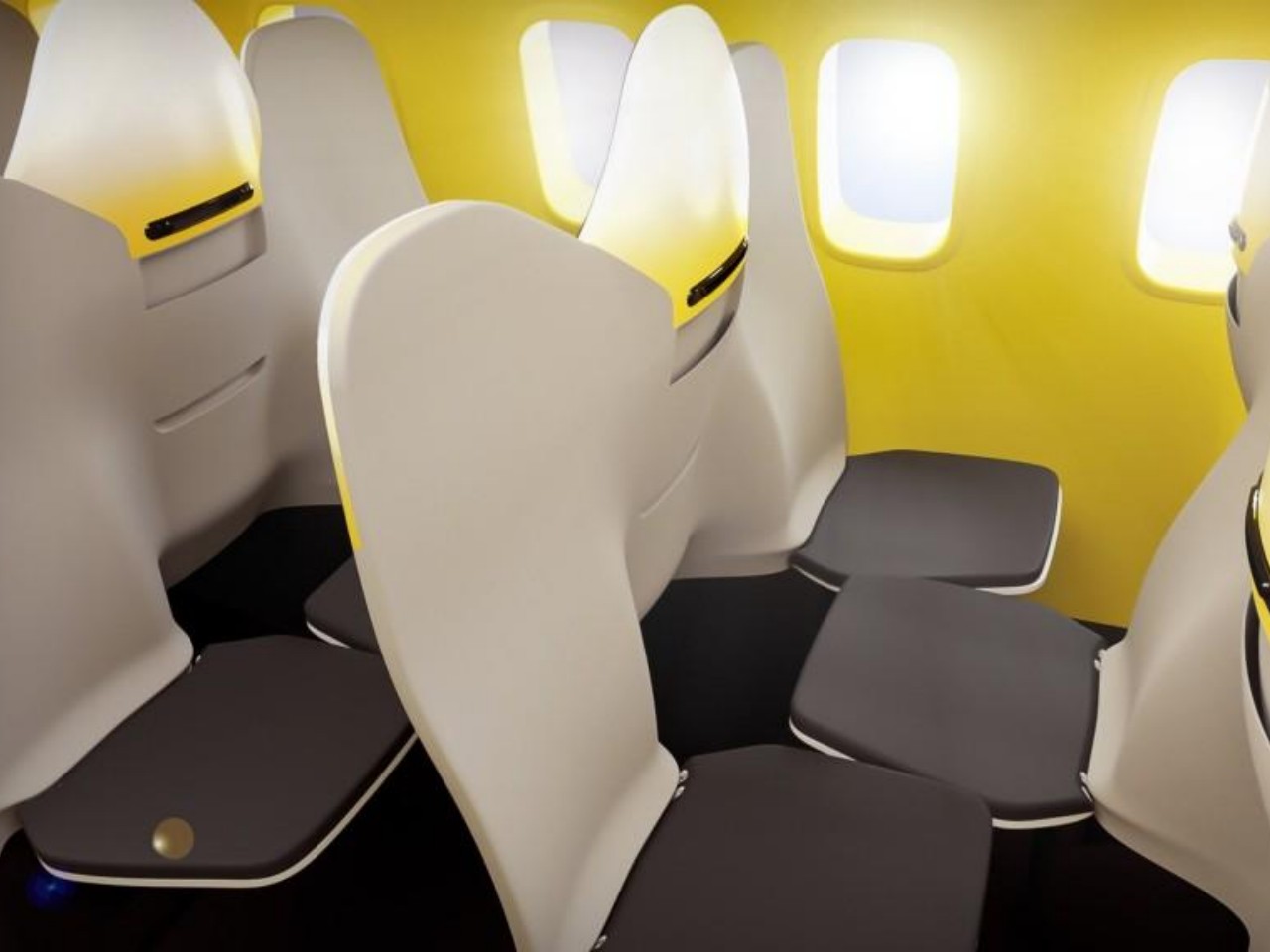

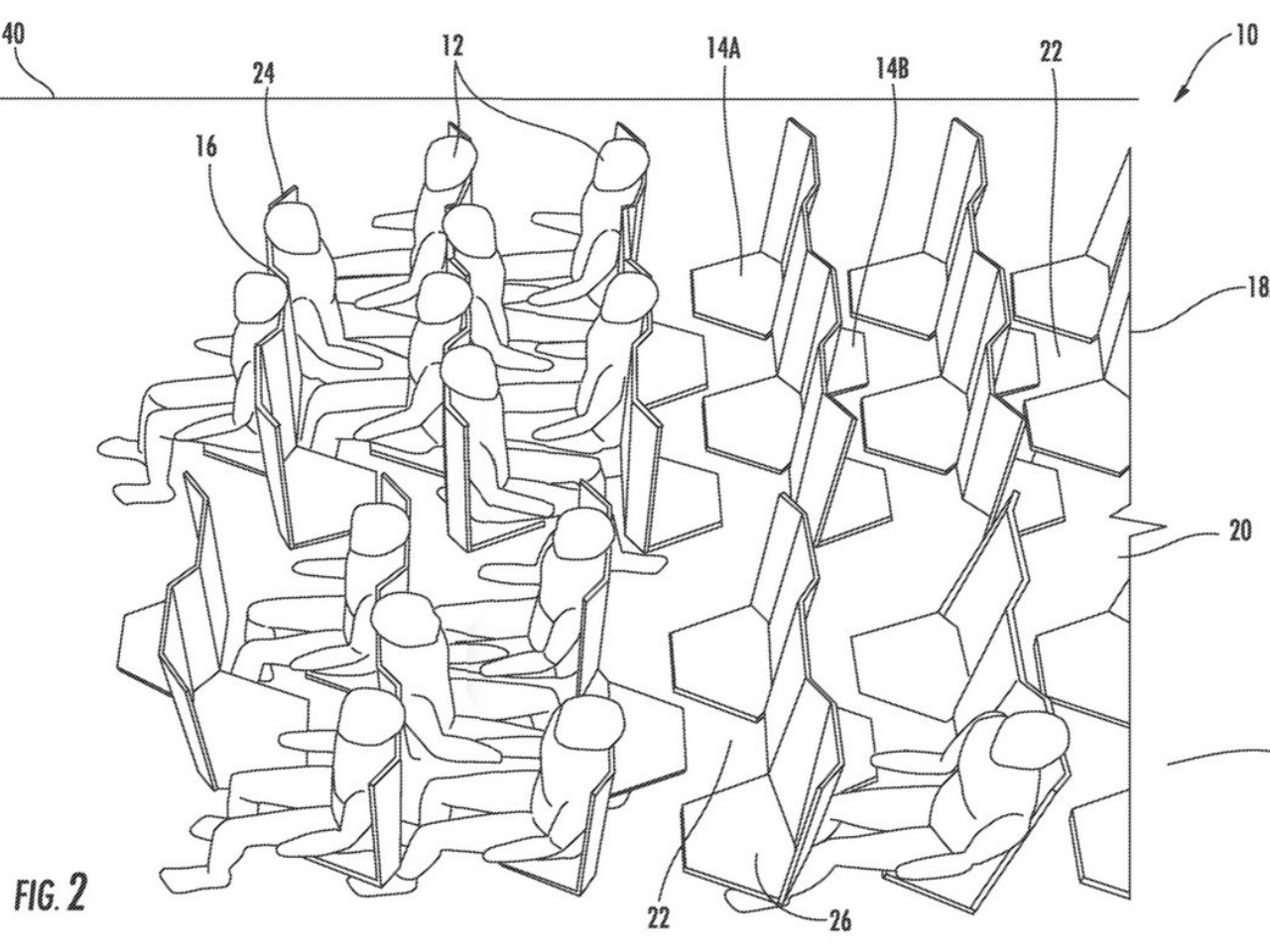

Designer: Zodiac Aerospace
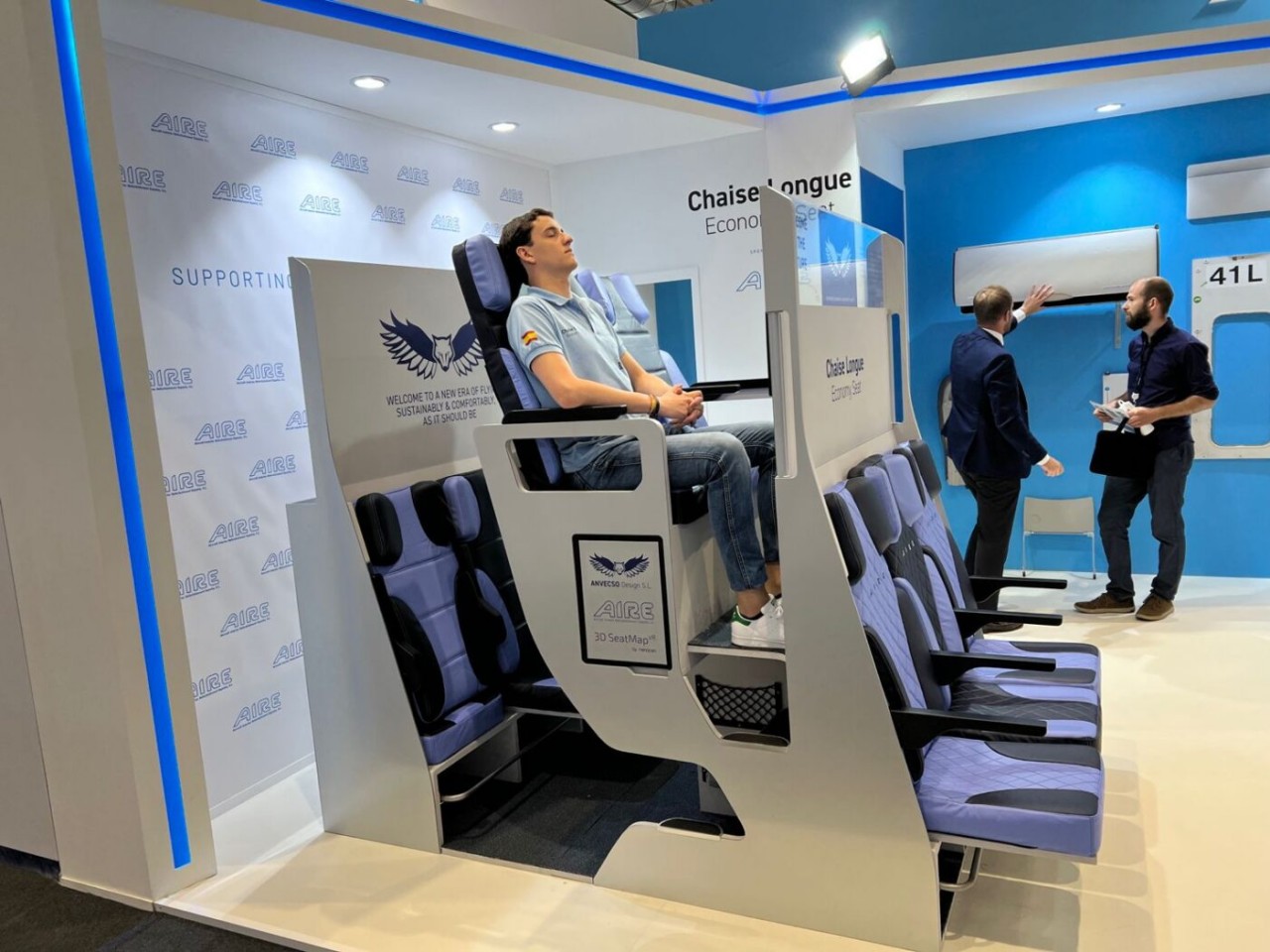
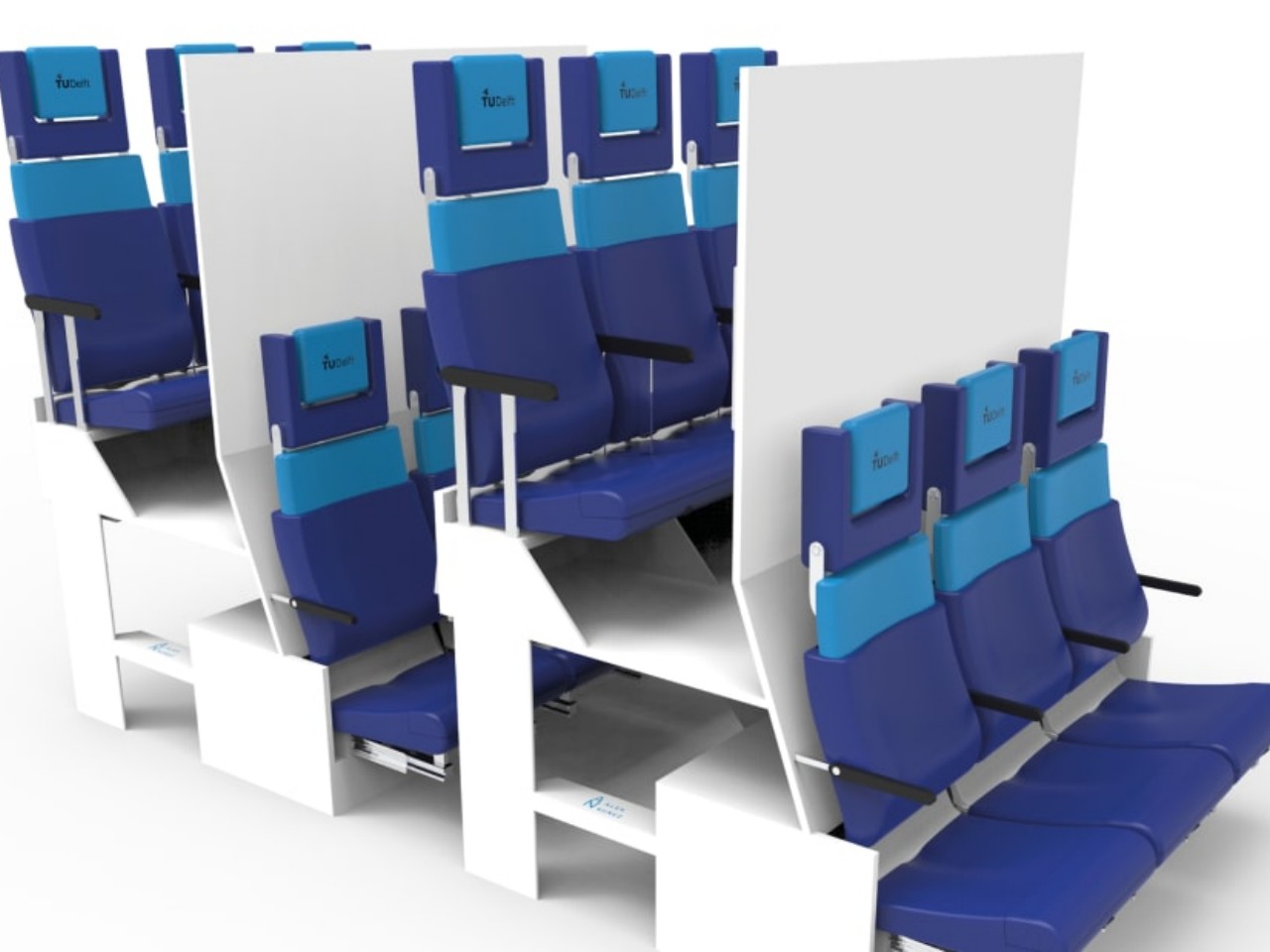
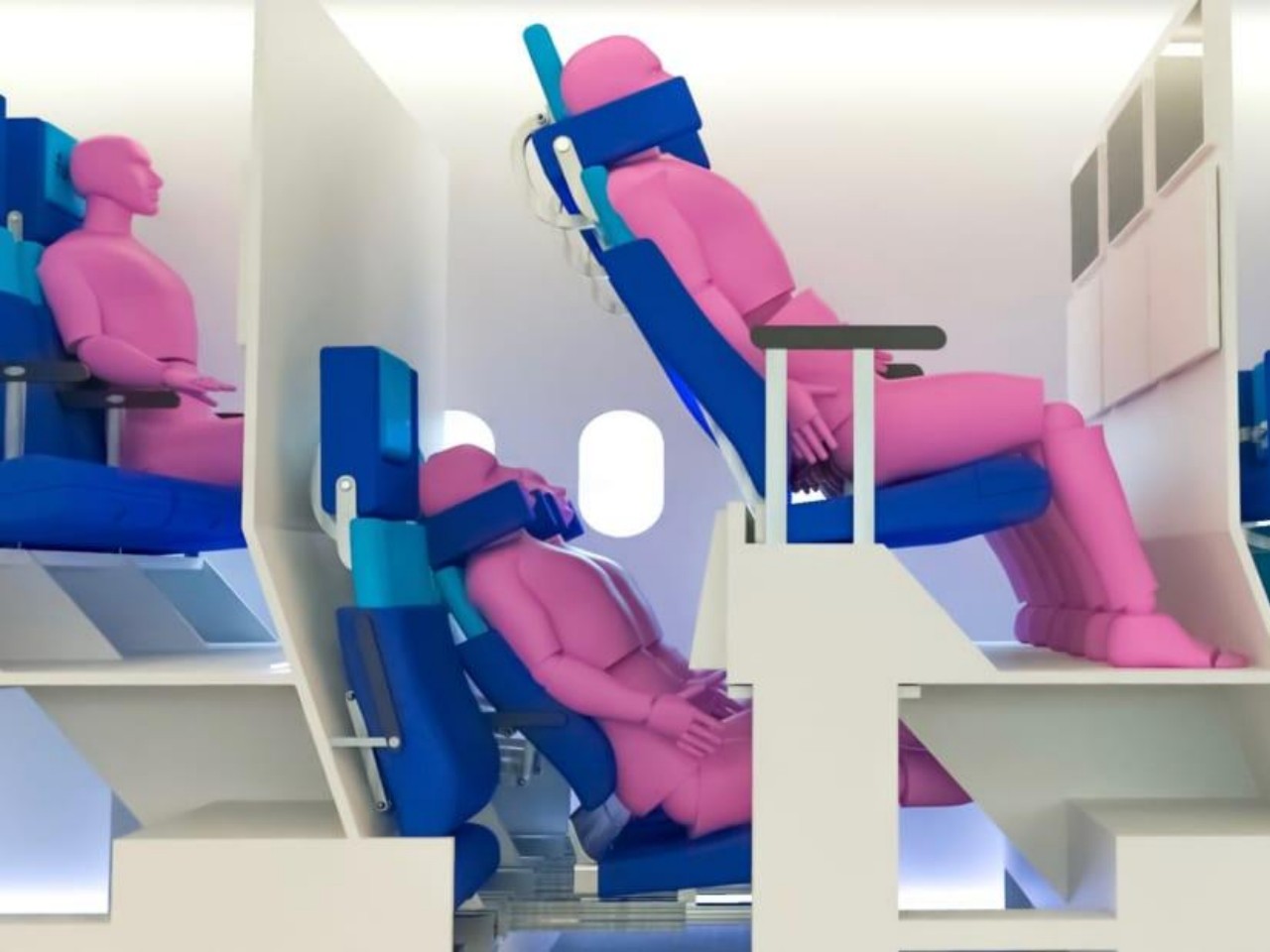
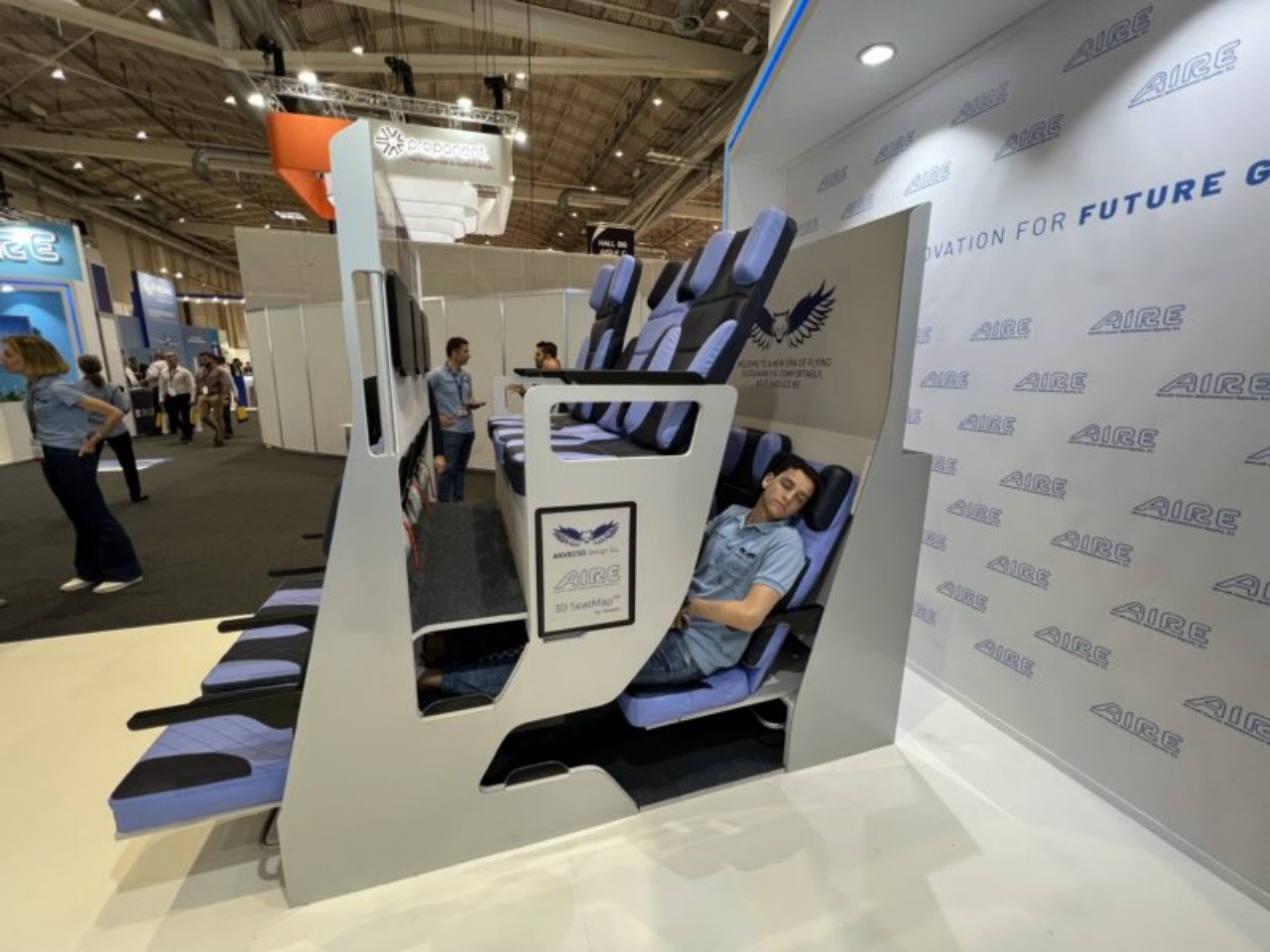





Designer: Chaise Longue
Final Thoughts
The design of airline seats is not a simple matter of choosing a form and a set of materials. There’s an ongoing tug-of-war between comfort and profit that also keeps changing over time. One generation might focus on comfort and luxury while succeeding generations might prioritize economy and efficiency. There’s also the matter of sustainability and eco-friendliness that is becoming just as important as these two factors. Airlines and designers must continually innovate and push the boundaries, looking not just for new materials but for better layouts and structures as well. Customers and regulators must also be vigilant that the interests of companies don’t overtake the experience of passengers. In the end, success in this domain hinges on understanding and anticipating passenger needs while crafting an economic model that sustains profitability amidst the ever-competitive skies.






