ASUS has long been recognized for its forward-thinking approach to technological innovation. With Ceraluminum, the company shifts focus, moving beyond performance metrics and engaging users on a sensory and emotional level. At the “Design You Can Feel” exhibition during the London Design Festival, ASUS presented this unique material in an artistic context, blending technology, material science, and human-centered design. This exhibition explored how technology doesn’t need to feel cold or distant but can foster emotional engagement and tactile experiences that draw users in.

Designer: ASUS
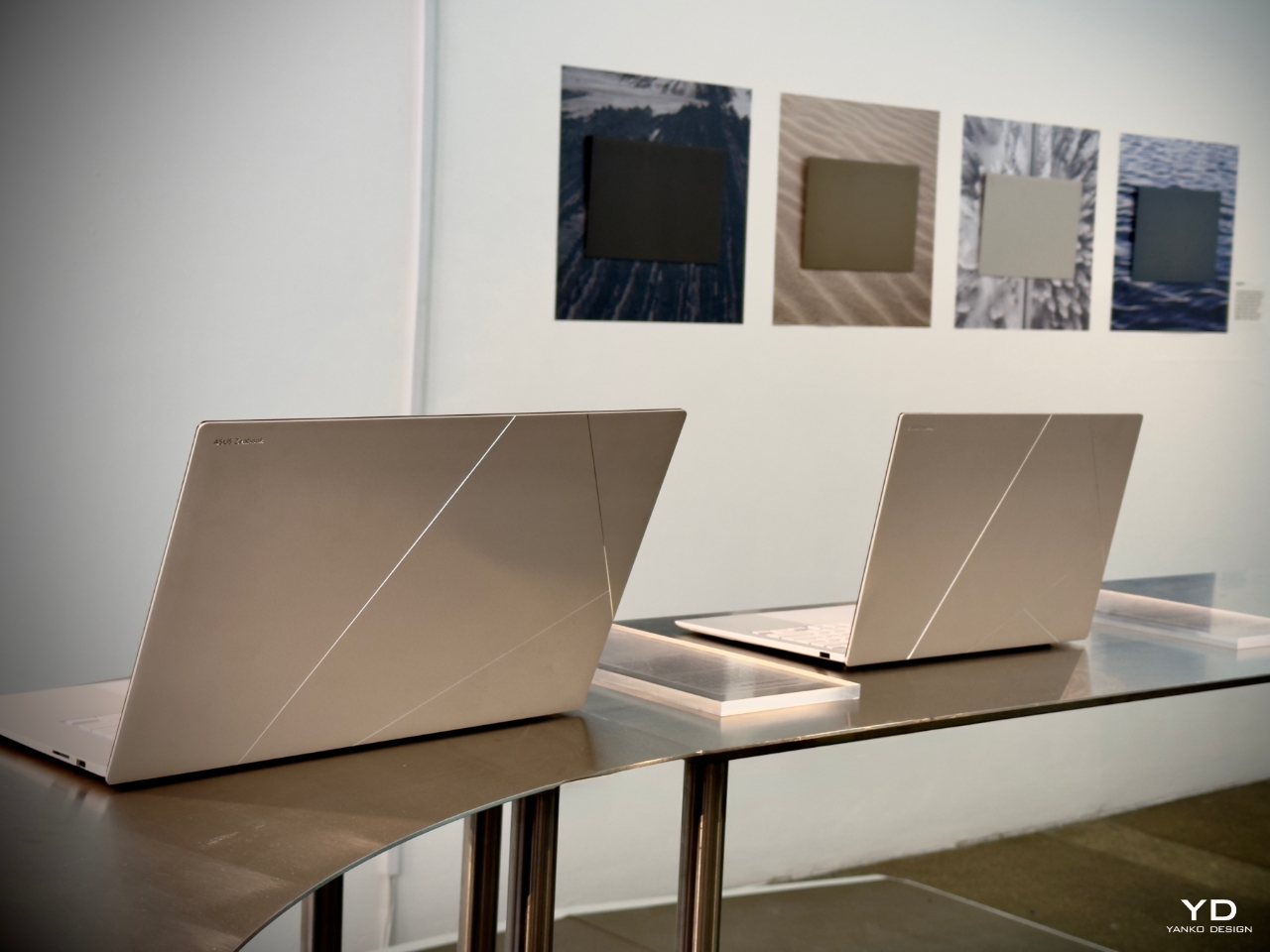
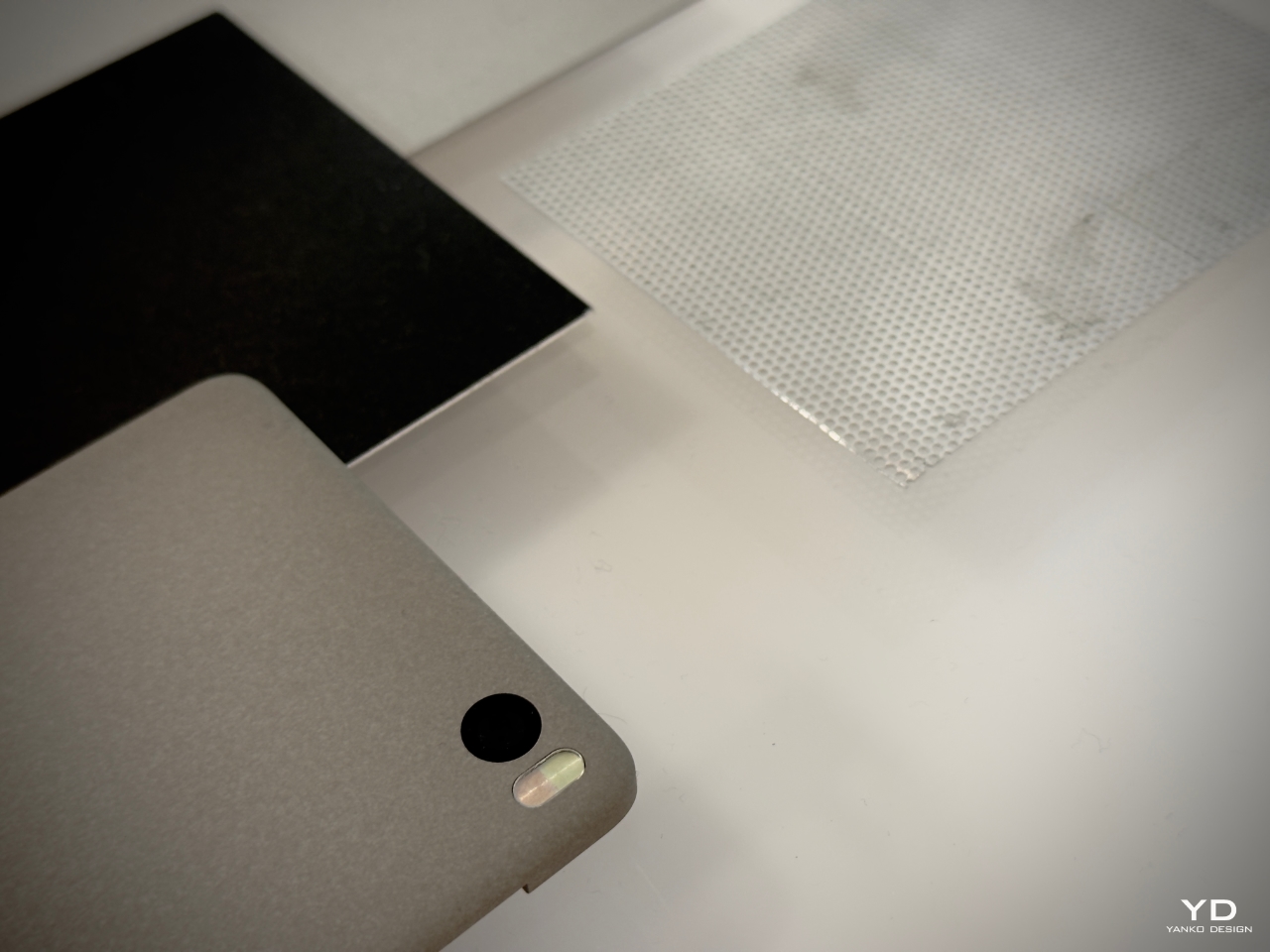
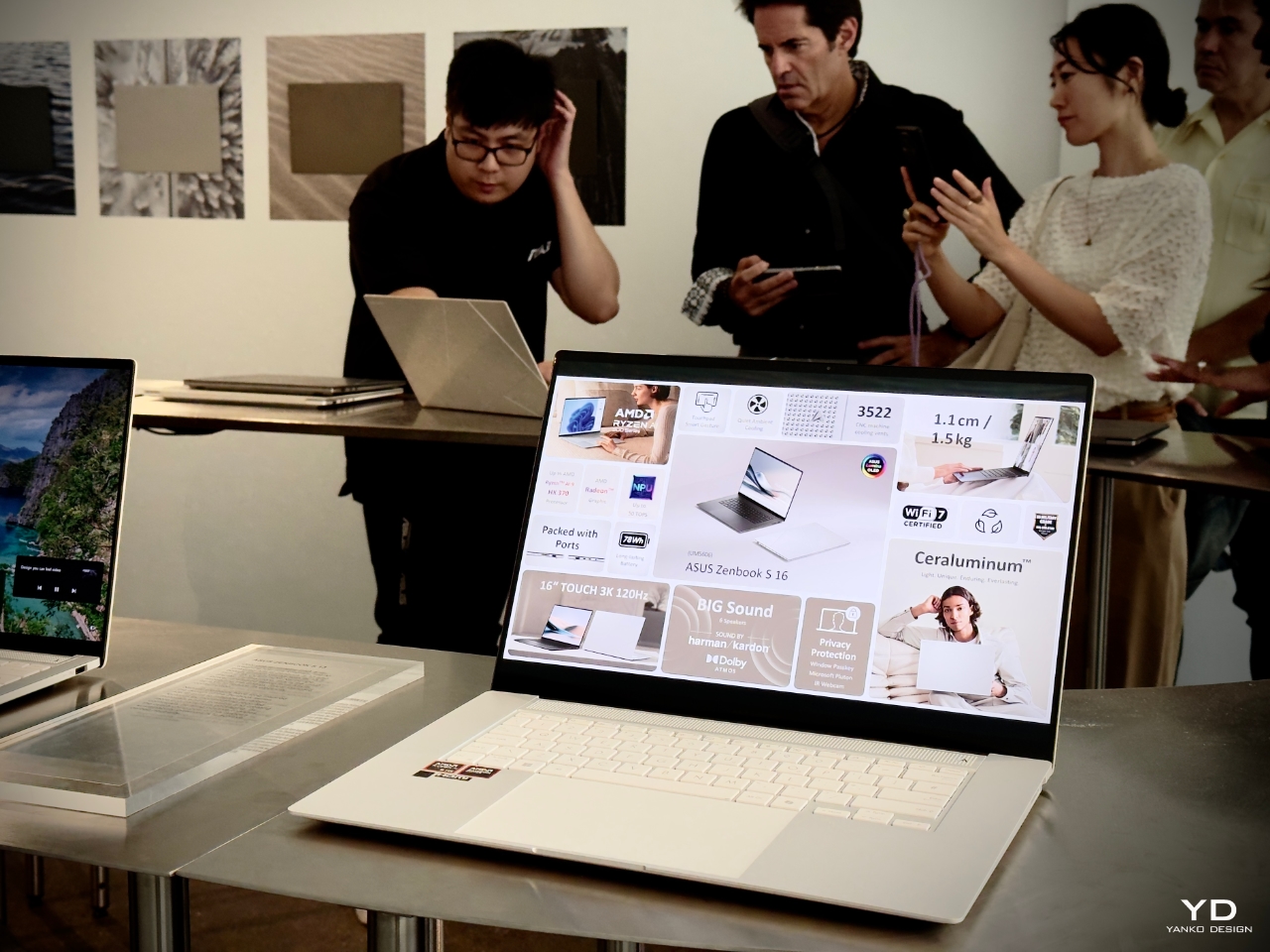
At the core of this shift is Ceraluminum, a revolutionary material that merges aluminum’s structural benefits with the tactile qualities of ceramic. With its four-year development, this material represents a significant leap forward in the functionality and aesthetics of ASUS’s products. Ceraluminum invites users to touch, explore, and experience their devices in a more intimate, human-centered way. It’s a breakthrough that combines art and technology, reshaping how we engage with our tech.
Ceraluminum: A Material with Presence
Ceraluminum reflects ASUS’s focus on creating materials that enhance functionality while fostering a more personal and tactile user experience. From my interpretation of their design philosophy, ASUS aims to develop materials that resonate emotionally with users, evoking a sense of warmth and connection—without suggesting metaphysical attributes like having a soul. Unlike traditional metals that feel cold and impersonal, Ceraluminum exudes warmth and tactility. It absorbs light and reduces glare while offering a textured, matte finish that invites interaction. Chief Design Officer Mitch Yang elaborated on the significance of this during the panel discussions, emphasizing that the texture and feel of Ceraluminum are key to fostering a deeper connection between users and their devices.
Developed through a unique micro-arc oxidation (MAO) process, Ceraluminum begins as lightweight aluminum and is transformed into a hybrid material through a high-voltage plasma discharge. This creates a ceramic oxide layer that maintains aluminum’s strength and lightness but offers ceramic’s hardness, scratch resistance, and tactile warmth. This unique combination gives ASUS’s devices a distinctive feel and presence, setting them apart from the sea of cold, reflective metal gadgets on the market.

Yang explained further, “Ceraluminum allows us to create devices that don’t just look good but feel meaningful to the touch. It changes how users interact with their technology, inviting them to explore the material with their hands, not just their eyes.”

SUSA: Embodying Calm Technology
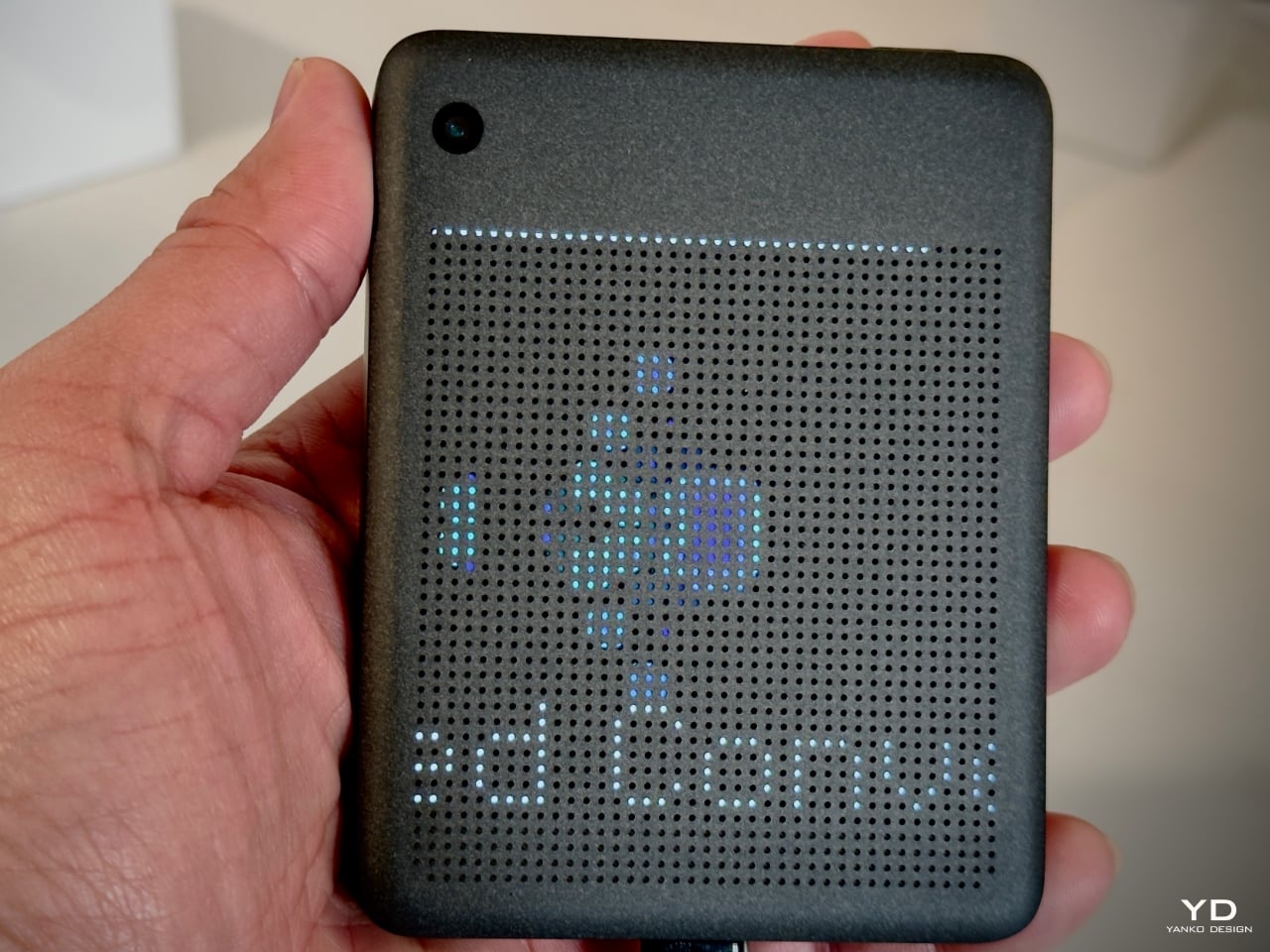

At the center of the “Design You Can Feel” exhibition was SUSA, a conceptual AI-powered device designed by London-based Future Facility. This device embodies ASUS’s philosophy of calm technology, where tech is designed to be intuitive, unobtrusive, and calming rather than overstimulating. Encased entirely in Ceraluminum, SUSA represents the potential of this material to facilitate more mindful, tactile interactions with technology.
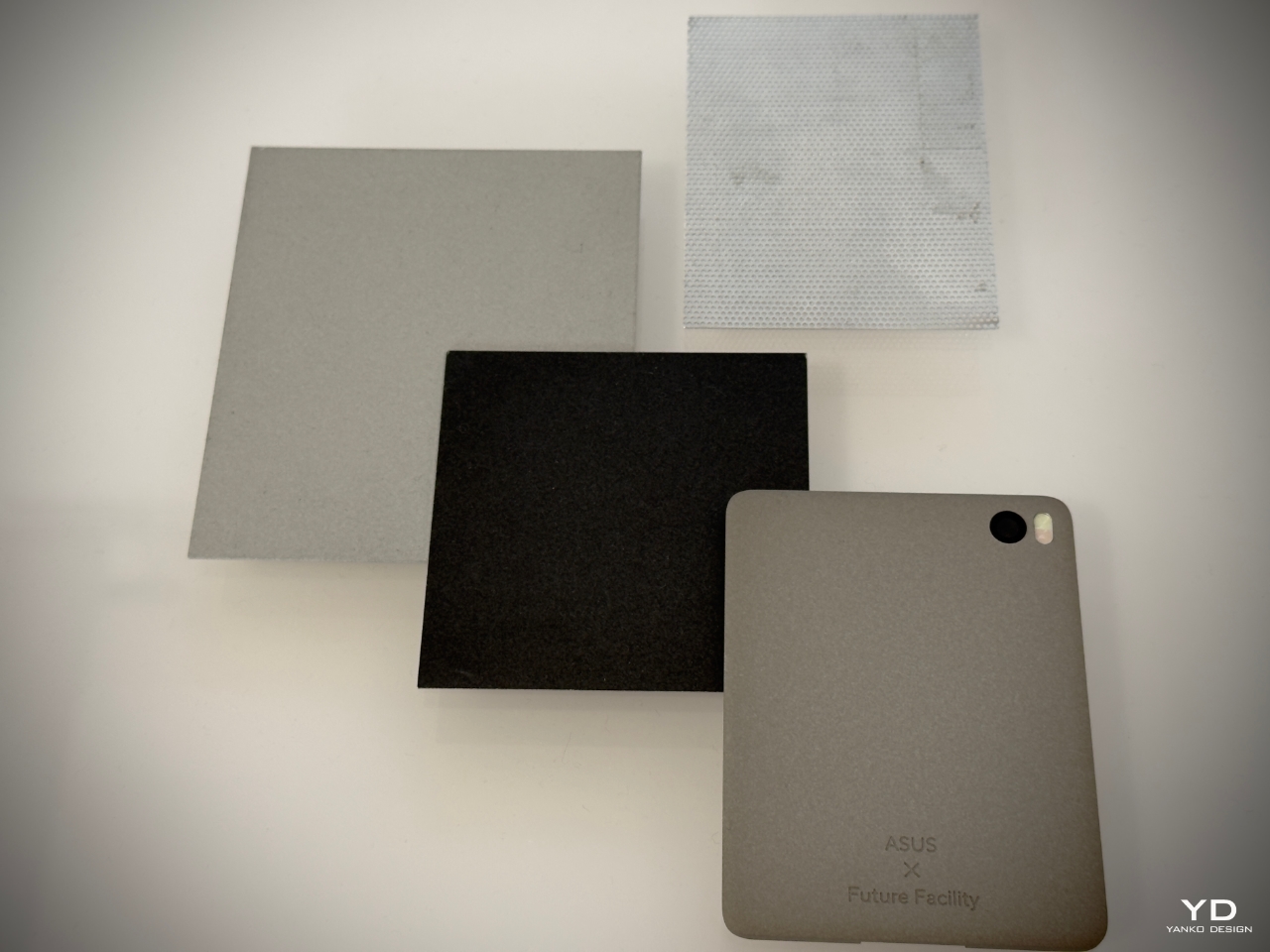

SUSA’s design is deliberately minimalist. It features a perforated screen that subtly filters its digital display, minimizing distractions while maintaining core functionalities such as photography, navigation, and calls. By encouraging users to engage with the physical object rather than becoming consumed by the screen, SUSA promotes a more intentional relationship with technology.
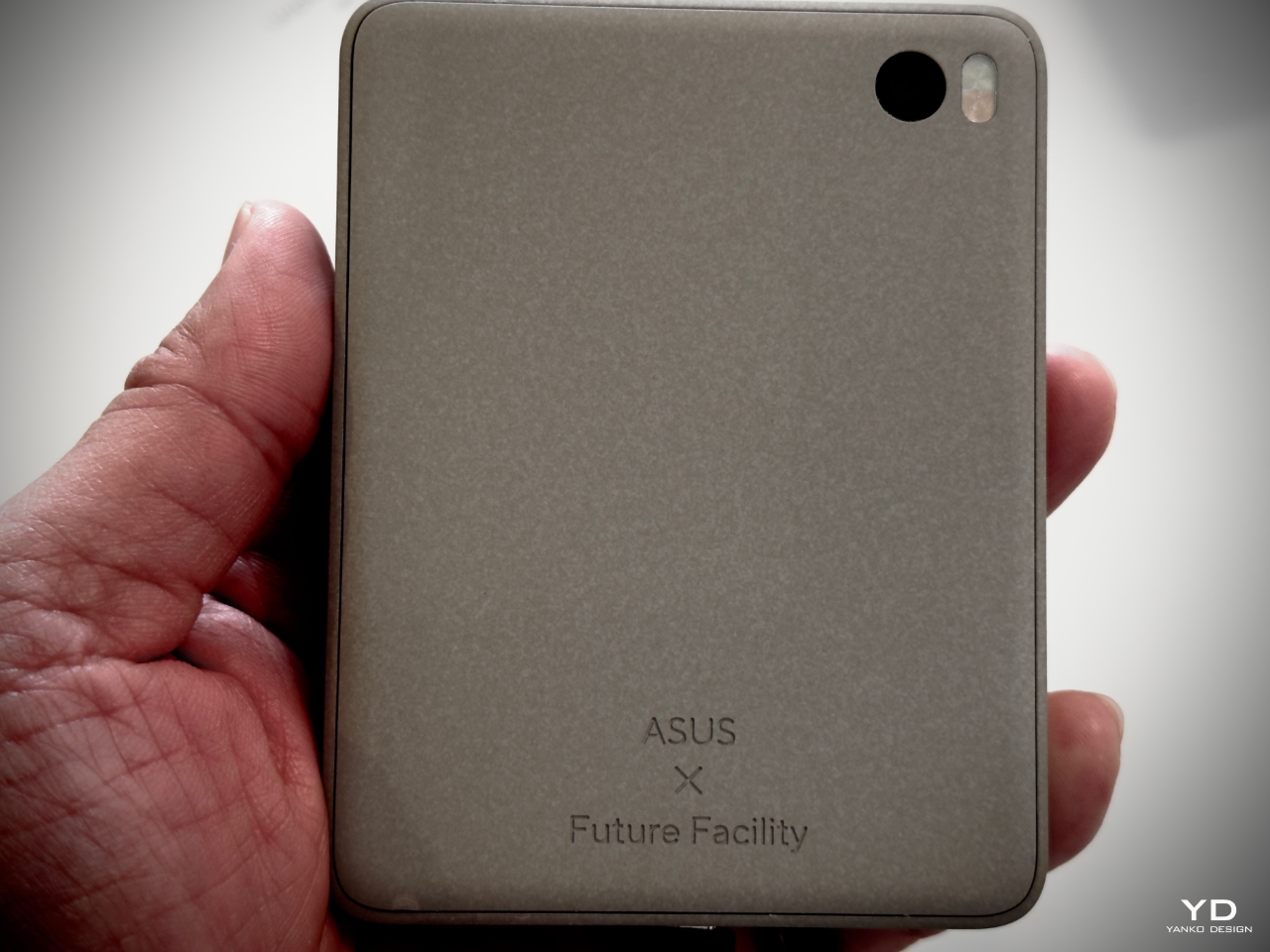

Leo Leitner, a designer at Future Facility, explained this during the panel discussion, stating, “SUSA is a reflection of how we can rethink the role of digital devices in our lives. By using Ceraluminum, we create a product that feels more natural and calming. It’s about slowing down, encouraging the user to focus on what’s important rather than being overwhelmed by constant notifications.”

Kim Colin, also from Future Facility, expanded on this by adding, “The tactile nature of Ceraluminum allowed us to create a product that feels inviting and grounded. It shifts the focus from what the device can do to how it feels when used. That tactile warmth is crucial to fostering a more mindful, human-centric interaction.”

SUSA is more than a concept. It represents a future where technology is integrated into our lives in ways that promote mental well-being, offering a calming influence rather than a constant source of overstimulation.
Collaborations with Global Designers: Ceraluminum Through the Eyes of Art
The “Design You Can Feel” exhibition also served as a platform for international designers to reinterpret and manipulate Ceraluminum in their own creative ways, showcasing its versatility beyond traditional tech applications. By inviting leading artists and designers to explore the material, ASUS highlighted how Ceraluminum can inspire new forms of user interaction. Each designer’s work emphasized tactile engagement and explored how material science can evoke emotional responses while remaining functional.

Giles Miller Studio (UK) approached Ceraluminum from a design perspective that blurred the lines between industrial application and artistic expression. Miller’s work focused on transforming the surface texture of Ceraluminum, turning it into a canvas for intricate patterns and reliefs. By manipulating its reflective qualities, Miller demonstrated how Ceraluminum could become a material that protects and decorates, elevating everyday technology into something more visually dynamic.
Designer: Giles Miller Studio
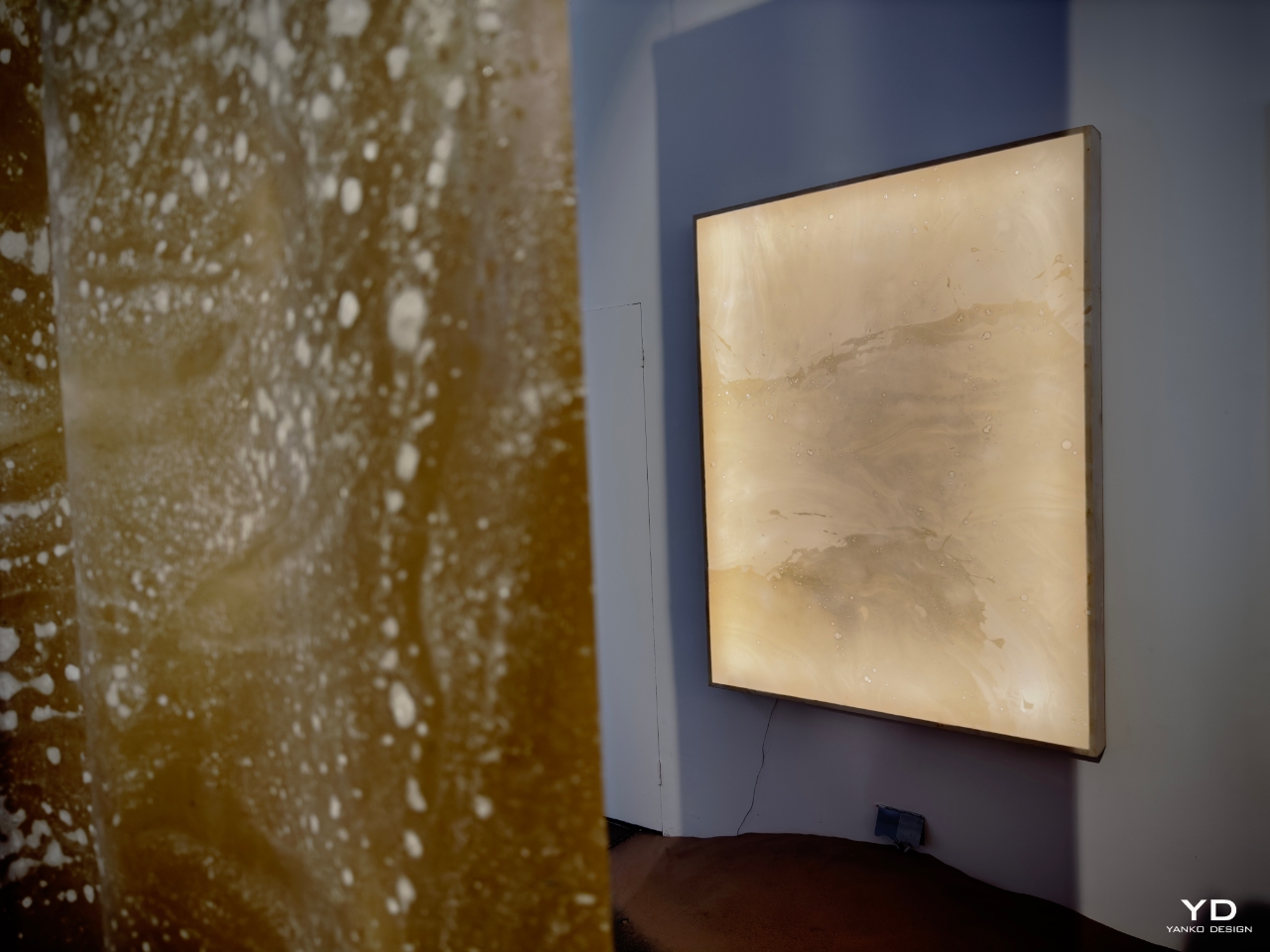

The studio used light to reveal hidden details in the material, inviting users to interact with their devices in new ways. Miller explained during the panel that they wanted to capture the subtle shifts in light as users moved their devices, turning a practical surface into an artistic experience. “Ceraluminum gave us the ability to create a surface that changes with the viewer’s movement, transforming the device from an object of utility into something more engaging,” Miller noted. This emphasis on the material’s light-reflecting properties invited deeper emotional engagement, making the device feel more personal.
Natural Material Studio (Denmark) took an organic approach to Ceraluminum, focusing on its ability to mimic natural textures. Their contribution aimed to highlight the material’s matte finish and tactile softness, drawing inspiration from natural elements like stone and sand. By working with Ceraluminum’s porosity, they created objects that felt grounded and familiar, offering a contrast to the typically sleek, hard surfaces of most technology.
Designer: Natural Material Studio
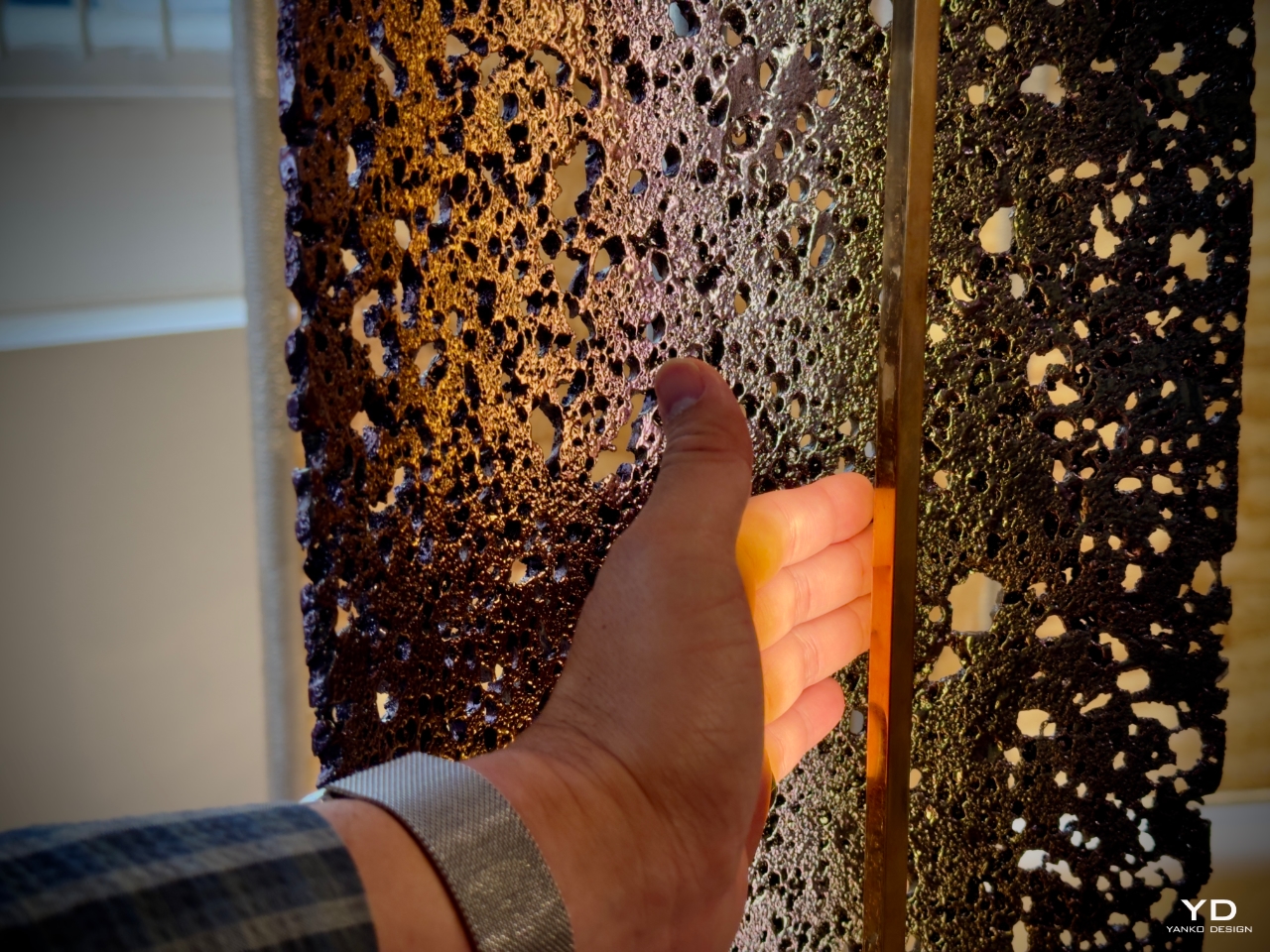

The goal was to craft a sensory experience that reminded users of nature. Their work emphasized the tactile qualities of Ceraluminum, offering an experience that felt like the material had been shaped by natural forces rather than human technology. “We wanted the object to feel as if it had always existed—like a pebble-shaped by the sea,” the studio shared during the exhibit. Their designs provided a sense of calm, reinforcing ASUS’s broader mission to create technology that connects users to the natural world while still harnessing advanced materials.
Nice Workshop (South Korea) explored the application of Ceraluminum in larger-scale objects with their “Aluminium Formwork Series”. Moving away from electronics, they demonstrated how Ceraluminum could be used in furniture design by applying ASUS’s ceramicization process to aluminum forms. This process resulted in furniture pieces with a textured, stone-like finish that invited touch and interaction. Founder Hyunseog Oh said their goal was to make aluminum—a traditionally cold, hard material—feel softer and more approachable.
Designer: Nice Workshop
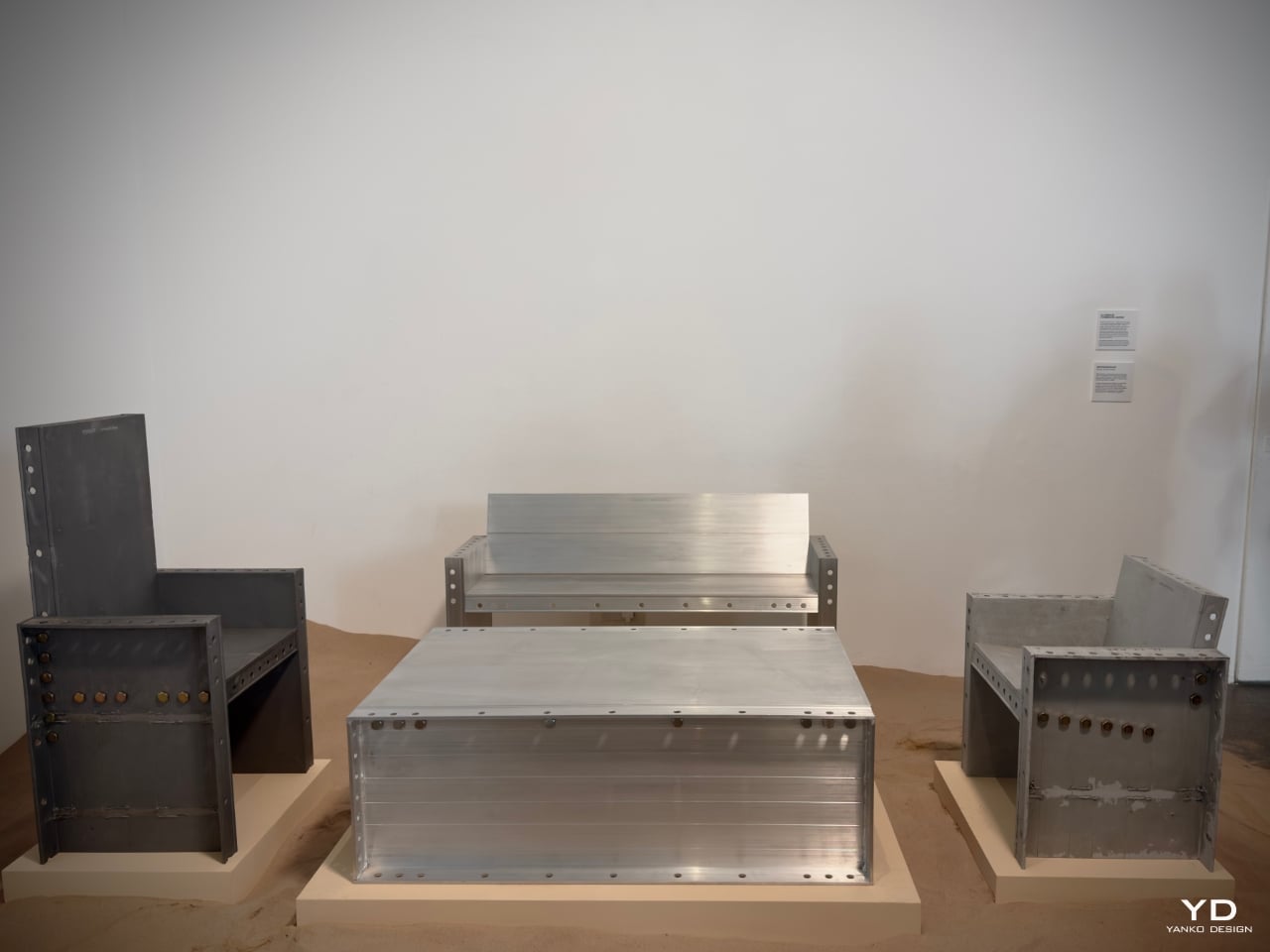

Their work showed how Ceraluminum’s unique texture could be adapted to everyday objects, making them more inviting and user-friendly. “We wanted people to feel comfortable interacting with furniture in the same way they interact with their devices,” said Oh. This exploration of Ceraluminum’s versatility in non-tech applications expanded the material’s potential, proving it could enhance electronics and the physical spaces we inhabit.
Fernando Laposse (Mexico) brought a sustainability-focused lens to the exhibition, concentrating on how Ceraluminum could be repurposed and recycled to reduce environmental impact. Known for his work with natural fibers, Laposse saw potential in Ceraluminum’s longevity and durability. He explored how the material could be integrated into sustainable design practices, offering a responsible alternative to more wasteful production methods.
Designer: Fernando Laposse

Laposse’s work aligned with ASUS’s vision for creating long-lasting products that reduce waste and contribute to a circular economy. By focusing on Ceraluminum’s recyclability, he highlighted its potential to contribute to sustainable design efforts. “Ceraluminum’s strength and durability mean it can be repurposed, not discarded, ensuring that our devices leave a smaller environmental footprint,” Laposse explained. His approach resonated with ASUS’s commitment to sustainability, demonstrating that high-tech materials and responsible design can coexist.
Studio Furthermore (UK) embraced a more experimental approach, pushing Ceraluminum’s potential beyond the traditional limits of material design. Their contribution focused on the material’s transformation through ceramicization, exploring how different textures and surface treatments could evoke new tactile experiences. By experimenting with forms and patterns, Studio Furthermore demonstrated how Ceraluminum could serve as a medium for creative exploration, where users could discover new ways to interact with their devices.
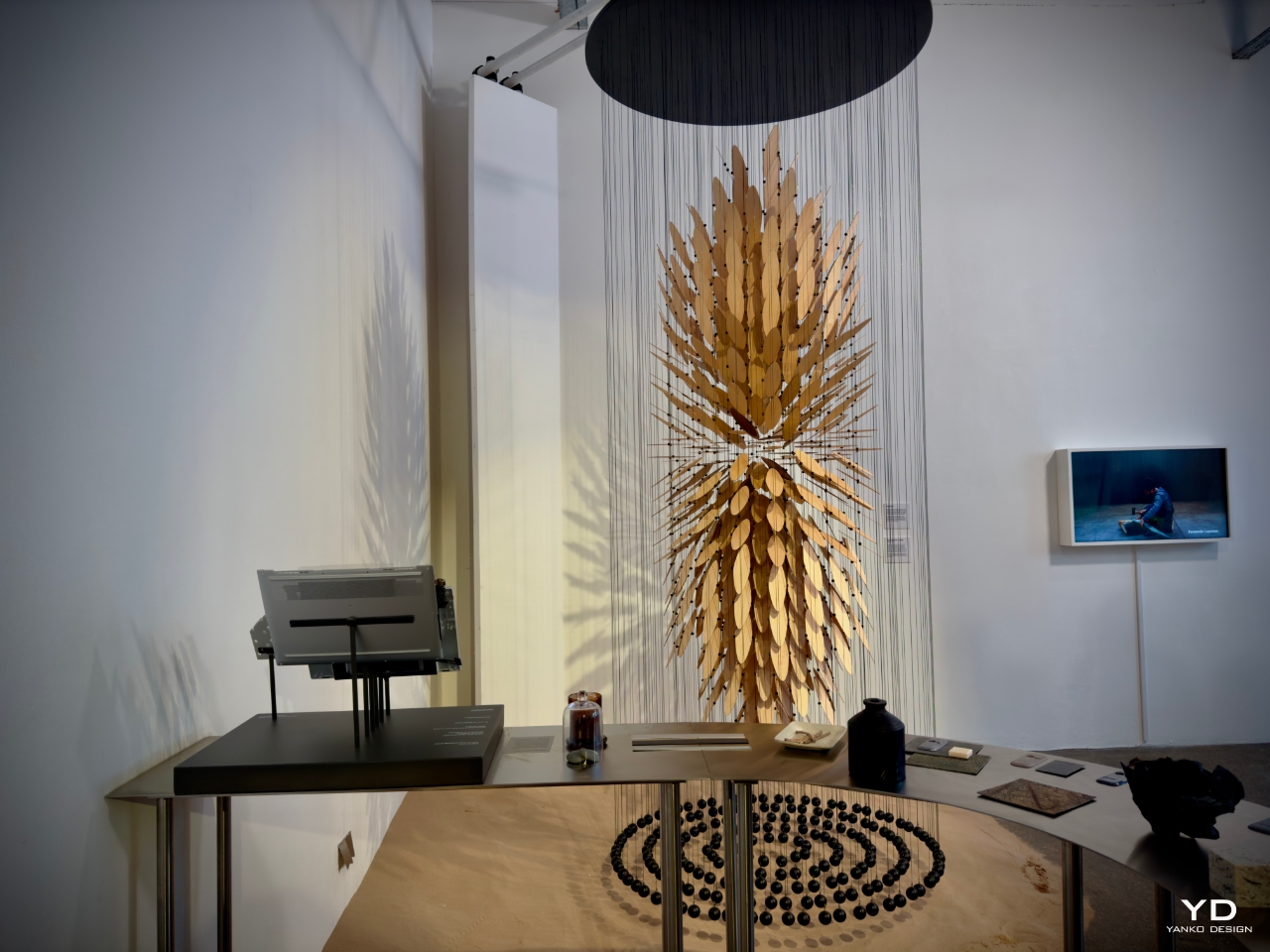

Designer: Studio Furthermore
The studio’s work underscored how Ceraluminum is durable and capable of provoking emotional and tactile connections. By emphasizing the material’s sensory qualities, they invited users to engage more profoundly and rigorously with their devices. “We wanted to encourage users to touch and feel their devices, not just see them as tools,” the studio remarked. Through their experimental processes, Studio Furthermore showcased how Ceraluminum could foster more profound, more meaningful interactions between users and the objects they use every day.
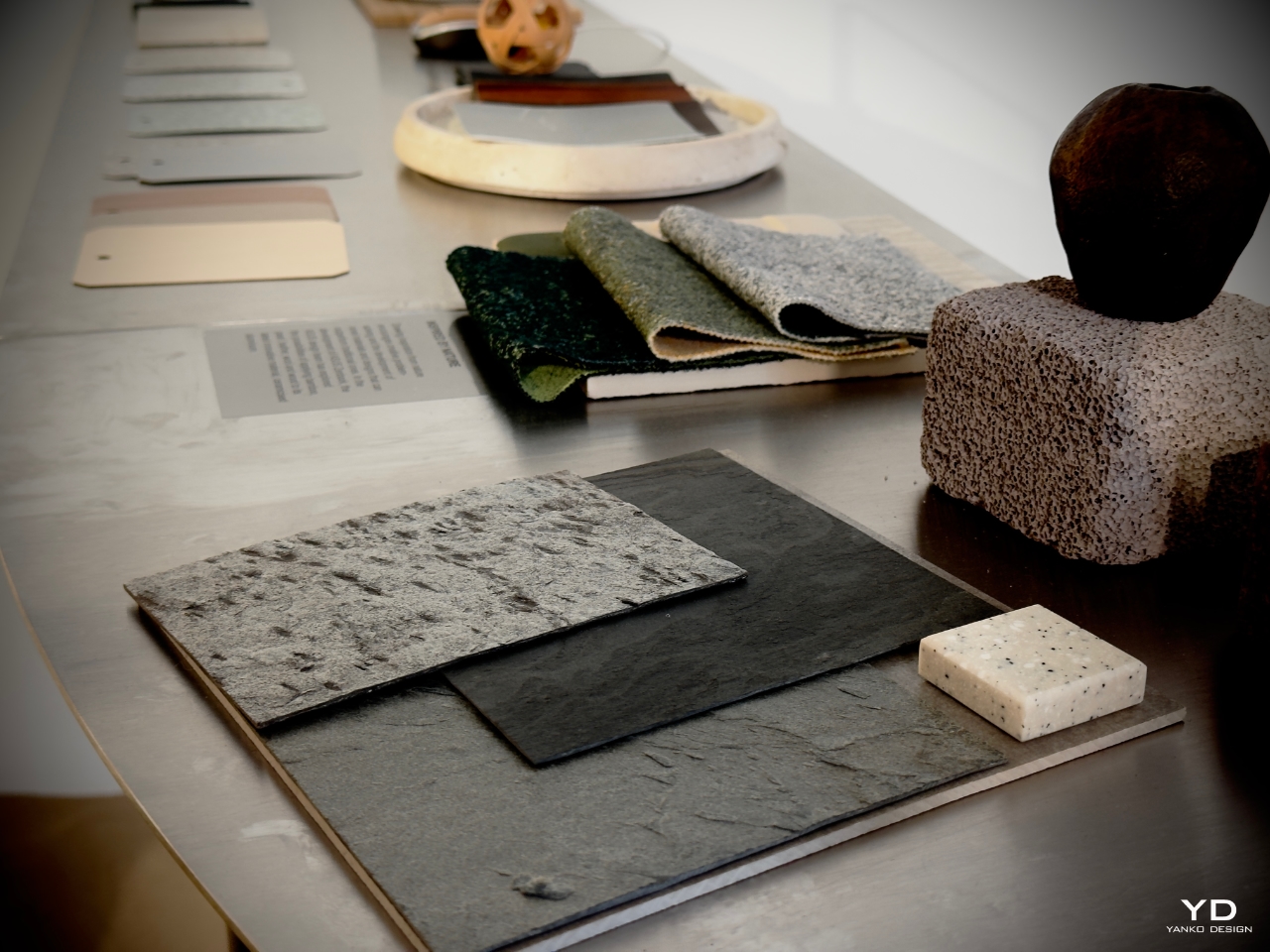

Final Thoughts: A Sensory Future for Technology and Design

ASUS’s “Design You Can Feel” exhibition and the development of Ceraluminum represent a forward-thinking approach to how technology integrates into our lives. With this material, ASUS bridges the gap between the tactile and the technological, offering users an experience that goes beyond performance to touch the soul of design.

Ceraluminum’s durability, tactile warmth, and matte finish go beyond aesthetic choices; they reshape how we interact with devices moving forward. This material reflects ASUS’s commitment to creating devices that resonate emotionally, offering comfort, engagement, and fostering a deeper connection.

Through collaborations with global designers, ASUS has highlighted the potential of Ceraluminum to transform not just technology but how we live, interact, and engage with the objects around us. As we move forward, Ceraluminum is poised to lead a new design wave that prioritizes emotional resonance, environmental responsibility, and the fusion of art with cutting-edge material science.







