
Despite the power that smartphones and tablets have these days, PCs and their Mac equivalents remain the workhorses of the modern world. Not only do they have more power, they also offer more flexibility thanks to decades of research, development, and innovation. Market analysts, however, have long been pointing to the demise of the PC market, especially desktops, and there has indeed been a great deal of stagnation not only in hardware but even in product designs. It’s not that there haven’t been any improvements, just that designs have become predictable and even sometimes forgettable. You can’t, after all, change the design formula too much unless you also drastically change the internals as well. That’s the kind of burst in innovation that awaits the PC market, both laptops and even desktops, if running Windows on the same hardware as smartphones and tablets finally becomes reliable and productive.
Designer: Qualcomm

Rough Start: Microsoft Surface
It’s not like the combination of Windows and ARM-based processors, the same silicon that powers mobile devices, hasn’t been done before, but almost all past attempts have come up short of expectations. Disregarding the antiquated Windows CE and Windows Phone variants, Microsoft has time and again tried to bring the benefits of phones and tablets to PCs without much success. One of the first ones in recent memory is the smaller Microsoft Surface. Although the Surface Pro has become something of an icon today, its base model didn’t enjoy the same level of fame, attention, and sales.

Microsoft Surface RT

Designer: Microsoft
The Surface RT and Surface 2 both ran on ARM-based NVIDIA Tegra processors that were normally quite capable on Android tablets. Even those, however, couldn’t bear the weight of Windows, even the watered-down Windows RT version. To add insult to injury, the apps available for that platform were a dismal number which didn’t include the software that people needed to use on Windows. Thus, these first attempts at Windows on ARM were considered to be abject failures, but surprisingly, Microsoft didn’t give up completely.
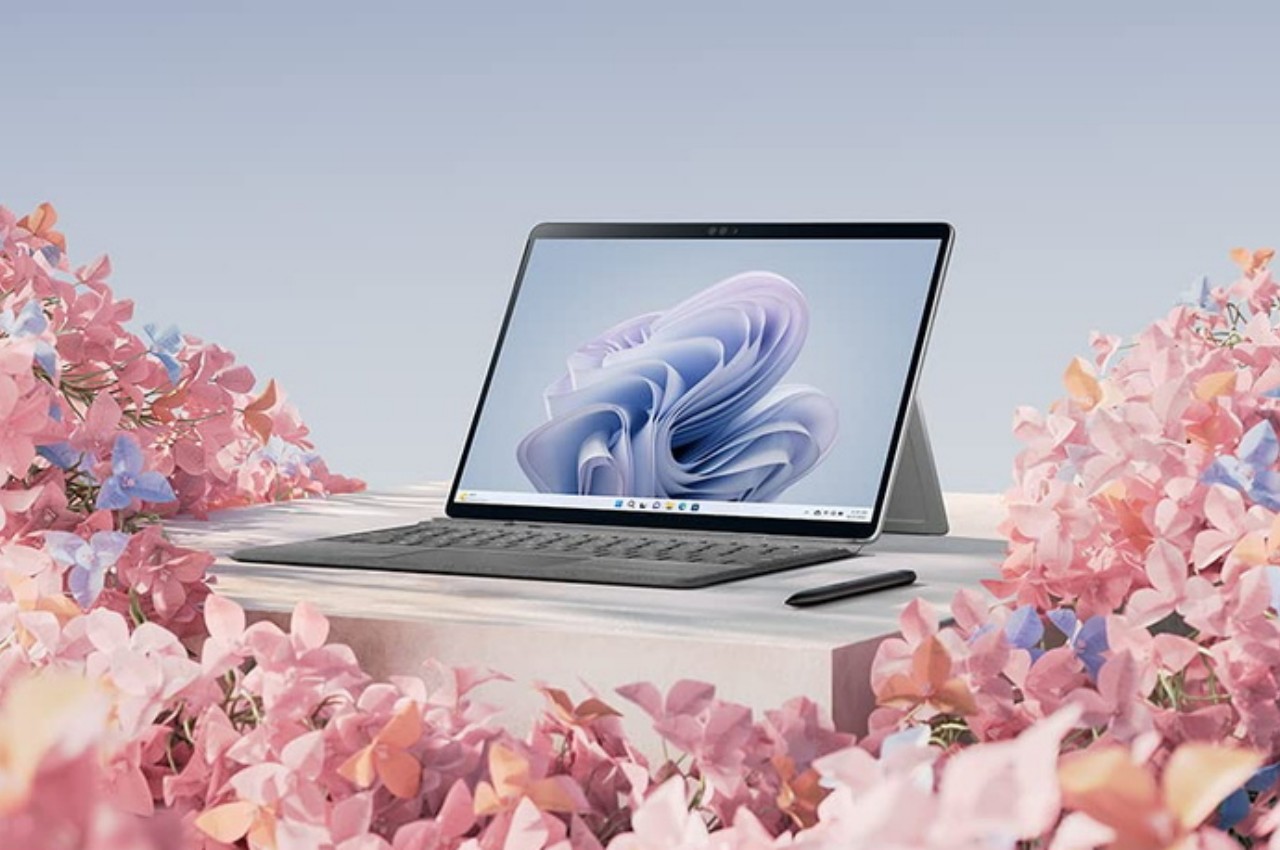

Microsoft Surface Pro 9

Fast-forward to today, there have been numerous attempts to improve the situation, both from the hardware and the software side. The Microsoft Surface Pro 9 now has a version that runs an even more powerful ARM Qualcomm processor, and the Microsoft Store has quite a selection of popular apps. There are also some emulation solutions for running “normal” Windows software on ARM laptops and tablets, but that’s not exactly a panacea. All these sound like too much effort for what seems like a niche design, but it’s an effort that could yield a bountiful harvest if it succeeds.
Faster, Slimmer, Cooler
Qualcomm announced last month its new Snapdragon X Plus and Elite processors, and while the “Snapdragon” name is popular for smartphones and tablets, the “X” chips are earmarked for use in Windows computers instead, particularly laptops. Qualcomm boasts numbers that would make the likes of Intel and AMD worry, though it’s also aiming squarely for Apple’s M series processors. That’s definitely a tall order, especially with the launch of the new Apple M4 chip, but if theory proves to be even remotely near the mark, it will be a huge win for the Windows market and PCs in general.
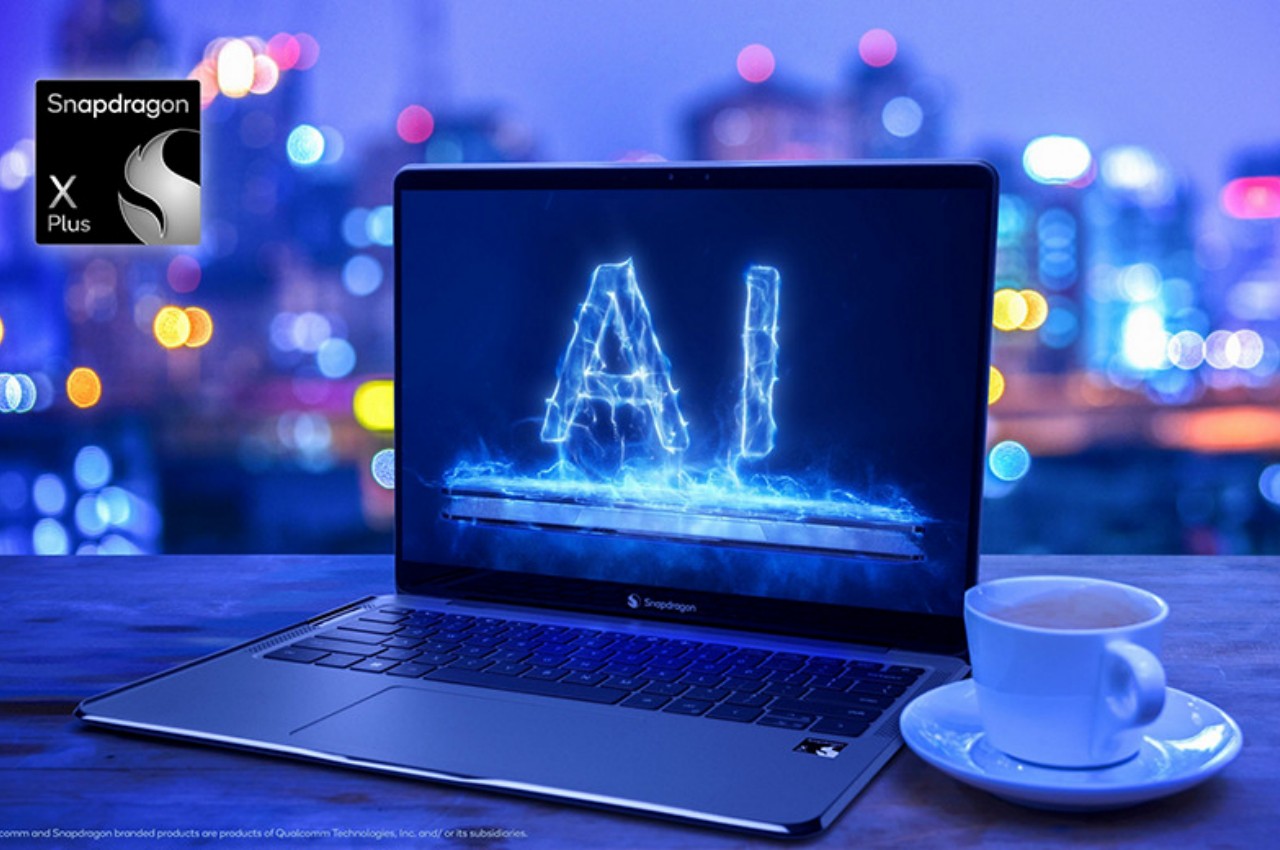

Designer: Qualcomm
The new Snapdragon X Plus and Elite unsurprisingly boast about being able to do heavy-duty generative AI work, something that would require a lot of processing power that is traditionally only available on “regular” laptops and desktops. What would set it apart, however, is how it delivers that performance with lower battery consumption, heat, and space compared to equivalent Intel and AMD processors. It’s too early to say if Qualcomm will be able to deliver those promises, but it’s definitely a big leap compared to previous generations.


ARM-based processors like those from Qualcomm and MediaTek have been used in mobile devices precisely because of these traits. They can keep the product compact without impacting performance, something that laptop makers aim for every year. More importantly, however, these small form factors open the doors to less conventional designs, paving the way for dual-screen, foldable, or rollable PCs that don’t sacrifice their power for the sake of their novel appearance and features.
Thinking Outside the Box
The very first benefit of Windows successfully and smoothly running on ARM devices would be thinner laptops with longer battery lives. It can’t be understated how significant that will be for creatives, especially those who will rely a lot on that generative AI that everyone’s talking about these days. But even if you do much of your designs manually, the idea that you can bring your work anywhere without breaking your back and stay unplugged for more than half a day is going to appeal to a lot of people
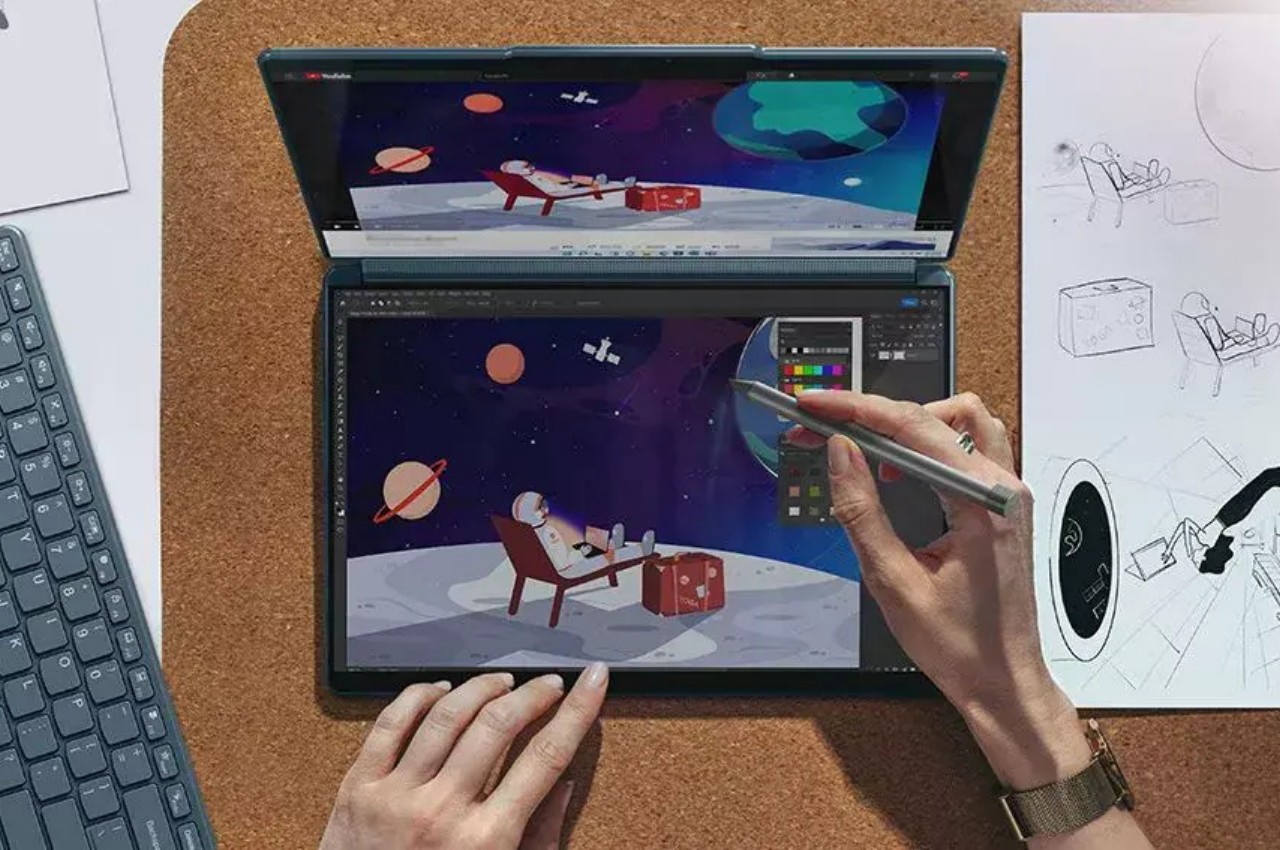

Lenovo Yoga Book 9i

Designer: Lenovo
Once that has become the norm, however, it will be time to explore the possibilities that thinner, more compact, or smaller devices can bring. Imagine those handheld gaming PCs becoming thinner and smaller, almost down to tablet or even phone sizes. Admittedly, being able to play just about any PC game is going to be tricky today, but that’s not going to be the case in the future.

And then there are the current novelties like laptops with two screens or foldable displays, designs that have to sacrifice performance for the sake of super thin bodies. It hasn’t arrived yet, but a rollable screen might even become a thing for computers. In other words, Windows on ARM would enable all these forms beyond desktop towers and laptops to become possible without sacrificing too much performance. We seem to be heading in that direction already, but hardware is only half the battle.
Uphill Battle
No matter how powerful ARM chips are, enough to smoothly run Windows, all of that will fall on deaf ears if Windows on ARM isn’t able to support as much as 80% of regular Windows software, including games and especially content creation tools. That was what killed the Surface RT and Surface 2, after all, and things have improved considerably but not yet to most PC users’ satisfaction. One of the available solutions right now is emulation, like making the software or game think it’s running on an Intel/AMD computer, but that incurs penalties in performance.
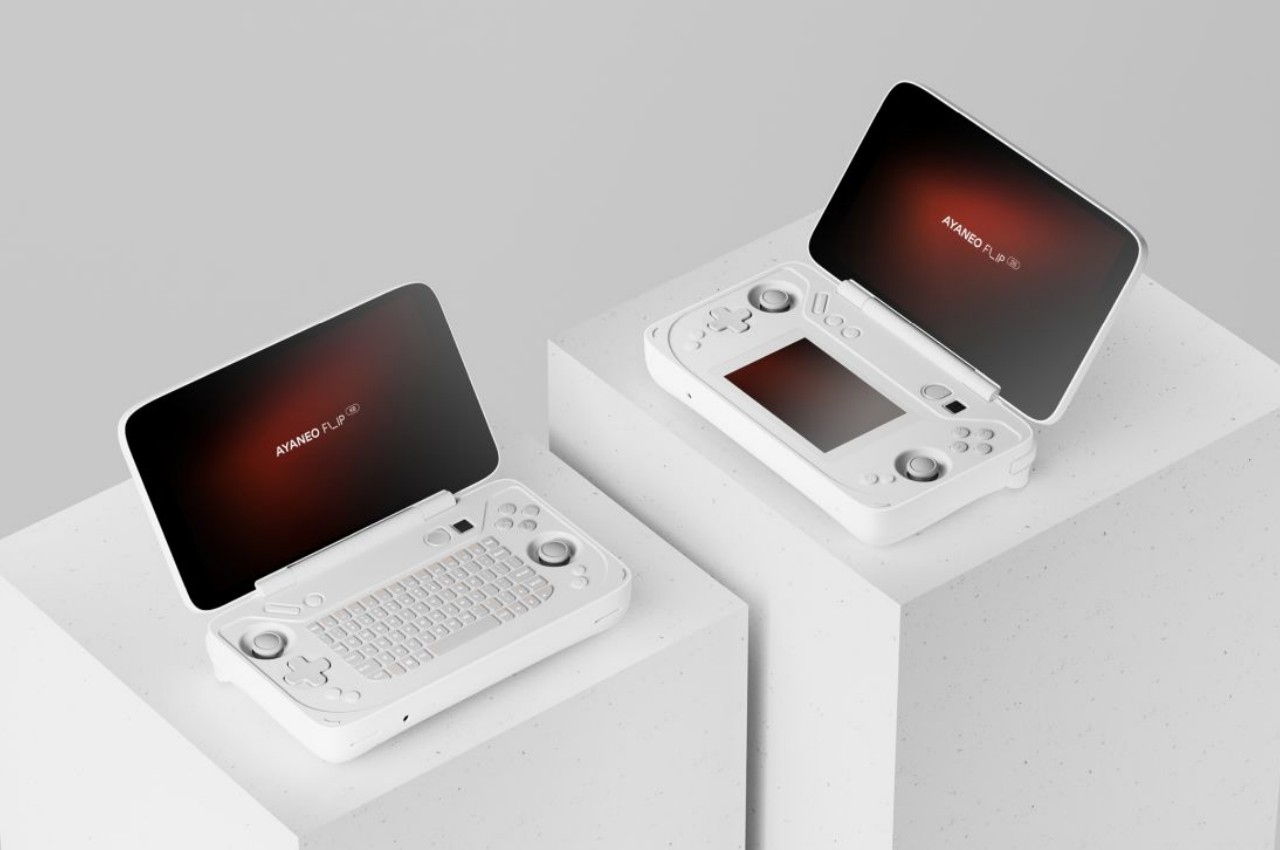

AYANEO Flip DS
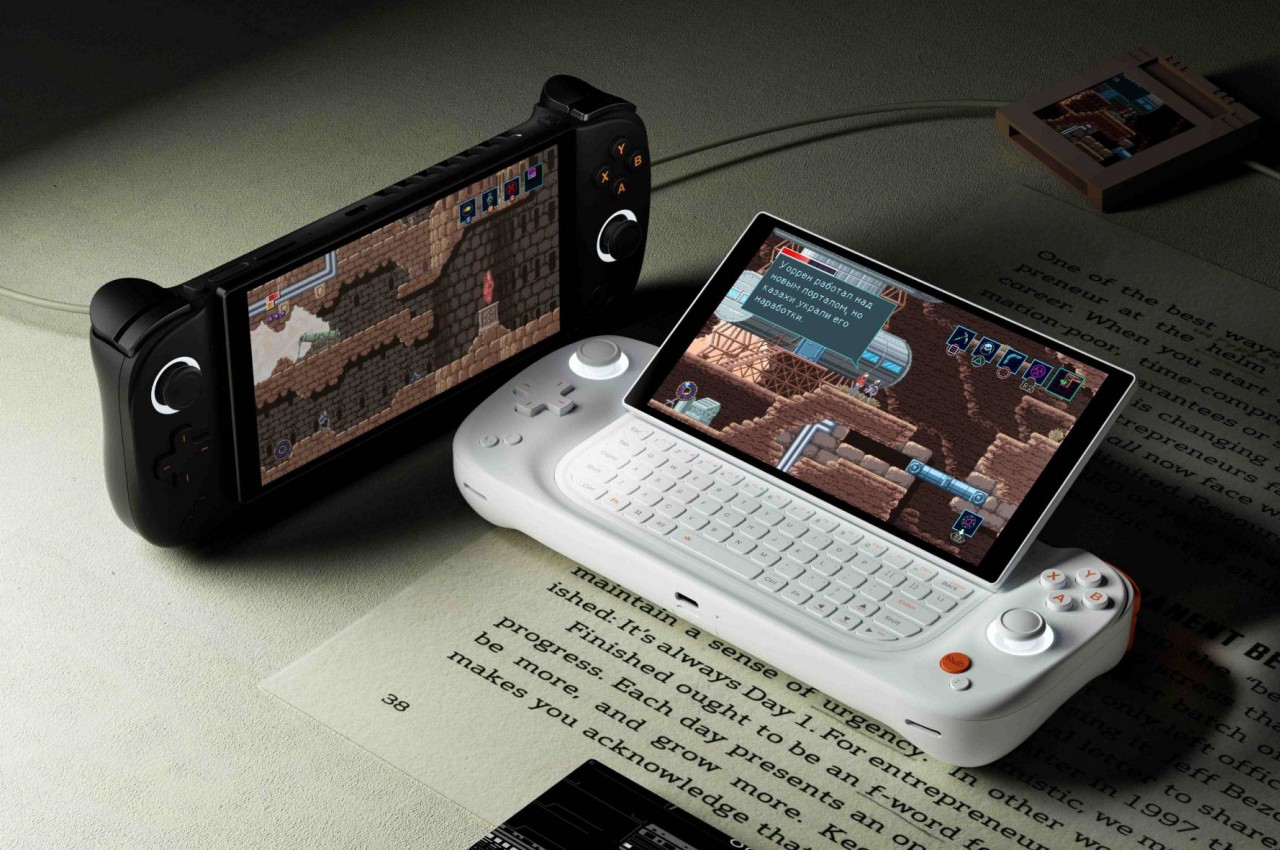

AYANEO Slide

Designer: AYANEO
There are also obstacles to be overcome on the hardware side. As strange as it might sound, PCs are a somewhat open ecosystem when it comes to the variety of things you can plug into a computer and have them working automatically. You lose some of that with Windows on ARM because of compatibility issues, and that might prevent less popular but heavily used peripherals from working, at least not at first. Unfortunately, that might be a huge deal breaker, especially for those who have already invested in devices for their workflow.
Designer: Qualcomm
Final Thoughts
Qualcomm’s announcement of the Snapdragon X Plus and Elite tried to preempt Apple’s new M4 chip and iPad Pros. Apple’s venture into the ARM world is both a boon and a bane for the likes of Qualcomm as it demonstrates what’s possible. But even Apple has remained within the boundaries of traditional devices like a tablet and a laptop. Not surprising for a company that is very meticulous and careful about the design of its products.
Designer: Apple
The Windows world, however, is a bit more daring thanks to the diversity of people involved. Unconventional and sometimes impractical designs pop up once in a while, but they’re all hampered by the limitations of hardware that’s commonly available for PCs. Windows on ARM isn’t new and it still has a long way to go to confidently match what Intel, AMD, and now Apple are selling, but stakeholders in the PC industry should probably consider rallying behind this if they want to breathe new life into the stagnating PC market.

Designer: Samsung






